What Is Trichology? Milady Chapter 11 Hair and Scalp Quiz
Quick, free chapter 11 practice test for hair and scalp basics. Instant results.
This quiz helps you check your understanding of trichology, hair anatomy, and scalp conditions for Milady Chapter 11. If you want more practice, try our hair and scalp properties quiz, a hair follicle anatomy quiz for key structures, and a shampooing and conditioning quiz to review care steps.
Study Outcomes
- Understand Hair Anatomy -
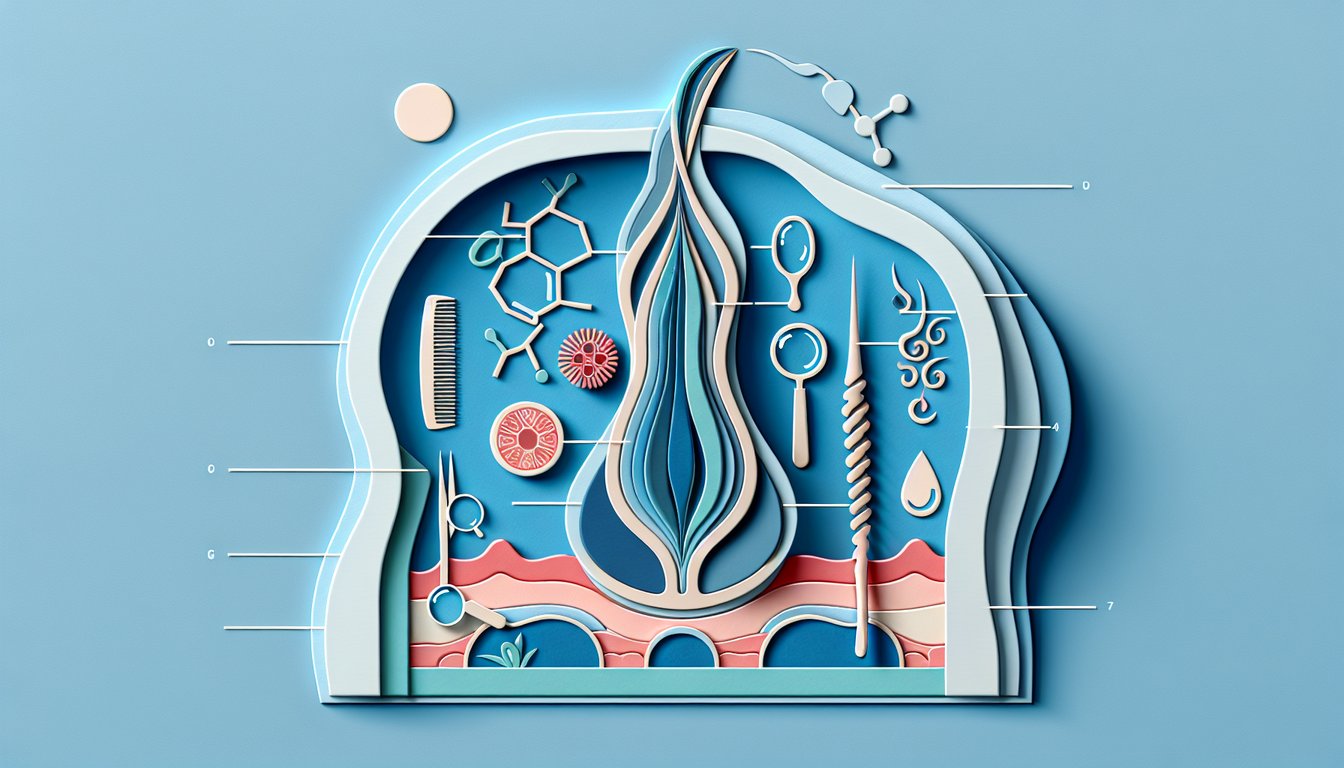
Describe the structure of the hair fiber, including the cuticle, cortex, and medulla as outlined in Milady Chapter 11.
- Analyze Trichology Concepts -
Explain what is trichology milady by exploring scalp science, hair growth, and common disorders.
- Identify Growth Stages -
Recognize each phase of the hair growth cycle - anagen, catagen, and telogen - and define what is anagen milady in detail.
- Evaluate Hair and Scalp Properties -
Assess key factors from properties of the hair and scalp chapter 11, such as texture, porosity, and elasticity.
- Apply Growth Rate Knowledge -
Calculate how fast does hair grows milady by reviewing average growth patterns and influencing factors.
- Differentiate Scalp Conditions -
Distinguish between healthy and compromised scalp states to support effective hair care solutions.
Cheat Sheet
- Hair Shaft Structure -
The hair shaft is composed of three layers - cuticle, cortex, and medulla - which each play a crucial role in strength, elasticity, and shine according to properties of the hair and scalp chapter 11. Remember the mnemonic "3 C's of Hair" (Cuticle, Cortex, Core) to recall the layers quickly when reviewing hair anatomy. Research published in the Journal of Cosmetic Science shows that cuticle damage leads to increased porosity and breakage.
- Phases of the Hair Growth Cycle -
The hair growth cycle consists of anagen (growth), catagen (transition), and telogen (rest) phases, each with a specific duration; anagen lasts about 2 - 6 years on the scalp. A simple mnemonic "ACT" (Anagen, Catagen, Telogen) helps recall the order when studying what is anagen milady. Research from the International Journal of Trichology confirms that up to 90% of scalp hairs are in the anagen phase at any time.
- Hair Growth Rate -
On average, scalp hair grows about 0.3 - 0.4 mm per day, translating to roughly 1 - 1.5 cm per month, influenced by genetics, hormones, and nutrition. When clients ask "how fast does hair grows milady," use the simple formula "0.35 mm/day × 30 ≈ 10.5 mm/month" to provide a clear estimate. Data from the American Academy of Dermatology highlights nutritional factors like biotin and iron as key modulators of growth speed.
- Scalp Physiology and pH Balance -
The healthy scalp maintains a slightly acidic pH of around 4.5 - 5.5, which supports lipid barrier function and microbiome balance. Remember "Acid Allies" to recall the scalp's natural acid mantle and why balancing pH prevents common disorders like dandruff and folliculitis. Studies by leading dermatology clinics show that shampoos formulated within this pH range minimize irritation and preserve hair integrity.
- Fundamentals of Trichology -
When students ask "what is trichology milady," explain it's the scientific study of hair and scalp disorders, combining biology, chemistry, and dermatology. As defined in Milady Chapter 11, trichology emphasizes evidence-based approaches and client consultation techniques to identify scalp issues accurately. According to the Institute of Trichologists, a thorough consultation chart and scalp analysis are essential first steps in any treatment plan.