Aerodynamics - week 2 - rotary

Helicopter Aerodynamics Quiz
Test your knowledge of rotary wing concepts and aerodynamics in this comprehensive quiz. Designed for aviation enthusiasts and students, this quiz covers the fundamental principles of helicopter mechanics and flight dynamics.
Key Topics:
- Aerodynamics Principles
- Rotor Mechanics
- Helicopter Forces
- Flight Operations
Every main rotor head and blade design needs to take into account movement around which of the axis combinations?
Pitching/feathering, flapping, lead/lag
Drag, thrust, weight
Speed, rotation, vertical
Vertical, lateral, horizontal
This effect is caused by the change in blade speed due to the blade center of gravity moving in when the blade flaps up
Centrifugal
Night
Coriolis
Precession
What is the name of the Rotary Wing Concept causing upward flexing of the blade as a result of the weight of the aircraft at the center of rotation and the center of lift for the blades near the tips?
Gyroscopic Procession
Blade Coning
Coriolis
Centrifugal
What is the name of the Rotary Wing Concept that is caused as the change in blade angle to create the lifting movement 90 degrees later in the direction of rotation?
Coriolis
Coning
Gyroscopic Precession
Centrifugal
What is the name of the Rotary Wing Concept that is caused as the blade flaps up and the center of mass moves in towards the center of rotation?
Centrifugal Force
Ground Effect
Coriolis Effect
Gyroscopic Precession
What is the name of the Rotary Wing Concept that causes a difference in flight forces between the advancing and retreating blades in forward flight?
Downwash
Dissymmetry of Lift
Coriolis Force
Centrifugal Force
During a hover, how are the four forces acting on a helicopter?
Lift is straight upward, thrust is straight downward, drag is straight upward and weight is straight downward
Lift is straight upward, weight is straight downward, thrust is straight forward and drag is straight rearward
Lift is straight upward, weight is straight downward, thrust is straight upward and drag is straight downward
Lift is straight upward, thrust is straight downward, weight is straight forward and drag is straight rearward
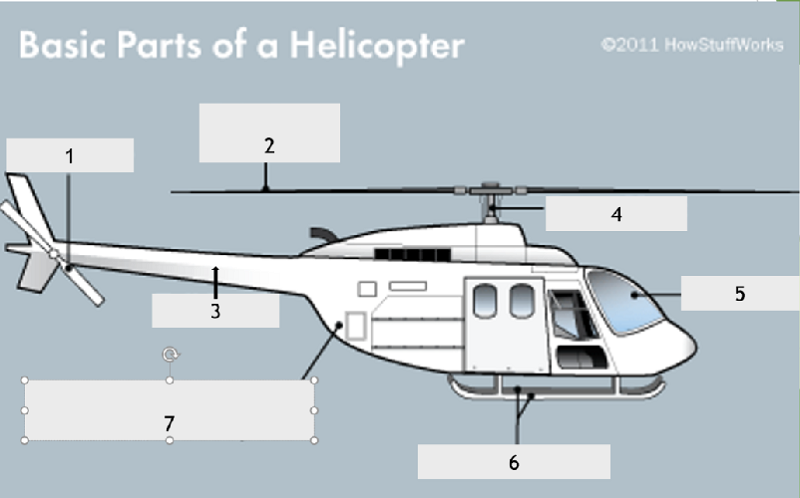
What is the name of the part if the helicopter identified by the number 1?
Tail boom
Main rotor
Tail rotor
Torque rotor
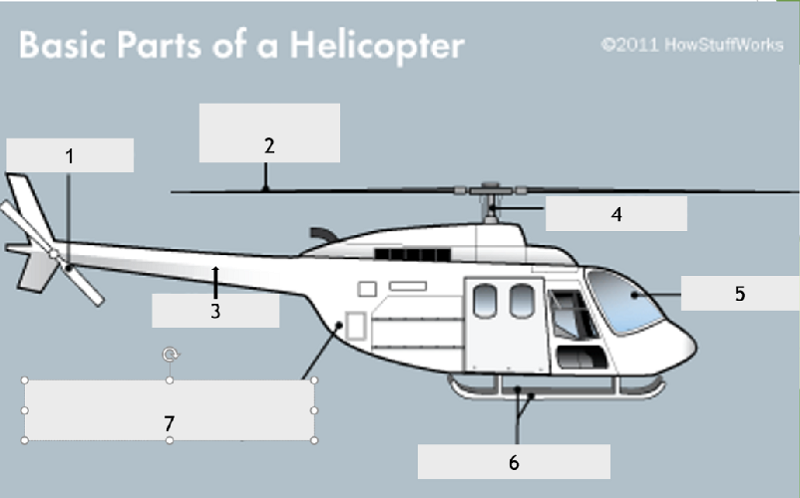
What is the name of the part if the helicopter identified by the number 4?
Tail rotor
Main rotor
Rotor mast
Tail boom
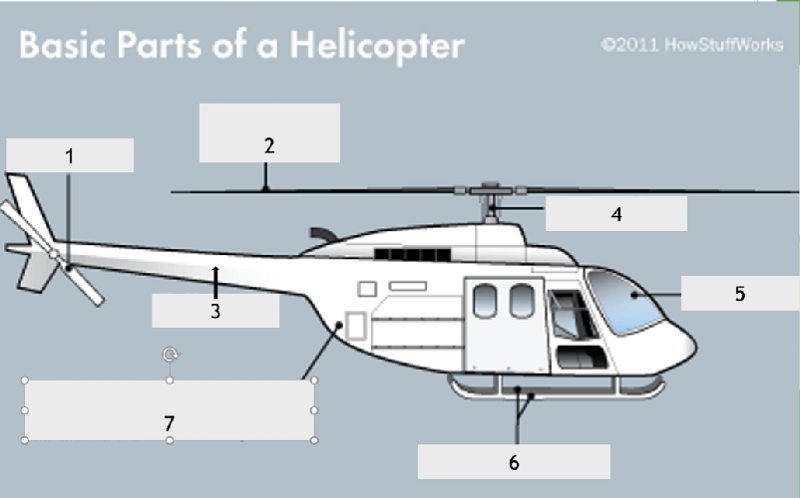
What is the name of the part if the helicopter identified by the number 3?
Tail boom
Main rotor
Tail rotor
Torque rotor
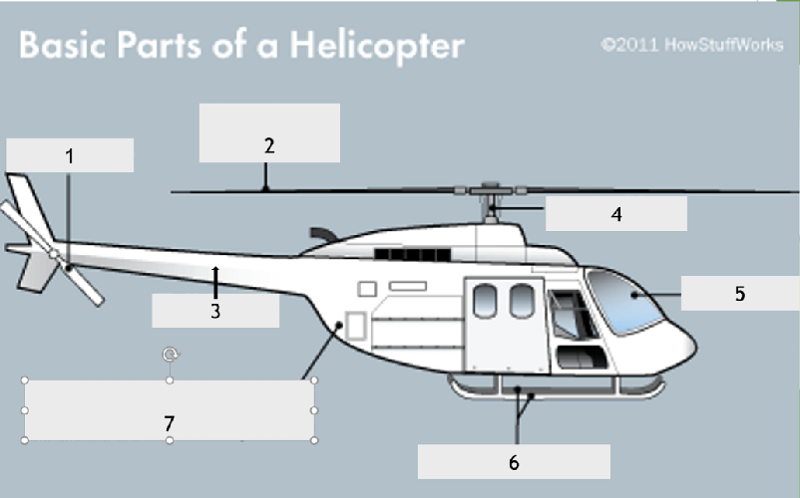
What is the name of the part if the helicopter identified by the number 2?
Tail boom
Main rotor
Tail rotor
Torque rotor
Which of the following statements are not correct about the various forces acting on the helicopter in a hover?
Lift is straight up
Weight is straight down
Thrust is straight up
Drag is pointing rearward
Which of the following statements is correct about the various forces acting on the helicopter in a climb or accent?
Upward lift and thrust are greater than downward weight and drag
Upward Lift and thrust are less than downward weight and drag
Upward Lift and drag are greater than downward weight and thrust
Upward lift and weight are greater than downward thrust and drag
Which of the following statements is correct about the various forces acting on the helicopter in a decent?
Upward lift and thrust are greater than downward weight and drag
Upward Lift and thrust are less than downward weight and drag
Upward Lift and drag are greater than downward weight and thrust
Upward lift and weight are greater than downward thrust and drag
Which of the following statements are not correct about the various forces acting on the helicopter in forward flight?
Lift is straight up
Thrust is rearward
Weight is straight down
Drag is rearward
What is the name of the angle between the relative wind vector and the chord line of the blade?
Pitch angle
Plane of rotation
Feathering angle
Angle of attack
What is the name of the tip path that is created if the blades are straight out from the mast, generating no lift?
Pitch angle
Plane of rotation
Feathering angle
Angle of attack
What is the name of the number of degrees of rotation of the airfoil between the plane of rotation and the chord line of the blade?
Pitch angle
Angle of attack
Angle of incidence
Hover angle
What is the name of the axis on which the blade will rotate to change the angle of the chord line of the blade?
Lateral axis
Chord axis
Feathering axis
Relative wind axis
Blades moving through the same point in space as they pass through the same point in the 360 degrees of rotation are said to be:
In balance
Out of balance
In track
Out of track
Which Force acting on the main rotor blade tends to sent it straight out from the center of rotation as it turns?
Coning force
Lifting force
Centrifugal force
Coning force
What is the name of the upward flexing of the blades caused by a combination of lift and centrifugal forces?
Thrust
Coning
Droop
Flapping
Which of the following is a hazard to equipment and personnel caused by the main rotor system during start-up and shut down?
Blade coning
Gyroscopic procession
Rigidity in space
Blade droop
When wanting to tilt the main rotor disk to the left on a rotor system rotating counter clockwise looking down from the top, where will the highest blade pitch angle be in the 360 degrees of rotation?
Over the front of the helicopter
Over the left side of the helicopter
Over the tail of the helicopter
Over the right side of the helicopter
When wanting to tilt the main rotor disk forward on a rotor system rotating counter clockwise looking down from the top, where will the highest blade pitch angle be in the 360 degrees of rotation?
Over the front of the helicopter
Over the left side of the helicopter
Over the tail of the helicopter
Over the right side of the helicopter
When wanting to tilt the main rotor disk to the back on a rotor system rotating counter clockwise looking down from the top, where will the highest blade pitch angle be in the 360 degrees of rotation?
Over the front of the helicopter
Over the left side of the helicopter
Over the tail of the helicopter
Over the right side of the helicopter
When wanting to tilt the main rotor disk to the right on a rotor system rotating counter clockwise looking down from the top, where will the highest blade pitch angle be in the 360 degrees of rotation?
Over the front of the helicopter
Over the left side of the helicopter
Over the tail of the helicopter
Over the right side of the helicopter
Due to the flapping up and down of the blades during forward flight caused by dissymmetry of lift, when is the angle of attack of the blade the greatest?
On the advancing blade
When the blade is over the tail
On the retreating blade
When the blade is over the nose
What is a key factor in limiting the maximum forward speed of the helicopter?
Coriolis effect
Dissymmetry of lift
Retreating blade stall
Coanda effect
What flight condition exists when the helicopter is in a hover less than one-half the diameter of the rotor system from the ground and lift generated is increased?
In ground effect
In translational lift
In ground resonance
In auto-rotation
What flight condition exists when the helicopter is moving forward at a speed of approximately 16 to 24 knots (15 to 20 mph) and lift generated is increased?
In ground effect
In translational lift
In ground resonance
In auto-rotation
What flight condition exists when the helicopter has landed and a self-excited vibration occurs that builds uncontrollably?
In ground effect
In translational lift
In ground resonance
In auto-rotation
Which stabilizing measure used in fixed wing stability is similar to the use of pre-coned blades as a stabilizing measure in rotary wing aircraft design?
The pendulum effect
Wing dihedral
The vertical stabilizer
The horizontal stabilizer
Which stabilizing system used in rotary wing design employs the concept of rigidity in space of a rotating mass?
The Bell stabilizer bar
Offset mast hinges
Pre-coned blades
Stability augmentation system
Which stabilizing system used in rotary wing design employs the use of an autopilot system?
The Bell stabilizer bar
Offset mast hinges
Pre-coned blades
Stability augmentation system
What does the acronym "Nr" mean when discussing the concepts of Autorotation?
The altitude of the helicopter
The speed of the rotor
The speed of the helicopter
The size of the rotor
What is the term "Deadman's Curve" relate to when discussing Autorotation?
A direction of turn that is prohibited during autorotation
An altitude or forward speed above which a successful autorotation is impossible
An altitude or forward speed below which a successful autorotation is impossible
A flight maneuver that will cause the rotor system to stop turning during an autorotation
What causes the blades to continue rotating during an autorotation?
Airflow down through the rotor system
Airflow up through the rotor system
The engine starter motor
An electric motor on the transmission
The engine power being applied to drive the rotor system will cause what equal and opposite reaction?
Tension
Torsion
Torque
Teetering
What is the name of the system that counteracts the equal and opposite reaction of the engine driving the rotors that uses two main rotors counter rotating placed one in front of the other?
Tandem rotor system
Coaxial rotor system
Dual intermeshing rotor system
Tail rotor system
What is the name of the system that counteracts the equal and opposite reaction of the engine driving the rotors that uses two main rotors counter rotating placed one beside the other?
Tandem rotor system
Coaxial rotor system
Dual intermeshing rotor system
Tail rotor system
What is the name of the system that counteracts the equal and opposite reaction of the engine driving the rotors that uses two main rotors counter rotating placed one above the other?
Tandem rotor system
Coaxial rotor system
Dual intermeshing rotor system
Tail rotor system
What is the name of the system that counteracts the equal and opposite reaction of the engine driving the rotors that uses smaller rotor mounted vertically at the back of the helicopter?
Tandem rotor system
Coaxial rotor system
Dual intermeshing rotor system
Tail rotor system
With reference to the tail rotor system what is the meaning of the term "translating tendency"?
The forward tilt of the helicopter caused by the centrifugal force of the vertical mounted tail rotor
The rearward tilt of the helicopter caused by the centrifugal force of the vertical mounted tail rotor
The right drift of the helicopter caused by the tail rotor thrust pushing to the left
The left drift of the helicopter caused by the tail rotor thrust pushing to the left
During vertical ascent (straight up) of a helicopter, how are the four forces vectors acting on a helicopter directed and how do they relating to each other?
Lift and weight directed upwards are less than the thrust and drag forces directed down
Lift directed up is greater than weight directed down and thrust directed forward is greater than drag directed rearwards or backwards
Upward directed lift and thrust forces are greater than the downward directed weight and drag force
Lift and thrust are up are greater than the weight force is down and drag is backwards
During vertical descent (straight down) of a helicopter, how are the four forces vectors acting on a helicopter directed and how do they relating to each other?
Lift and thrust are up are greater than the weight force is down and drag is backwards
Lift directed up is greater than weight directed down and thrust directed forward is greater than drag directed rearwards or backwards
Upward directed lift and thrust forces are less than the downward directed weight and drag force
Lift and weight directed upwards are less than the thrust and drag forces directed down
Which Main Rotor Head design has only one axis of movement?
Fully Articulated Rotor Head
Soft in the Plane Rotor Head
Semi-Rigid Rotor Head
Rigid Rotor Head
Which type of Main Rotor Head design has three axis of rotation?
Teetering Rotor Head
Rigid Rotor Head
Semi-Rigid Rotor Head
Fully Articulated Rotor Head
Which Main Rotor Head design has only two axis of movement?
Fully Articulated Rotor Head
Soft in the Plane Rotor Head
Semi-Rigid Rotor Head
Rigid Rotor Head
Every main rotor head and blade design needs to take into account movement around which of the axis combinations?
Vertical axis, Lateral axis and Horizontal axis
Speed axis, Rotational axis and Vertical axis
Drag axis, Thrust axis and Lift axis
Pitch or Feathering axis, Flapping axis and Lead & Lag axis
What type of main rotor design uses two main rotors one mounted at the back of the fuselage and the other mounted at the front of the fuselage to counteract engine driving torque?
Tail Rotor System
Counter-rotating Co-Axial Main Rotor System
Counter-rotating Tandem Mounted Main Rotor System
Counter-rotating Dual Inter-meshing Main Rotor System
Which helicopter control will increase and decrease the lift equally throughout the rotation of the blades to increase or decrease lift & thrust?
Collective Pitch Control
Anti-Torque Controls
Swash Plate
Cyclic Pitch Control
Which helicopter control will increase and decrease the lift differently throughout the rotation of the blades to tilt the rotor disk for directional flight?
Cyclic Pitch Control
Collective Pitch Control
Swash Plate
Anti-Torque Controls
Which helicopter control is used to compensate for the force created by the engine driving the main rotor system?
Collective Pitch Control
Cyclic Pitch Control
Anti-Torque Controls
Swash Plate
What is the name of the device that transmits linear movements from the Cyclic & Collective Pitch controls to the rotating mast and rotor head
Collective Pitch Control
Cyclic Pitch Control
Anti-Torque Controls
Swash Plate
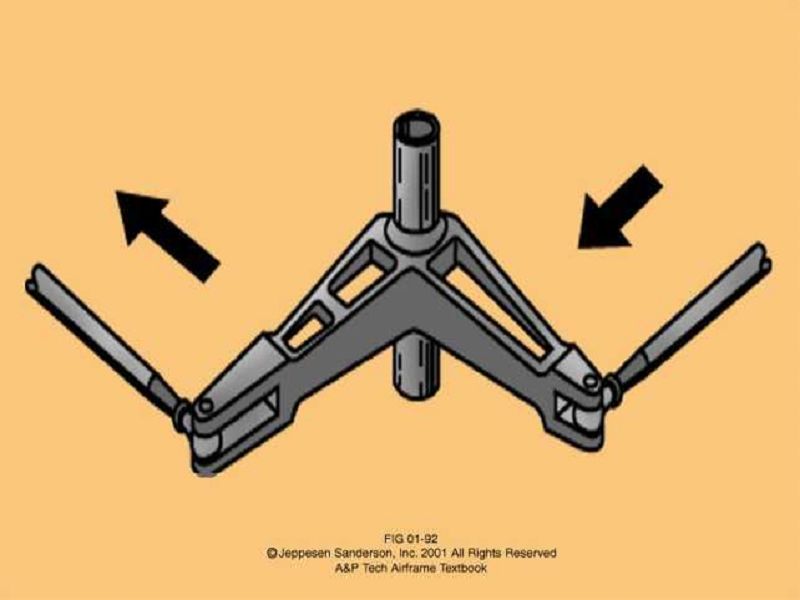
What is the name of this device?
Bellcrank
Linkage
Pivot Block
Quadrant
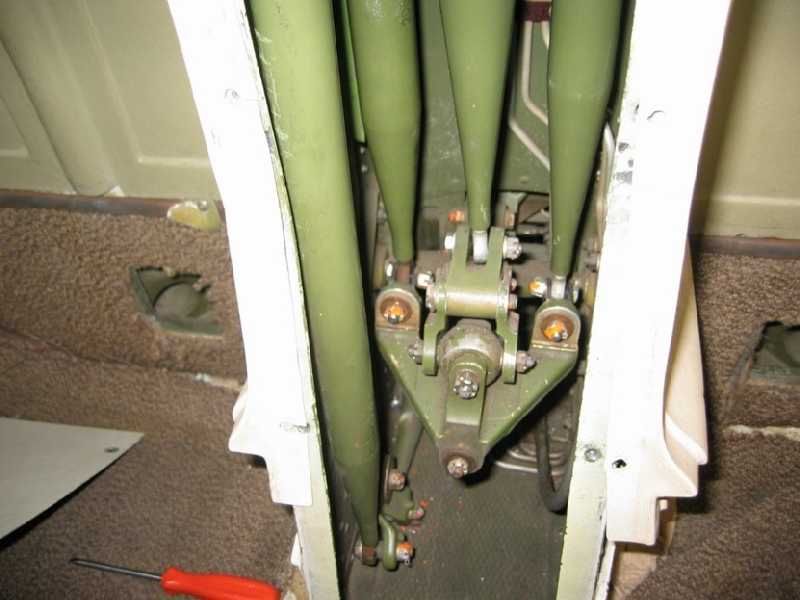

What is the name of this inverted triangular shaped device at the bottom of this picture?
Bellcrank
Quadrant
Mixing Unit
Torque Tube
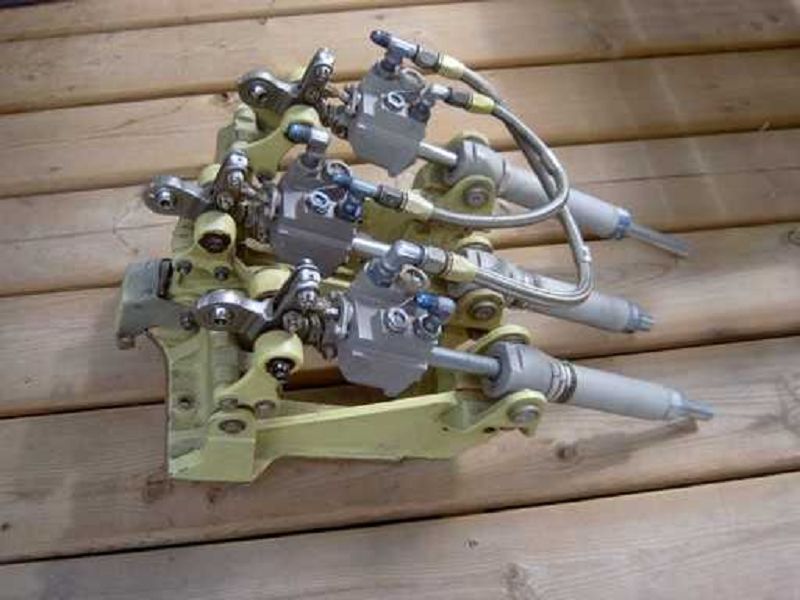

What is the name of these units?
Hydraulic Servers
Hydraulic Servos
Pitch change links
Torque Actuators
When pulling up on the collective pitch control, what is the equal and opposite reaction experienced by the helicopter to the increase in engine power to needed to maintain rotor speed?
Gyroscopic Procession
Coriolis Effect
Torque
Blade Coning
Engine Power Control is attached to or is a part of which flight control system on the helicopter?
Anti-Torque Control
Cyclic Pitch Control
Collective Pitch Control
Synchronized Horizontal Stabilizer System
What is the purpose of the "Sprag Clutch Assembly" or "Free Wheeling Unit a\Assembly" on a Helicopter?
Provide a mechanism that will allow you to disengage the engine from the transmission when you want to change the gear ratio in flight to reduce power draw
Disconnect the engine from the main transmission and tail rotor drive system during auto-rotation
Connect the engine and the main rotor transmission and tail rotor during auto-rotation
Disconnect tail rotor drive system from the main rotor transmission during auto-rotation
{"name":"Aerodynamics - week 2 - rotary", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge of rotary wing concepts and aerodynamics in this comprehensive quiz. Designed for aviation enthusiasts and students, this quiz covers the fundamental principles of helicopter mechanics and flight dynamics. Key Topics: Aerodynamics Principles Rotor Mechanics Helicopter Forces Flight Operations","img":"https:/images/course8.png"}
More Quizzes
Atp copa
2021010
LN-BTT
10513
Which wings of fire series 1 character are you?
5244
Who wants to be a millionaire
7483
Shadow Self - What Is My Shadow?
201017346
Free Wonderlic Test - Cognitive Ability Practice
201018102
Acronym Trivia Questions - Play the Free Abbreviation
201017411
Wave Test - Free Physics Practice onMaker
201015965
Smith System Forward Motion Practice - Free
201015965
Pharmacology Made Easy 5.0: Cardiovascular System
201020221
Instrumentation Technician Knowledge - Free
201015914
AP Biology Properties of Water - Polarity & Cohesion
201019931