Papilla Supplies Nourishment: Hair Follicle Anatomy Quiz
Quick, free dermal papilla quiz to test your knowledge. Instant results.
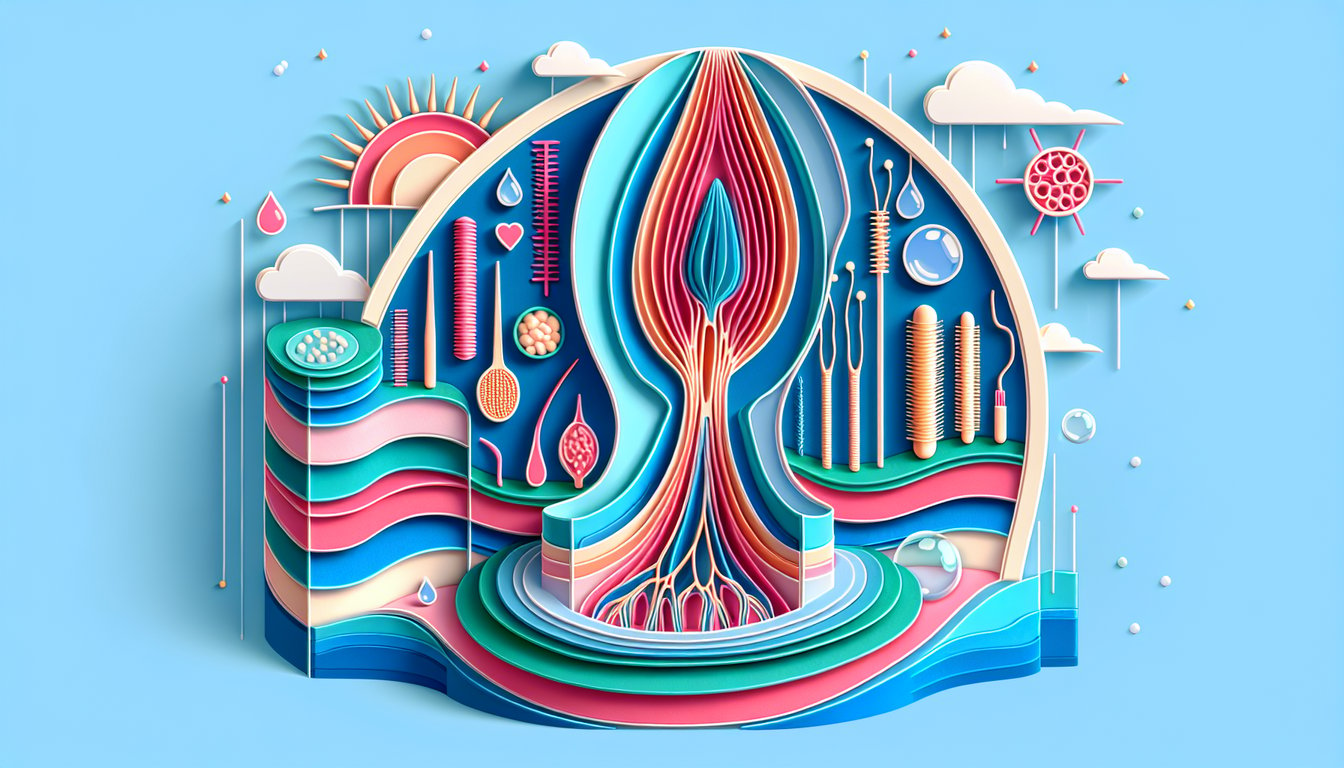

This quiz helps you check your grasp of papilla and hair follicle anatomy and how the papilla supplies nourishment to the bulb. Reinforce the basics with hair follicle nourishment, then practice structure ID in a hair follicle labeling quiz, and round it out with an anagen phase quiz to connect growth stages.
Study Outcomes
- Apply Trichology Basics -
Integrate fundamental trichology principles into practical hair care scenarios to build a solid foundation.
- Identify Hair Structure Anatomy -
Recognize the key components of hair structure anatomy and understand their roles in maintaining hair integrity.
- Explain Hair Bulb Nourishment -
Detail which hair structure supplies nourishment to the hair bulb and how it supports hair growth.
- Describe Hair Growth Cycle Phases -
Outline the anagen, catagen, and telogen stages as tested in the hair growth cycle quiz to deepen your understanding of hair development.
- Evaluate Scalp Health Assessment -
Use scalp health assessment techniques to identify scalp conditions and recommend appropriate treatments.
- Utilize the Cosmetology Trichology Quiz -
Leverage the quiz results to pinpoint strengths and knowledge gaps for continued skill improvement.
Cheat Sheet
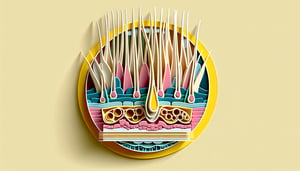
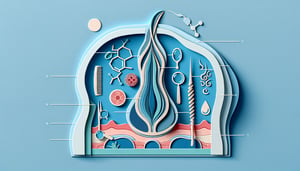
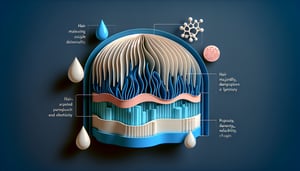
- Dermal Papilla: Nourishment Hub -
In both the cosmetology trichology quiz and real-world practice, the dermal papilla is the key hair structure that supplies nourishment to the hair bulb via its dense capillary network (American Academy of Dermatology). Common quiz questions, like "which hair structure supplies nourishment to the hair bulb," focus on papilla function in cell division. Remember the memory trick "Papilla = Powerhouse" to reinforce its pivotal role.
- Anagen, Catagen, Telogen: Growth Cycle Phases -
The hair growth cycle consists of anagen (active growth), catagen (transitional), and telogen (resting) phases, with anagen lasting 2 - 6 years according to NIH studies. Use the mnemonic "A.C.T." to breeze through any hair growth cycle quiz question: Anagen, Catagen, Telogen. Recognizing phase durations and cellular activities helps solidify your trichology basics.
- Hair Shaft Anatomy: Cuticle, Cortex, Medulla -
Hair structure anatomy covers three primary layers: the cuticle (protective outer scale), the cortex (strength and pigment), and the medulla (central core), as detailed in the Journal of Cosmetic Science. Quiz-takers should note that cuticle damage increases porosity and breakage. The phrase "C-C-M" (Cuticle - Cortex - Medulla) can guide you from outside in.
- Scalp Vasculature and Nutrient Delivery -
Trichology basics emphasize the rich vascular network beneath the scalp that delivers oxygen and nutrients, including biotin and iron, to hair follicles (Dermatologic Clinics). Effective blood flow modulation supports the anagen phase and prevents premature telogen entry. Recall that healthy microcirculation is the foundation of follicle vitality.
- Scalp Health Assessment Indicators -
In any scalp health assessment, evaluate sebum distribution, pH balance, and microbial flora to detect issues like dandruff or folliculitis (American Academy of Dermatology). Keep an eye out for dryness, inflammation, or excessive oiliness as part of your quiz prep. Remember the acronym "O.D.I." (Oil, Dermis, Integrity) to cover key assessment parameters.