Week 1 Chapters 12-14

Neuroscience Action Potential Quiz
Test your knowledge on the intricacies of action potentials and neuronal fun
- 30 thought-provoking multiple choice questions
- Immediate feedback with scoring
- Enhanced understanding of neurophysiology concepts
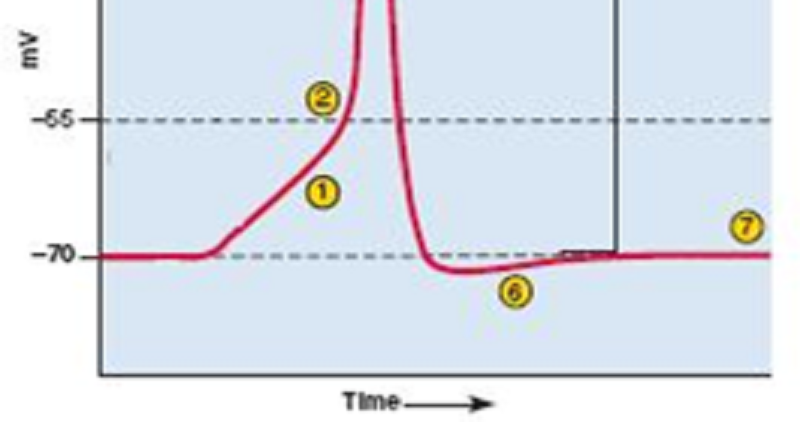
This image shows an action potential. What does "6" represent?
Hyperpolarization of the membrane
A critical voltage called threshold
Depolarization of the membrane
Repolarization of the membrane
Resting membrane potential
During the absolute refractory period
If a neuron reaches threshold, the action potential goes to completion
The neuron fires at its maximum voltage if a stimulus depolarizes the neuron to threshold
The signal grows weaker with distance
It is possible to trigger a new action potential, but only with an unusually strong stimulus
No stimulus of any strength will trigger a new action potential
When the voltage of a plasma membrane shifts from +35mV towards 0 mV, we say the cell is
Depolarizing
Repolarizing
Hyperpolarizing
Reaching the threshold
Exiting the threshold
During hyperpolarization (or afterpotential)
Sodium ions are entering the cells
Sodium ions are leaving the cell
Potassium ions are entering the cell
Potassium ions are leaving the cell
Both sodium and potassium ions are leaving the cell
Local potentials are ___, whereas action potentials are ____.
Irreversible; reversible
Self-propagating; local
Graded; all or none
Nondecremental; decremental
Produced by voltage-regulated channels; produced by gated channels
Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) are associated with
Depolarization of the cell membrane
Repolarization of the cell membrane
Hyperpolarization of the cell membrane
No change of the cell membrane potential
No change of the threshold
A cholinergic synapse employs ___ as its neurotransmitter.
Monoamine
Acetylcholine
Epinephrine
Norepinephrine
Catecholamine
An inhibitory local potential
Depolarizes the plasma membrane
Hyperpolarizes the plasma membrane
Repolarizes the plasma membrane
Neutralizes the plasma membrane
Drifts the membrane potential towards the resting membrane potential
Which of these is an example of an EPSP in a typical neuron?
A voltage change from 0 mV to +0.35 mV
A voltage change from -70 mV to -69.5 mV
A voltage change from -69.5 mV to -70 mV
A voltage change from +35 mV to 0 mV
A voltage change from -70 mV to -70.5 mV
A neuron can receive thousands of EPSPs from different neurons, and responds by triggering or not triggering an action potential. This addition and response to the net effect of postsynaptic potentials is called
Temporal summation
Neural summation
Spatial summation
Neuronal coding
Recruitment
Which of these is an ascending tract of the spinal cord?
The lateral tectospinal tract
The medial reticulospinal tract
The ventral corticospinal tract
The vestibulospinal tract
The gracile fasciculus
The ventral rami of the spinal nerves form nerve plexuses in all regions except:
The thoracic region
The brachial region
The cervical region
The lumbar region
The sacral region
Tendon organs are
Chemoreceptors
Visceral receptors
Proprioceptors
Pain receptors
Nociceptors
___ keep(s) nerve fibers insulated from one another
Perineurium
Endoneurium
Fascicles
Epineurium
Blood vessels
The bundle of nerve roots that occupy the vertebrals canal from L2 to S5 is called the
Medullary cone
Cauda equina
Lumbar enlargment
Cervical enlargement
Spinal cord
The upper motor neurons that control skeletal muscles begin with a soma in
The posterior horn of the spinal cord
The anterior horn in the spinal cord
The motor association cortex of the cerebrum
The postcentral gyrus of the cerebrum
The precentral gyrus of the cerebrum
The quickest reflex arcs involve only two neurons, thus forming ____ reflex arcs.
Ipsilateral
Contralateral
Polysynaptic
Monosynaptic
Autonomic
Which of the following nerves originates in the lumbosacral plexus?
Axillary
Sciatic
Phrenic
Ilioinguinal
Obturator
Cerebrospinal fluid fills in the space between the
Dural sheath and dura mater
Dural sheath and vertebral bones
Dura mater and arachnoid mater
Arachnoid mater and pia mater
Dura mater and pia mater
A ganglion is a
Bundle of axons in the CNS
Cluster of dendrites in either the CNS or the PNS
Cluster of neurosomas in the PNS
Bundle of axons in the PNS
Cluster of neurosomas in the CNS
Cerebrospinal fluid is secreted by choroid plexuses in the _____ ventricles and reabsorbed by arachnoid villi in the ____.
Lateral, third, and fourth; superior sagittal sinus
Lateral, and third; superior sagittal sinus
Lateral, third, and fourth; central canal of the spinal cord
Lateral; central canal of the spinal cord
Lateral, third, and fourth; superior saggital sinus
The ___ is not a motor cranial nerve.
Trochlear nerve (IV)
Abducens nerve (VI)
Hypoglossal nerve (XII)
Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)
Accessory nerve (XI)
The blood brain barrier (BBB) consists of
Gap junctions between endothelial cells taht form the capillary walls
Tight junctions between endothelial cells that form the capillary walls
Gap and tight junctions between astrocytes and endothelial cells that form the capillary walls
Desmosomes and tight junctions between astrocytes and ependymal cells that form the capillary walls
Gap junctions between ependymal cells and endothelial cells that form the capillary walls
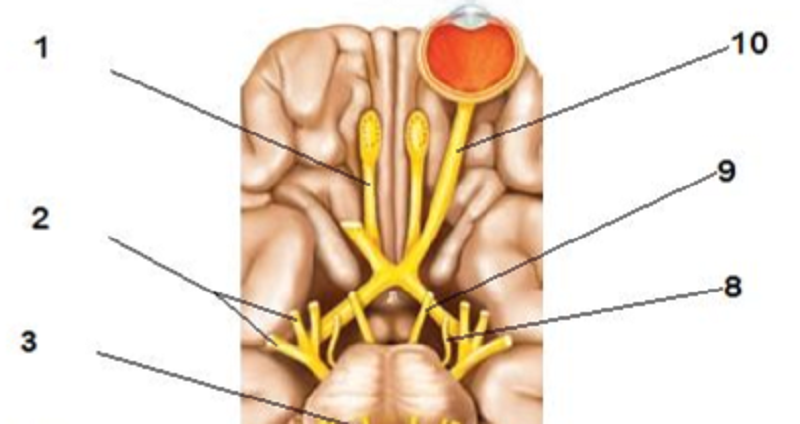
This figure shows the base of the brain. What does "8" represent?
The trochlear nerve (IV)
The oculomotor nerve (III)
The abducens nerve (VI)
The facial nerve (VII)
The vagus nerve (X)
Sex drive, body temperature, and food and water intake are regulated by
The limbic system
The thalamus
The pineal gland
The hypothalamus
The pituitary gland
This is the largest of the cranial nerve and the most important sensory nerve of the face.
The accessory nerve (XI)
The facial nerve (VII)
The trigeminal nerve (V)
The hypoglossal nerve (XII)
The abducens nerve (VI)
The hippocampus and amydala are structures found in
The medulla oblongata
The basal nuclei
The limbic system
The midbrain
The cerebral cortex
A patient is experiencing a high fever, stiff neck, drowsiness, and intense headaches. A spinal tap showed bacteria and white blood cells in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). This individual most likely has
Parkinson disease
Alzheimer disease
Meningitis
Hydrocephalus
A stroke
Destruction of the amygdala would most likely affect
Memory
Awareness of objects
Recognition and identification of objects
Expression of emotional feelings
Cognition
The ___ association area is responsible for perceiving and attending to stimuli, and the ___ association area is responsible for identifying them.
Temporal; parietal
Temporal; occipital
Frontal; occipital
Parietal; temporal
Occipital; frontal
{"name":"Week 1 Chapters 12-14", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge on the intricacies of action potentials and neuronal functions with our comprehensive quiz. Designed for students and enthusiasts of neuroscience, this quiz covers key concepts across chapters 12 to 14.30 thought-provoking multiple choice questionsImmediate feedback with scoringEnhanced understanding of neurophysiology concepts","img":"https:/images/course8.png"}
More Quizzes
Physiology - Action Potential Quiz
520
The nervous system
10519
Health - Lily Newman - Period 3
740
Tectónica de Placas
320
Quran Test Questions - Free Online
201027535
Cyber Security for Employees - Free Online
201018179
Colic - Is Your Baby Showing the Signs?
201020370
NCT Dream - Test Your NCTzen Knowledge
201028532
Which Sentence Contains a Dangling Modifier? - Free
201020151
Dragon Ball Z Personality - Which Character Are You?
201021066
Skyrim - Are You the Ultimate Dragonborn? (Free)
201022816
The Minimal Requirement for a Theatre Building Is -
201019630