Mock AfL

Colorectal Cancer and Immunotherapy Quiz
Test your knowledge on pivotal concepts in oncology and immunotherapy with this engaging quiz. This assessment covers essential topics such as cancer biology, immunological responses, and infectious diseases, specifically designed for students and professionals in the medical field.
The quiz includes questions on:
- Key tumor suppressor genes
- Mechanisms of immunotherapy
- Pathophysiology of oncogenic viruses
- Metabolic disturbances in liver disease
Loss of which tumour suppressor gene is often shown as the first step in the progression model of colorectal cancer?
APC
B-Raf
P16
Rb
P14
Immunotherapy based on inhibition of immune checkpoint receptors aims to induce:
Apoptosis of B lymphocytes
Reactivation of B lymphocytes
Reactivation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Apoptosis of both B and T lymphocytes
Apoptosis of cytotoxic T lymphocytes
CpG islands can be linked to cancer by which of the following?
Mismatch repair mutations within CpG islands
A general increase in methylation during tumorigenesis
Development of CpG islands in genes during tumorigenesis
Transcriptional activation of proto-oncogenes
Epigenetic silencing of tumour suppressor genes
Which of the following describes the nature of hereditary (familial) cancers?
Caused by inherited mutations in genes that result in a recessive cellular phenotype
Caused by inherited mutations in genes that result in a dominant cellular phenotype
Display an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance
Caused by inherited mutations in proto-oncogenes
More common than sporadic cancers
TERT oncogene activation in malignant melanoma occurs via which of the following?
Mutations in TERT gene
Mutations in TERT gene promoter
Amplification of TERT gene
Viral insertion in TERT gene
Deletions in TERT gene
The human papilloma virus causes cervical and some types of head and neck cancers. Which of the following best explains its oncogenicity?
The virus inactivates the p53 and RB proteins to promote cancer as part of the viral life cycle
The virus is an obligate mutagen and must integrate the viral genomic DNA into the host cell chromosomal DNA as part of the normal life cycle of the virus
The virus has a double stranded DNA genome
The virus replicates in differentiated epithelial cells
The virus inactivates the p53 and RB proteins to promote cell cycle progression as part of the viral life cycle
KRAS oncogenic mutations can be best mapped to which of the following hallmarks of cancer?
Evading growth suppressors
Sustaining proliferative signalling
Inducing angiogenesis
Enabling replicative immortality
Activating invasion and metastasis
Which of the following suppresses the inflammatory activity associated with sepsis?
Tissue hypoperfusion
Extracellular release of DNA and histones
Neutrophil extracellular traps
Regulatory T-cells
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
Norovirus belongs to which of the following families of virus?
Paramyxoviridae
Caliciviridae
Adenoviridae
Hepadnaviridae
Orthomyxoviridae
Which of the following cell types blocks CD8+ T-cell recruitment and proliferation?
Cancer cell
Cancer associated fibroblast (CAF)
Pericyte
Regulatory T-cell (Treg)
Endothelial cell
Which of the following is a component of the innate immune system?
IgM
MHC class II receptor
IL-4
CD4 receptor
Toll-like receptor 4
Which of the following measures the transmissibility of an infectious disease?
Incidence
Infectious period
Basic Reproductive number
Incubation period
Proportion susceptible
Which of the following anti-infective drug targets are unique to prokarytic cells ?
Penicillin-binding proteins
Thymidine kinase
Lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase
Reverse transcriptase
Dihydrofolate reductase
Which is the best method to investigate whether H. Pylori has been eradicated by antibiotic therapy?
urea breath test
H. Pylori serology
H. pylori IgM test
H. pylori IgG test
diagnostic endoscopy
Which of the following is a unique feature of the cell wall of Gram positive organisms?
Outer membrane
Lipoteichoic acid
Peptidoglycan
Porins
Lipopolysaccharide
Which pathological process does the abnormal mucosa in Barrett’s oesophagus represent?
Hyperplasia
Metaplasia
Carcinoma in situ
Hypertrophy
Neoplasia
What metabolic disturbance in the liver is most likely to have contributed to disease in a 50-year-old man who regularly consumes 50 units of alcohol per week?
Production of acetate
Production of lactic acid
Inhibition of fatty acid oxidation
Production of ketone bodies
Inhibition of gluconeogenesis
What is the best procedure for the management of bleeding oesophageal varices
Surgery
permissive hypervolaemia
rubber band ligation during oesophago-gastro-duodenoscopy (OGD)
emergency diagnostic gastroscopy
fluid resuscitation
A patient with a crush injury to the body of the pancreas requires embolisation of his splenic artery which is bleeding. From where will the spleen now derive its blood supply?
Short gastric arteries
Superior mesenteric artery
Coeliac axis
Left gastric artery
True hepatic artery
In obstructive jaundice, reduction of which substance results in pale stools?
Bilirubin
Urobilinogen
Mucus
Blood
Stercobilin
Secretion of intrinsic factor occurs from which type of cell in the stomach?
Chief cells
D cells
G cells
Parietal cells
Enterochromaddin-like cells
A patient with gall stones is admitted with jaundice. How would the jaundice best be classified?
Hepatic
Pre-hepatic
Peri-hepatic
Post-hepatic
Supra-hepatic
Which of the following is classical for cerebellar disease?
Bradykinesia
Severe expressive aphasia
Impaired limb coordination
Prosopagnosia (face blindness)
Sensory ataxia
Which of the following best applies to Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease?
characterised by death before puberty
a primary inflammatory disorder of peripheral nerves
a progressive disease
a genetic disease, primarily of the central nervous system
usually clinically apparent at birth
Which of the following best applies to Guillain-Barré syndrome?
is a chronic degenerative disease of peripheral nerves
is a progressive disease which leads eventually to permanent paralysis
can affect the peripheral nerves that supply the muscles of respiration
generally, includes upper motor neuron signs
is the result of immunosuppression
Which of the following best applies to Huntington’s disease?
is associated with hypertrophy of the neostriatum
affects only males
is a triplet-repeat genetic disorder
cannot be predicted using a genetic test
tends to present progressively later onset in each generation of a family
AChR (acetylcholine receptor) antibodies act at the neuromuscular junction in myasthenia gravis by which mechanism?
Reducing the number of voltage dependent calcium channels
Reducing the speed of the action potential
Blocking the binding of acetylcholine to the receptor
Blocking the release of acetylcholine into the synaptic cleft
Decreasing the degradation rate of AChR
Which of the following is an aggressive form of glial cell tumour?
Oligodendroglioma
Meningioma
Glioblastoma multiforme
Melanoma
Ependymoma
Which neurotransmitter is most likely to be deficient in a patient with Parkinson’s disease?
Acetylcholine
Dopamine
Serotonin
GABA
Noradrenaline/norepinephrine
A 19 year old man is stabbed in his upper back. He has weakness in his right leg, with loss of pain and temperature sensation in his left leg. Which type of spinal injury has he sustained?
Posterior cord syndrome
Anterior cord syndrome
Cauda equina syndrome
Central cord syndrome
Hemisection of the spinal cord
Compression of which left-sided cranial nerve is most likely to result in the left pupil being fixed and dilated in a patient with an intracranial haemorrhage?
Trochlear
Optic
Oculomotor
Facial
Abducens
A young woman presents because she has difficulty in seeing things on either side. On examination, she is found to have difficulty in both temporal fields. What is the most likely cause?
Frontal meningioma
Occipital stroke
Partial seizure
Migraine
Pituitary tumour
In Beauchamp & Childress’s four principles approach, the principle of non-maleficence is associated with which of the following?
the concept of paternalism
Equity
self-governance
the obligation to minimise harm
Equality
Mr Y has been admitted to Emergency Department after a serious car accident. He is unconscious and in need of immediate life-saving treatment. What should the doctors do?
Not treat Mr Y
Treat Mr Y immediately
Attempt to contact Mr Y's next of kin before acting
Attempt to wake Mr Y up and ask for his consent
Obtain a court mandated treatment order before treating Mr Y
Mrs X has been admitted for a knife injury which she tells the F1 Doctor she sustained while cooking. However, given the nature of the injury, the F1 doctor doubts that her explanation is true. In addition to treating Mrs X, what should the doctor do?
Consult with a senior colleague about their suspicions before taking any further action
Ignore their suspicions
Notify the police of their suspicions (without telling Mrs X)
Notify the police of their suspicions (and inform Mrs X that they are going to do so)
Ask a senior colleague to call the police
Which of the following best applies when a child is judged to be Gillick competent?
The child’s consent to treatment is required in addition to the consent of their parents
They can consent and dissent to a treatment that has been classified as minor or routine only
They can consent and dissent to any treatment
They can consent to some treatment but not necessarily dissent
They can consent to a treatment that has been classified as minor or routine only
Henrietta Lacks died of cervical cancer in 1951 but cells derived from her cancer are still being used in academic and commercial research. In retrospect what would be considered the greatest breach of good clinical practice in this case?
Confidentiality: The cells were named HeLa after the patient
Benefits justifying risks: The patient died with no benefit from donating the samples
Autonomy: The patient did not give informed consent for the use of her samples in research
Reproducibility and bias: There was no audit trail maintained for the use of the samples
Justice: Considerable financial benefit was obtained from the samples none of which benefitted the patient
Ordinarily a child is presumed to be Gillick competent from what age?
16
17
14
15
18
A patient in a coma requires a routine procedure. The patient's son has been appointed as a surrogate decision-maker. Who should the doctor share information about this procedure with?
Information should be shared with the patient's son
No one - the procedure cannot go ahead unless the patient is able to consent
Information should be shared with the patient and their son
No one - the procedure can be undertaken without anyone's consent
Information should be shared with the patient as their ability to understand cannot be assessed
A group of researchers undertook a Cohort study to investigate the impact of alcohol consumption on the development of liver problems. They recruited participants living in England and aged over 30 years. They followed-up the participants for 15 years. The primary outcome for the study was the development of any alcohol related liver condition. In this study what would be the unexposed group?
Participants aged over 30 who had never ever consumed alcohol
Participants aged over 30 who rarely consumed alcohol
Participants aged over 30 who consumed large amounts of alcohol
Participants aged over 30 who were currently not consuming alcohol
Participants aged over 30 who consumed alcohol
A research study found the risk of stroke amongst those on anti-hypertensive treatment was 0.15 and those not on anti-hypertensive treatment was 0.05. What is the difference in risk of stroke between those on anti-hypertensive treatment and those not on treatment?
0.1
0.2
0.3
3.0
2.0
An ecological study finds an association between rates of caesarean section (CS) and Gross Domestic Product (GDP) within individual countries. What is a common pitfall to be aware of when interpreting these data?
Association at group level may not reflect association at individual level
Researchers cannot be blinded to the information that they are collecting
Countries may have different indications for performing a caesarean section
There may not be adequate recall of number of caesarean sections
There are questionable ethics in examining the GDP of a country
In the UK all healthcare workers who have been exposed to blood borne viruses at work are followed up to gather data on their exposure. What type of surveillance is being undertaken?
Enhanced surveillance
Passive surveillance
Sentinel surveillance
Syndromic surveillance
Active surveillance
When interpreting a case control study, which of the following measures of effect can we directly calculate?
Risk ratio
Rate difference
Odds ratio
Prevalence
Rate ratio
Which of the following is described as the maximum amount of air moved in and out of the lungs in a single respiratory cycle?
FEV1
Total lung capacity
Tidal Volume
Functional respiratory capacity
Vital Capacity
A 42 year old lady with a history of intermittent cough and breathlessness is sent for a number of tests to look for asthma. She is obese with a BMI of 40 kg/m2. She does not smoke. Which of the following would support a diagnosis of asthma?
Spirometry does not improve with bronchodilators
The PC 20 to histamine is <8mg/ml
Spirometry is normal
The diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO) is low
IgG levels are elevated
An 65 year old man is admitted with a cough and fever. He has a history of COPD. On examination, he is wheezy throughout. A chest x-ray shows overinflation but is clear. On admission his oxygen saturation is 88% on air. His arterial blood gas result is shown here (normal range in brackets): pH 7.37 (7.35-7.45) PaO (kPa) 6.8 (11.0-13.0) PaCO (kPa) 6.9 (4.7-6.0) HCO (mmol/L) 26 (22-26) Base excess 0 (-2-+2) What do the blood gases show?
A compensated metabolic acidosis
A compensated respiratory alkalosis
Type 2 respiratory failure
Type 1 respiratory failure
Normal
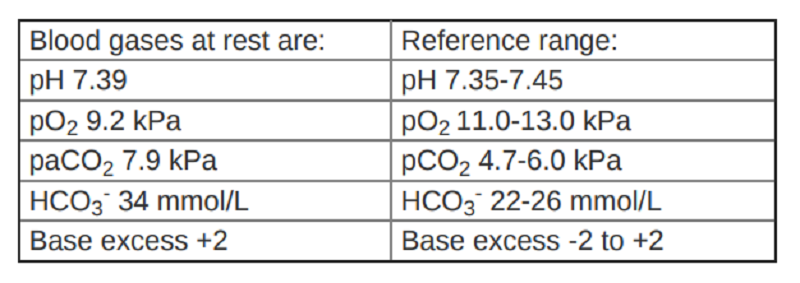
A 58 year old woman with a BMI of 42 kg/m2 has an overlap between obstructive sleep apnoea and obesity hypoventilation. She uses home overnight non-invasive ventilation (NIV) with no supplementary oxygen. Her arterial blood gases at rest are: Which abnormalities do these show?
Compensated respiratory acidosis
Metabolic alkalosis
Compensated metababolic acidosis
Type 2 respiratory failure
Type 1 respiratory failure
Which is the commonest causative pathogen in community acquired pneumonia?
Moraxella catarrhalis
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Chlamydophilia pneumoniae
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Legionella pneumoniae
In premature infants born before 32 weeks, lack of surfactant may impair which of the following?
Alveolar expansion
Mucociliary clearance
Biofilm formation
Diaphragmatic contraction
Mucus secretion
Which of the following is most likely to be associated with sudden and frequent waking at night, high BMI and alcohol consumption?
Sleep apnoea
Depression
Alcohol dependency
Hypomania
Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnoea
Which area of the brain stem is likely to have been damaged if a 58 year old patient has great difficulty with forced expiration both at rest and during exercise?
Apneustic centre
Phrenic nerve centre
Dorsal respiratory group
Ventral respiratory group
Pneumotaxic centre
What blood gas change would lead to these central chemoreceptors being stimulated in COPD?
A decrease in arterial pH
A decrease in arterial PO2
A decrease in venous PO2
An increase in venous PCO2
An increase in arterial PCO2
A 55 year old man with lung cancer has persistent hiccups. Pathology involving which of the following nerves is likely to have resulted in this symptom?
Recurrent laryngeal
Glossopharyngeal
Phrenic
Hypoglossal
Vagus
In the management of chronic asthma, which of the following medications requires therapeutic drug monitoring?
Corticosteroids
Theophylline
Omalizumab
Long acting β2 agonists
Leukotriene receptor antagonists
Salbutamol acts via which of the following receptors to relax airway smooth muscle in acute asthma?
Muscarinic receptor
Glucocorticoid receptor
Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor
Adenosine receptor
β2-adrenoreceptor
When comparing two drugs, which of the following best describes the more potent agent?
Requires a lower dose to produce the same biological effect
Will produce a greater biological effect
Has a longer half life
Has a shorter half life
Requires a higher dose to produce the same biological effect
Which of the following is an anti-IgE monoclonal antibody used in the treatment of asthma?
Omalizumab
Rituximab
Reslizumab
Benralizumab
Mepolizumab
Salbutamol and Salmeterol, used in asthma management to relax airway smooth muscle, are chemically related to which of the following?
Thyroxine
Adrenaline
Serotonin
Acetylcholine
Cortisol
Which structure fuses to form the penile urethra?
Urogenital folds
Cloacal membrane
Labioscrotal swellings
Urogenital sinus
Genital tubercle
When interpreting urinary flow rates Q max refers to which of the following?
Maximum urethral pressure
Maximum detrusor pressure
Maximum flow rate
Maximum voided volume
Maximum bladder capacity
Which investigation would be most appropriate to predict if a 56 year old woman with a 4cm right ovarian cyst seen on transvaginal ultrasound scan has an ovarian cancer?
serum CA19-9
abdomino-pelvic ultrasound
serum CA125
CT of abdomen and pelvis
hysteroscopy
Which symptom is most closely associated with an overactive bladder?
Post micturition dribbling
Double micturition
Poor stream
Hesitancy
Urgency
Which blood test would indicate persistence of trophoblastic disease?
CA125
Alpha-fetoprotein
Carcinoembryonic antigen
Lactate dehydrogenase
hCG
Which is the most likely cause of a urinary tract infection in a 40 year old female with dysuria, urinary frequency and non-visible haematuria?
Proteus mirabilis
Bacteroides fragilis
Escherichia coli
Enterococcus faecalis
Candida albicans
Which organism converts glycogen to lactic acid within the vagina?
Group A Streptococci
Pseudomonas
Lactobacilli
Proteus
Chlamydia
Which area does adenocarcinoma of the prostate most predominantly affect?
Central zone
Anterior fibromuscular stroma
Urethra
Peripheral zone
Transition zone
What is the most common clinical finding in chronic kidney disease (CKD)?
Shortness of breath
Anorexia
Haematuria
Asymptomatic
Pallor
{"name":"Mock AfL", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge on pivotal concepts in oncology and immunotherapy with this engaging quiz. This assessment covers essential topics such as cancer biology, immunological responses, and infectious diseases, specifically designed for students and professionals in the medical field.The quiz includes questions on:Key tumor suppressor genesMechanisms of immunotherapyPathophysiology of oncogenic virusesMetabolic disturbances in liver disease","img":"https:/images/course4.png"}
More Quizzes
Part 20 (164)
164820
Micro GIT
221134
Biology Labs :)
158770
Time and Activity Quiz
420
Free Amortization: Analyze & Understand
201024540
Health Finance
15821988
Unlock Mind Tricks and Answers - Try the Fun
201025190
Which Desperate Housewife Are You? Ultimate Personality
201027428
Test Your Density Skills: Questions on Density
201036293
Discover Your Katekyo Hitman Reborn Character - Free
201030943
Physical Activity & Cognition
15827155
Free Heart Failure Diagnosis
201023545