RHM 1 ESAT PART 2

RF and Modulation Mastery Quiz
Test your knowledge on radio frequency modulation and related concepts with our comprehensive quiz! Perfect for aspiring engineers and RF enthusiasts, this quiz covers a wide array of topics to challenge your understanding and enhance your learning.
Get ready to dive into questions about:
- Amplitude and Frequency Modulation
- Transmission Line Theory
- SSB and DSB Technologies
- Noise and Bandwidth
One of the advantages of the base modulation over collector modulation of a transistor class C amplifier is
A. The lower modulating power required
B. Higher power output per transistor
C. Better efficiency
D. Better linearity
Determine the deviation ratio and bandwidth for the worst-case (widest-bandwidth) modulation index for an FM broadcast-band transmitter with a maximum, frequency deviation of 75 kHz and a maximum modulating-signal frequency of 15 kHz.
A. 5; 240kHz
B. 5; 120kHz
C. 2.5; 240kHz
D. 2.5; 120kHz
What is the ratio of modulating power to total power at 100 percent modulation?
A. 1:3
B. 1:2
C. 2:3
D. None of the above
What is the low-level carrier called that is sometimes transmitted along with the two sidebands in DSB?
A. Pilot carrier
B. Suppressed carrier
C. Composite carrier
D. Sideband carrier
Amplitude modulation is used for broadcasting because
A. It is more noise immune than other modulation systems.
B. Compared with other systems it requires less transmitting power
C. Its use avoids receiver complexity
D. No other modulation system can provide the necessary bandwidth for high fidelity
The characteristic impedance of a transmission line is:
A. The impedance of a section of the line one wavelength long
B. The dynamic impedance of the line at the operating frequency
C. The ratio of the power supplied to the line to the power delivered to the termination
D. Equal to the pure resistance which, if connected to the end of the line, will absorb all the power arriving along it
A sine wave carrier cannot be modified by the intelligence signal through which of the following?
A. Amplitude modulation
B. Pulse modulation
C. Frequency modulation
D. Phase modulation
Determine the characteristics impedance for an air dielectric two-wire parallel transmission line with a D❄r ratio of 12.22.
A. 50 ohms
B. 300 ohms
C. 75 ohms
D. None of the above
In a CW transmitter, the output from the _______ is connected to the driver/buffer.
A. Power amplifier
B. Telegraph key
C. Master oscillator
D. Power supply
A carrier is simultaneously modulated by two sine waves with modulation indices of 0.3 and 0.4; the total modulation index
A. is 1
B. Cannot be calculated unless the phase relations are known
C. is 0.5
D. is 0.7
In a typical CW transmitter, the _______ is the primary source of direct current.
A. driver/buffer
B. Power supply
C. Power amplifier
D. Master oscillator
In a CW transmitter, the _______ is in between the driver/buffer stage and the antenna.
A. Power supply
B. Power amplifier
C. Telegraph key
D. Master oscillator
Indicate the false statement regarding the advantages of SSB over double sideband full-carrier AM
A. More channel space is available.
B. Transmitter circuits must be more stable, giving better reception
C. The signal is more noise-resistant
D. Much less power is required for the same signal strength
The outputs of a differential amplifier taken from collectors to ground are
A. In phase
B. 45° out of phase
C. 90° out of phase
D. 180° out of phase
In an SSB transmitter, one is most likely to find a
A. class C audio amplifier
B. Tuned modulator
C. class B RF amplifier
D. class A RF output amplifier
Circuits that accept modulated signals and recover the original modulating information are called
A. modulators
B. detectors
C. Nonlinear circuits
D. Balanced filters
What is a coaxial cable?
A. Two wires side-by-side in a plastic ribbon
B. Two wires side-by-side held apart by insulating rods
C. Two wires twisted around each other in a spiral
D. A center wire inside an insulating material which is covered by a metal sleeve or shield
Indicate the false statement regarding the Armstrong modulation system
A. The system is basically phase, not frequency modulation.
B. AFC is not needed, as crystal oscillator is used.
C. Frequency multiplication must be used.
D. Equalization is unnecessary
An FM signal, 2000sin(2π×10^8t+2sinπ10^4 t)is applied to 50 ohm antenna. Determine the mf and ft.
A. 1 and 3 kHz
B. 1 and 5 kHz
C. 2 and 3 kHz
D. 2 and 5 kHz
What is parallel-conductor feed line?
A. Two wires twisted around each other in a spiral
B. A center wire inside an insulating material which is covered by a metal sleeve or shield
C. A metal pipe which is as wide or slightly wider than a wavelength of the signal it carries
D. Two wires side-by-side held apart by insulating rods
A pre-emphasis circuit provides extra noise immunity by
A. Boosting the bass frequencies
B. Amplifying the higher audio frequencies
C. pre-amplifying the whole audio band
D. Converting the phase modulation to FM
The crystal component of the crystal radio receivers that were widely used in the past is the
A. capacitor
B. transistor
C. diode
D. Integrated circuit
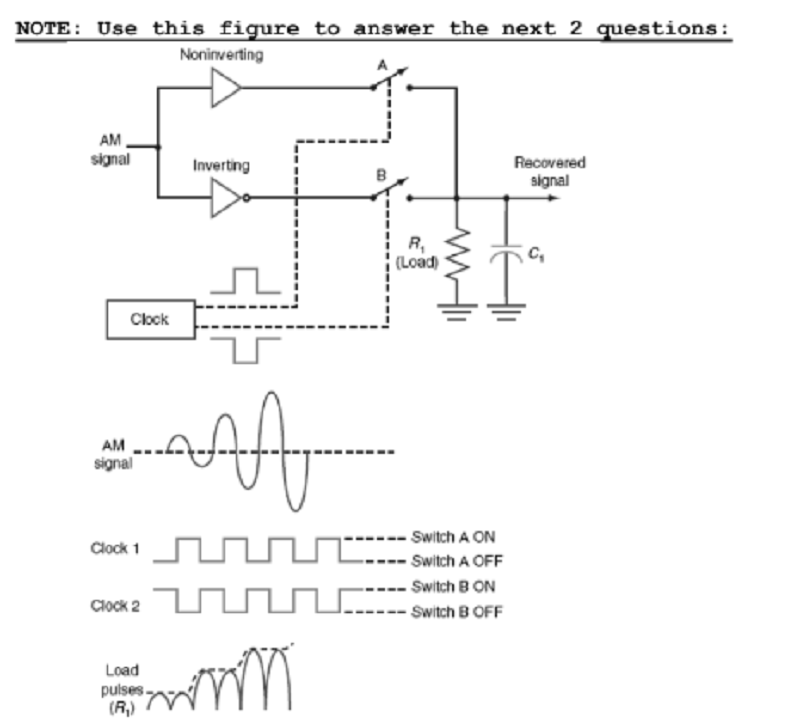
(1)How is the noninverted AM output of positive half- cycles fed to the load?
A. Clock turns on switch A
B. Clock turns on switch B
C. Inverting amp turns on
D. Noninverting amp turns off

(2)What is the result (output)?
A. half-wave rectification of the signal
B. full-wave rectification of the signal
C. dc
D. ac
An FM signal with a modulation index mf is passed through a frequency tripler. The wave in the output of the tripler will have a modulation index of
A. mf/3
B. mf
C. 3mf
D. 9mf
A receiver has a noise power bandwidth of 10 kHz. A resistor that matches the receiver input impedance is connected across its antenna terminals. What is the noise power contributed by that resistor in the receiver bandwidth, if the resistor has a temperature of 27 °C?
A. 3.72 x 10^-18 W
B. 4.14 x 10^-17 W
C. 3.23 x 10^-19 W
D. 4.11 x 10^-17 W
If your antenna feed line gets hot when you are transmitting, what might this mean?
A. You should transmit using less power
B. The conductors in the feed line are not insulated very well
C. The feed line is too long
D. The SWR may be too high, or the feed line loss may be high
A circuit that generates a DSB signal, suppresses the carrier and leaves only sum and difference frequencies at the output is the
A. Unbalanced detector
B. Balanced modulator
C. Carrier recovery circuit
D. demodulator
In DSB and SSB, the carrier that was suppressed at the DSB and SSB transmitter
A. Must be reinserted at the receiver
B. Must be transmitted after the signal was received
C. Must be replaced by a pilot carrier
D. Must be lower than 1500 kHz
An FM signal with a deviation δ is passed through a mixer, and has its frequency reduced fivefold. The deviation in the output of the mixer is
A. 5δ
B. Indeterminate
C. δ/5
D. δ
The process of phase-modulating a carrier with binary data is called
A. frequency-shift keying
B. multiplexing
C. Carrier phasing
D. phase-shift keying
The controlled oscillator synthesizer is sometimes preferred over the direct one because
A. It is a simpler piece of equipment
B. Its frequency stability is better
C. It does not require crystal oscillator
D. It is relatively free of spurious frequency
In a single sideband and CW receiver, the _______ is in between the mixer and intermediate frequency amplifier.
A. filter
B. Radio frequency amplifier
C. Beat frequency oscillator
D. Product detector
In a single sideband transmitter, the output of the _______ is connected to the filter.
A. microphone
B. Balanced modulator
C. mixer
D. Radio frequency oscillator
Any modulation process produces
A. carriers
B. sidebands
C. noise
D. amplification
In a ratio detector
A. The linearity is worse than in phase discriminator
B. Stabilization against signal strength variations is provided
C. The output is twice that obtainable from a similar phase discriminator
D. The circuit is the same as in a discriminator, except that the diodes are reversed
Why does coaxial cable make a good antenna feed line?
A. It is weatherproof, and its impedance is higher than that of most amateur antennas
B. It is weatherproof, and its impedance matches most amateur antennas
C. It can be used near metal objects, and its impedance is higher than that of most amateur antennas
D. You can make it at home, and its impedance matches most amateur antennas
A diode noise generator is required to produce 10 μV of noise in a receiver with an input impedance of 75 Ω, resistive, and a noise power bandwidth of 200 kHz (these values are typical of FM broadcast receivers.)
A. 133 mA
B. 92.3 pA
C. 276 mA
D. 133 nA
The typical squelch circuit cuts off
A. An audio amplifier when the carrier is absent
B. RF interference when the signal is weak
C. An IF amplifier when the AGC is maximum
D. An IF amplifier when the AGC is minimum
Which of the following is not an advantage of FM over AM?
A. Noise immunity
B. Capture effect
C. Circuit simplicity
D. Transmitter efficiency
Indicate the false statement in connection with communications receivers.
A. The noise limiter cuts off the receiver’s output during a noise pulse.
B. A product demodulator could be used for the reception of Morse code.
C. Double conversion is used to improve image rejection
D. Variable sensitivity is used to eliminate selective fading
A semiconductor device operated in reverse-bias mode whose capacitance can change in response to a modulating signal is the
A. Zener diode
B. Tunnel diode
C. Varactor diode
D. Unijunction transistor
In the spectrum of a frequency-modulated wave
A. The carrier frequency disappears when the modulation index is large
B. The amplitude of any sideband depends on the modulation index
C. The total number of sidebands depends on the modulation index
D. The carrier frequency cannot disappear
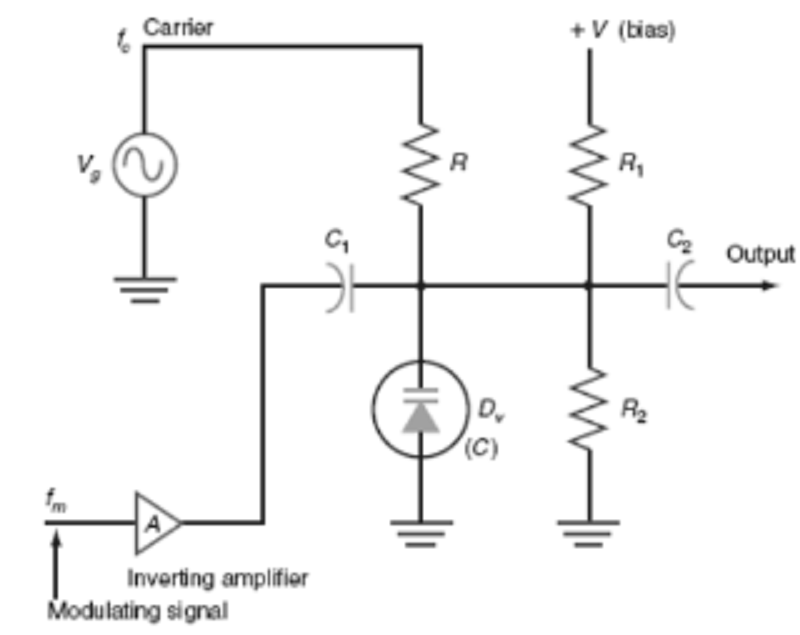
In the circuit shown above, if the modulating signal amplitude at the output of amplifier A becomes more positive the
A. Varactor becomes forward biased
B. varactor’s capacitance increases
C. Circuit produces more phase shift
D. Circuit produces less deviation
The frequency generated by each decade in a direct frequency synthesizer is much higher than the frequency shown; this is done to
A. Reduce the spurious frequency problem
B. Increase the frequency stability of the synthesizer
C. Reduce the number of decades
D. Reduce the number of crystals required
For an AM DSBFC modular with a carrier frequency fc=100 kHz and a maximum modulating signal frequency fm(max)=5 kHz, determine the upper and lower side frequencies produced when the modulating signal is a single-frequency 3kHz tone.
A. 103 kHz; 97 kHz
B. 101.5 kHz; 98.5 kHz
C. 108 kHz; 92 kHz
D. 104 kHz; 96 kHz
Most phase modulators are capable of producing an amount of phase shift essentially limited to
A. ± 5°
B. ± 10°
C. ± 15°
D. ± 20°
Indicate which one of the following advantages of the phase cancellation method of obtaining SSB over the filter method is false:
A. Switching from one sideband to the other is simpler.
B. It is possible to generate SSB at any frequency.
C. SSB with lower audio frequencies present can be generated
D. There are more balanced modulators; therefore the carrier is suppressed better
Circuits used to recover the original modulating signal from an FM transmission are called
A. modulators
B. synthesizers
C. discriminators
D. deflectors
In a single sideband and CW receiver, the _______ is connected to the radio frequency amplifier and the high frequency oscillator.
A. Beat frequency oscillator
B. Product detector
C. mixer
D. filter
An FM communication transmitter has a maximum frequency deviation of 5 kHz and a range of modulating frequencies from 300 Hz to 3 kHz. What is the maximum phase shift that it produces?
A. 1.67 rad
B. 1.52 rad
C. 20.2 rad
D. 16.7 rad
In a single sideband and CW receiver, the output of the _______ is connected to the mixer.
A. Intermediate frequency amplifier
B. High frequency oscillator
C. Beat frequency oscillator
D. Product detector
Which of the following is probably the most widely used FM demodulator?
A. Quadrature detector
B. Slope detector
C. pulse-averaging discriminator
D. PLL detector
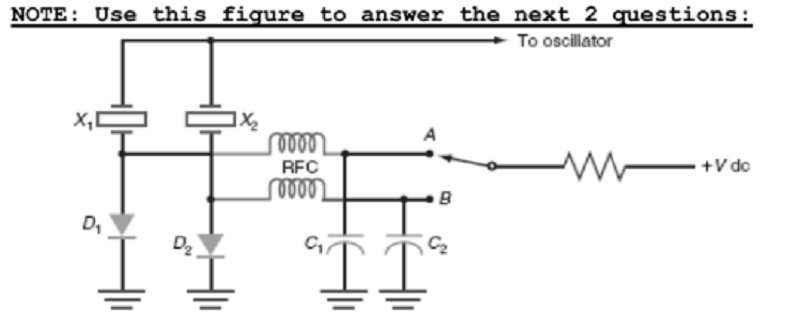
(1)What is the purpose of D1 in the circuit show?
A. Keep the RF signal out of the dc bias circuits
B. Sets a reference voltage when X1 is selected
C. connects X1to ground when selected
D. keeps X2 off
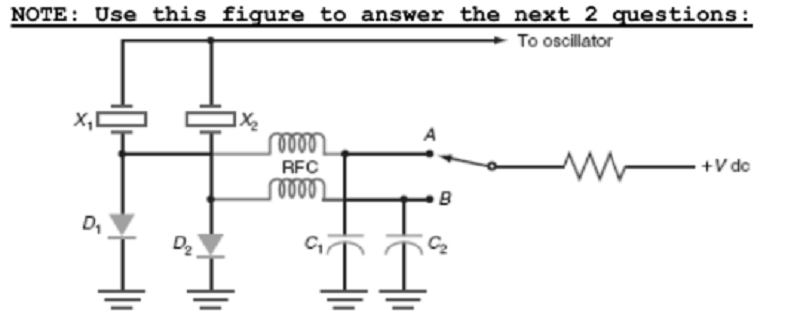
(2)What is the purpose of the RFCs in the circuit shown?
A. Keep the RF signal out of the dc bias circuits
B. Sets a reference voltage when X1 is selected
C. Form an oscillator with capacitors C1 and C2
D. Connect the RF signal to the dc bias circuits
In the stabilized reactance modulator AFC system,
A. The discriminator must have a fast time constant to prevent demodulation
B. The higher the discriminator frequency, the better the oscillator frequency stability
C. The discriminator frequency must not be too low, or the system will fail
D. Phase modulation is converted into FM by the equalizer circuit
Since noise phase-modulates the FM wave, as the noise sideband frequency approaches the carrier frequency, the noise amplitude
A. Remains constant
B. Is decreased
C. Is increased
D. Is equalized
A collector-modulated Class C amplifier has a carrier output power Pc of 100 W and an efficiency of 70%. Calculate the supply power and the transistor power dissipation with 100% modulation.
A. 150W; 45W
B. 214W; 64W
C. 150W; 105W
D. 214W; 149.8W
To reduce harmonic output from a transmitter, you would put a _______ in the transmission line as close to the transmitter as possible.
A. High pass filter
B. Low pass filter
C. Band reject filter
D. Wave trap
One of the following is an indirect way of generating FM. This is the
A. reactance FET modulator
B. Varactor diode modulator
C. Armstrong modulator
D. Reactance bipolar transistor modulator
What connects your transceiver to your antenna?
A. The power cord
B. A ground wire
C. A feed line
D. A dummy load
Which class of amplifier is not linear?
A. A
B. AB
C. B
D. C
An FM signal has a frequency deviation of 5 kHz and a modulating frequency of 1 kHz. The signal-to-note ratio at the input to the receiver detector is 20 dB. Calculate the approximate signal-to-noise ratio at detector output.
A. 34 dB
B. 17 dB
C. -6.0 dB
D. -3.0 dB
Which of the following amplifiers is used between the carrier oscillator and the final power amplifier to isolate the oscillator from the load?
A. class A buffer
B. high-power linear
C. class B push-pull
D. class C
What may happen if an SSB transmitter is operated with the microphone gain set too high?
A. It may cause interference to other stations operating on a higher frequency band
B. It may cause atmospheric interference in the air around the antenna
C. It may cause splatter interference to other stations operating near its frequency
D. It may cause digital interference to computer equipment
Which of the following oscillators can provide a highly accurate carrier frequency and have frequency stability over a wide temperature range?
A. Colpitts
B. crystal
C. Hartley
D. Armstrong
When the modulating frequency is doubled, the modulation index is halved, and the modulating voltage remains constant. The modulation system is
A. Amplitude modulation
B. Phase modulation
C. Frequency modulation
D. Any of the three
What is the usual bandwidth of a singlesideband amateur signal?
A. 1 kHz
B. 2 kHz
C. Between 3 and 6 kHz
D. Between 2 and 3 kHz
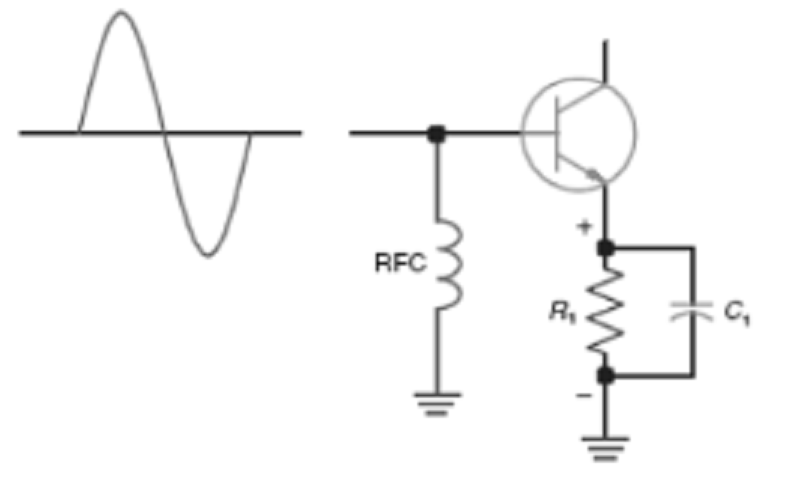
What biasing method is used by the circuit shown in below?
A. fixed
B. external
C. self-bias
D. internal
The exchange of energy between an inductor and a capacitor in a parallel tank circuit is referred to as the
A. Flywheel effect
B. Derating factor
C. Harmonic generation
D. Resonant frequency
Indicate which one of the following is not an advantage of FM over AM:
A. Better noise immunity is provided
B. Lower bandwidth is required
C. The transmitted power is more useful
D. Less modulating power is required
In a single sideband transmitter, the _______ is in between the balanced modulator and the mixer.
A. Radio frequency oscillator
B. Speech amplifier
C. filter
D. microphone
Find the modulation index if a 10V carrier is amplitude-modulated by three different frequencies with amplitudes of 1V, 2V and 3V, respectively.
A. 0.374
B. 0.361
C. 0.578
D. 0.636
In a single sideband transmitter, the _______ is connected to the speech amplifier.
A. Radio frequency oscillator
B. filter
C. mixer
D. microphone
Multipliers can be constructed to increase the input frequency by any integer up to approximately
A. 2
B. 3
C. 6
D. 10
What may your FM hand-held or mobile transceiver do if you shout into its microphone?
A. It may cause interference to other stations operating near its frequency
B. It may cause digital interference to computer equipment
C. It may cause atmospheric interference in the air around the antenna
D. It may cause interference to other stations operating on a higher frequency band
Frequency conversion which is a form of amplitude modulation is carried out by a mixer by a process known as
A. phasing
B. Heterodyning
C. demodulating
D. Multiplexing
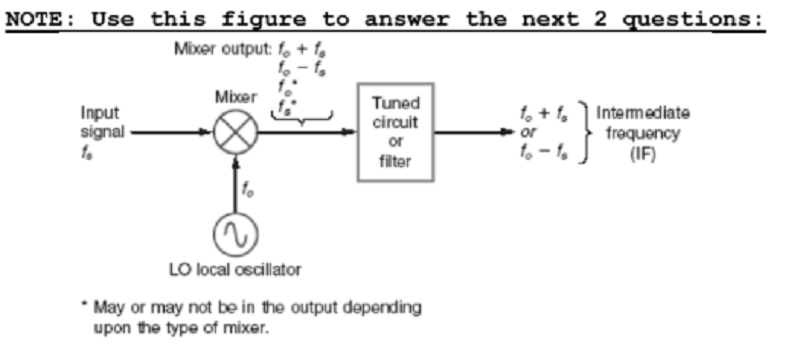
(1)Which of the following signals do not appear at the output of the mixer shown?
A. Input signal
B. Audio signal
C. Local oscillator signal
D. Local oscillator signal plus input signal
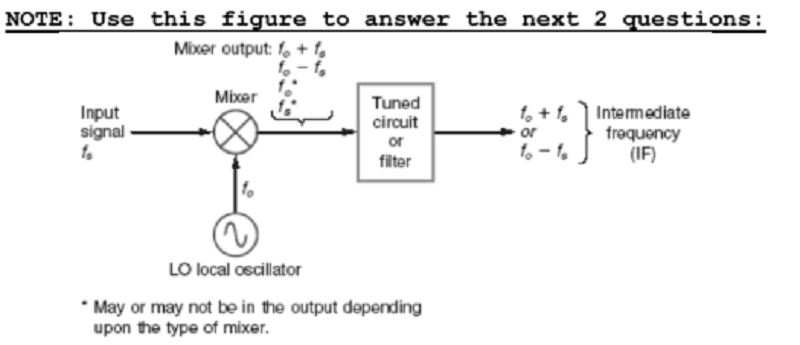
(2)What is the purpose of the tuned circuit shown?
A. Local oscillator
B. amplify RF signals
C. Mix oscillator and input signals
D. Select desired signal and reject all others
For an AM DSBFC transmitter with an unmodulated carrier power Pc=100W that is modulated simultaneously by three modulating signals with coefficients of modulation m1=0.2,m2=0.4,and m3=0.5, determine the upper and lower sideband power and the total transmitted power.
A. 22.445W; 122.445W
B. 22.445W; 144.89W
C. 44.89W; 144.89W
D. 11.2225W; 111.2225W
An electronic signal that is a mixture of many random frequencies at many amplitudes is
A. A harmonic
B. An overtone
C. noise
D. An infrared wave
Which of the following indicates the relative strengths of the signal and the noise in a communication system?
A. signal-to-noise ratio
B. Field strength
C. dB-to-noise factor
D. Field level noise ratio
A 300 Ω resistor is connected across the 300 Ω antenna input of a television receiver. The bandwidth of the receiver is 6 MHz, and the resistor is at room temperature (293 K or 20 °C or 68°F). Find the noise power and noise voltage applied to the receiver input.
A. 24.2 fW; 2.7 μV
B. 24.2 fW; 5.4 μV
C. 24.2 fW; 29 pV
D. 24.2 fW; 311 nV
In what emission type does the instantaneous amplitude (envelope) of the RF signal vary in accordance with the modulating audio?
A. Frequency modulation
B. Pulse modulation
C. Amplitude modulation
D. Frequency shift keying
Indicate the false statement. From the transmitter the signal deterioration because of noise is usually
A. Unwanted energy
B. Predictable in character
C. Present in the transmitter
D. Due to any cause
What may happen if an SSB transmitter is operated with too much speech processing?
A. It may cause digital interference to computer equipment
B. It may cause atmospheric interference in the air around the antenna
C. It may cause interference to other stations operating on a higher frequency band
D. It may cause splatter interference to other stations operating near its frequency
An intelligence signal is amplified by a 70% effecient amplifier before being combined with a 10kW carrier to generate the AM signal. If it is desired to operate at 100% modulation what is the dc input power to the final intelligence amplifier.
A. 7.14 kW
B. 9.08 kW
C. 4.68 kW
D. 2.03 kW
The time it takes a signal applied at one end of a transmission line to appear at the other end of the line is called
A. Signal time
B. Time constant
C. Transit time
D. Transmission delay
When the load impedance does not exactly match the line impedance and the load has reactive components in addition to its resistance, the line is said to be
A. open
B. shorted
C. reactive
D. resonant
What should you do for safety when operating at 1270 MHz?
A. Keep antenna away from your eyes when RF is applied
B. Make sure that an RF leakage filter is installed at the antenna feed point
C. Make sure the standing wave ratio is low before you conduct a test
D. Never use a horizontally polarized antenna
Assertion (A): A Smith chart can be used for a number of calculations of a transmission line Reason (R): Smith chart is basically a polar impedance diagram.
A. Both A and R are correct and R is correct explanation of A
B. Both A and R are correct but R is not correct explanation of A
C. A is correct but R is wrong
D. A is wrong but R is correct
In an ideal case where there are no standing waves, the standing wave ratio is
A. 0
B. 1
C. 100
D. infinite
Which of the following is not used to offset antenna reactance and to produce an impedance match?
A. π LC network
B. T LC network
C. π RC network
D. L LC network
What sound is heard from a public address system if audio rectification of a nearby single-sideband phone transmission occurs?
A. Clearly audible speech from the transmitter's signals
B. On-and-off humming or clicking
C. Distorted speech from the transmitter's signals
D. A steady hum whenever the transmitter's carrier is on the air
Leak-type bias is used in a plate-modulated class C amplifier to
A. Prevent tuned circuit damping
B. Prevent excessive grid current
C. Prevent overmodulation
D. Increase the bandwidth
What sound is heard from a public address system if audio rectification of a nearby CW transmission occurs?
A. Audible, possibly distorted speech
B. Muffled, severely distorted speech
C. A steady whistling
D. On-and-off humming or clicking
How can you minimize the possibility of audio rectification of your transmitter's signals?
A. By installing bypass capacitors on all power supply rectifiers
B. By using CW emission only
C. By ensuring that all station equipment is properly grounded
D. By using a solid-state transmitter
Special transmission lines constructed with copper patterns on a printed-circuit board that can be used as tuned circuits, filters, or impedance-matching circuits are called
A. microchip
B. stripline
C. PCB lines
D. Special lines
In a frequency modulation receiver, the _______ is in between the antenna and the mixer.
A. Audio frequency amplifier
B. High frequency oscillator
C. Intermediate frequency amplifier
D. Radio frequency amplifier
In a frequency modulation receiver, the _______ is connected to the input of the radio frequency amplifier.
A. mixer
B. Frequency discriminator
C. antenna
D. limiter
{"name":"RHM 1 ESAT PART 2", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge on radio frequency modulation and related concepts with our comprehensive quiz! Perfect for aspiring engineers and RF enthusiasts, this quiz covers a wide array of topics to challenge your understanding and enhance your learning.Get ready to dive into questions about:Amplitude and Frequency ModulationTransmission Line TheorySSB and DSB TechnologiesNoise and Bandwidth","img":"https:/images/course1.png"}
More Quizzes
RHM 1 ESAT PART 1
102510
EST
251245
Muscle and Bone Quiz
8420
Mega Man 1 Weakness Quiz
210
IPhone or Android - Discover Your Tech Persona
201018256
Business Aviation Knowledge Test - Free Online
201015831
Which Hazbin Hotel Character Would Date You? Free
201017167
Anime Music - How Many Openings Can You Name?
201021719
Is Melting Butter Physical or Chemical? 3rd Grade
201023126
0.05ml to ul Conversion - Free Metric Practice
201017756
Which of the Following Is True About Epithelia? Free
201017554
Accounting Test - Principles of Accounting (Free)
201017422