C2 lab 2019

Clinical Competency Quiz: Diabetes and Hematology
Test your knowledge on diabetes mellitus, hematologic disorders, and related diagnoses with our comprehensive quiz. Featuring 20 multiple-choice questions, this quiz covers essential symptoms, diagnostic criteria, and laboratory values crucial for medical professionals.
Key Topics Covered:
- Diabetes Mellitus Symptoms
- Anemia Types and Diagnoses
- White Blood Cell Disorders
- Clinical Laboratory Values
All of the following are symptoms suggesting the presence of diabetes mellitus except:
Polyuria
Heat intolerance
Increased thirst
Unexplained weight loss
Fatigue and somnolence
If no symptoms of diabetes mellitus are present (or when symptoms are present) and random blood glucose (RBG) is below 200 mg/dl (<11.1mmol/L), you should:
Perform an OGTT
Measure fasting glucose once
Measure fasting glucose twice
Perform a RBG on separate day
Follow-up the patient in one month
If no symptoms of hyperglycemia are present and random blood glucose is >200 mg/dl (>11.1mmol/L, you should:
Perform an OGTT
Measure fasting glucose once
Measure fasting glucose twice
Perform a RBG on separate day
Follow-up the patient in one month
A definitve diagnosis of LADA requires:
Anti-GAD65, and /or a low serum peptide C level
Absence of autoantibodies typical for DM type 1
No insulin dependence
HNF1A gene mutation
A3243G gene mutation
A distinction between hypo- and hyperproliferative anemias can be made based on:
MCV, MCH
Reticulocyte count and/or reticulocyte index
RDW
MCHC
RDW-SD
Red blood cell fragments on microscopy of the blood film are found in:
Iron deficiency Anemia
MAHA
AIHA
Folic acid deficiency anemia
Vitamin B12 deficiency anemia
All of the following are hypoproliferative microcytic anemias except:
Megaloblastic anemia
Iron deficiency anemia
Thalassemia
Sideroblastic anemia
Anemia of chronic disease
Which of the following is true?
The normal lymphocyte cound in adults is 1500 to 4800 /uL; in children <2yr, 3000 to 4800/uL , at age 6yr the lower limit of normal is 1500/uL
The normal lymphocyte cound in adults is 1000 to 4800 /uL; in children <2yr, 3000 to 4800/uL , at age 6yr the lower limit of normal is 3000/uL
The normal lymphocyte cound in adults is 1000 to 4800 /uL; in children < 2yr, 3000 to 9500/uL , at age 6yr the lower limit of normal is 1500/uL
The normal lymphocyte cound in adults is 3000 to 4800 /uL; in children < 2yr, 3000 to 4800/uL , at age 6yr the lower limit of normal is 1500/uL
The normal lymphocyte cound in adults is 1500 to 4800 /uL; in children < 2yr, 4800 to 9500/uL , at age 6yr the lower limit of normal is 3000/uL
Which of the following is true?
Leukopenia is a reduction in the WBC count <4000/uL, lymphocytopenia is a total number of lymphocytes <1000/uL, neutropenia is neutrophil count <1500/uL
Leukopenia is a reduction in the WBC count <4000/uL, lymphocytopenia is a total number of lymphocytes <1500/uL, neutropenia is neutrophil count <1000/uL
Leukopenia is a reduction in the WBC count <4000/uL, lymphocytopenia is a total number of lymphocytes <1000/uL, neutropenia is neutrophil count <500/uL (in whites)
Leukopenia is a reduction in the WBC count <4000/uL, lymphocytopenia is a total number of lymphocytes <1500/uL(in whites), neutropenia is neutrophil count <1500/uL(in blacks)
Leukopenia is a reduction in the WBC count <1000/uL, lymphocytopenia is a total number of lymphocytes <1000/uL, neutropenia is neutrophil count <1000/uL(in blacks)
Causes of aplastic anemia include:
Benzene, Radiation, Drugs, Pregnancy, Epstein Barr Virus, Hepatitis(seronegative for hepatitis virus)
Benzene, Radiation, Drugs, Pregnancy, Hookworm infection, Hepatitis(seronegative for hepatitis virus)
Iron deficiency, Radiation, Drugs, Pregnancy, Epstein Barr Virus, Hepatitis(seronegative for hepatitis virus)
Benzene, Radiation, Drugs, periods of rapid growth in children, Epstein Barr Virus, Hepatitis(seronegative for hepatitis virus)
Benzene, anaphylactic reaction, Drugs, Pregnancy, Epstein Barr Virus, Hepatitis(seronegative for hepatitis virus)
Myeloproliferative disorders include all of the following except:
Essential thrombocytopenia
Primary myelofibrosis
Polycythemia Vera
Secondary Polycythemia
Chronic myelogenous Leukemia
Which of the following are the causes of hyperproliferative anemias(haemolytic)?
Iron deficiency, kidney disease, folate deficiency, hypersplenism, paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria
B12 deficiency, cold agglutitin disease, spherocytosis
Hypersplenism, TTP, HUS, hereditary spherocytosis
Sickle cell disease, TTP , Myelodysplasia, myelophtisis
Chronic disease, thalassemias, iron utilization defect, pure red cell aplasia
Ceruloplasmin:
Scavenges Fe from the serum and after binding iron has a half-life of 5 days, and converts iron II to Iron III
Scavenges Mg from the serum and after binding Magnesium has a half-life of 5 days, and converts iron II to Iron III
Scavenges Cu from the serum and after binding iron has a half-life of 5 days, and converts iron III to Iron II
Scavenges Cu from the serum and after binding copper has a half-life of 5 days, and converts iron II to Iron III
er binding copper has a half-life of 5 hours, and converts iron II to Iron III
Reference ranges for white blood cells are:
Total WBC ̝s 4000 to 10.000, Basophils 0 to 100; Monocytes 0-800, eosinophils 0-350; monocytes 0-800, neutrophils 1500-7500, lymphocytes 1000- 4000
Total WBC ̝s 4000 to 11.000, Basophils 0 to 100; Monocytes 0-800, eosinophils 0-100; monocytes 0-800, neutrophils 1500-7500, lymphocytes 1000- 4000
Total WBC ̝s 4000 to 10.000, Basophils 0 to 350; Monocytes 0-800, eosinophils 0-100; monocytes 0-800, neutrophils 1500-7500, lymphocytes 1000- 4000
Total WBC ̝s 4000 to 10.000, Basophils 0 to 800; Monocytes 0-100, eosinophils 0-350; monocytes 0-800, neutrophils 1500-7500, lymphocytes 1000- 4000
Total WBC ̝s 4000 to 10.000, Basophils 0 to 100; Monocytes 0-800, eosinophils 0-350; monocytes 0-800, neutrophils 1500-7500, lymphocytes 1500- 7500
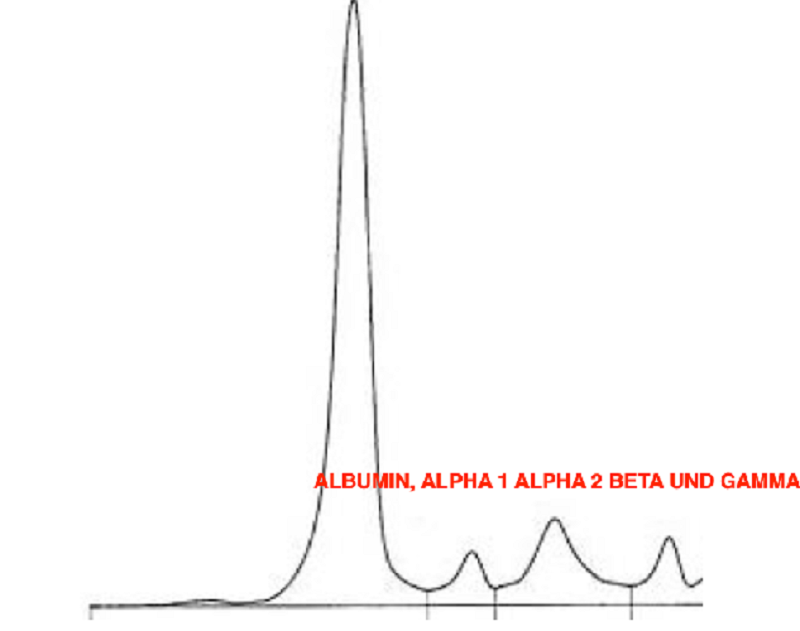
The electrophoregram shows(albumin on the left):
Acute phase response
Chronic inflammation
Advanced liver disease
Monoclonal hypergammaglobulinemia
Agammagloblulinemia
Normal range of serum bilirubin;and limit above which jaundice is detectable, are:
15-34 micromolar; >70 micromolar
12-31 micromolar; >60 micromolar
9-28 micromolar; >30 micromolar
6-25 micromolar; >40 micromolar
3-22 micromolar; >60 micromolar
The following results of complete blood count: RBC:2,9x10^6/uL, HB: 8,2 g/dL, Hematocrit: 27%, MCV: 93fl, MCHC 34g/dL, reticulocyte percentage 0,20% are consistent with:
Anemia - normocytic, hypoproliferative, normochromic
Normal levels
Anemia - normocytic, hypoproliferative, hypochromic
Anemia - microcytic, hyperproliferative, hyperchromic
Anemia - microcytic, hypoproliferative, normochromic
A general target level for HbA1C in patients with DM is:
<8%
<7%
<6,5%
<6%
<7,5%
Agranulocytosis is defined as the level of neutrophils below(per microliter):
100
200
500
600
800
All of the following are causes of the right shift in white blood cells except:
CML
Neutropenia(e.g. Megaloblastic anemia)
Liver disease
Cancer
Drugs
{"name":"C2 lab 2019", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge on diabetes mellitus, hematologic disorders, and related diagnoses with our comprehensive quiz. Featuring 20 multiple-choice questions, this quiz covers essential symptoms, diagnostic criteria, and laboratory values crucial for medical professionals.Key Topics Covered:Diabetes Mellitus SymptomsAnemia Types and DiagnosesWhite Blood Cell DisordersClinical Laboratory Values","img":"https:/images/course1.png"}
More Quizzes
Lab C3 ENTRY 2023
331677
Lab cycle 2 RBC WBC
40200
DM
5220
Therapeutic quiz " lab investigations "
5257
QCM 2 semestre
834242
Exam Part 5(1056-1095)nana 2
100500
Acute Kidney Injury
1169
THE CRANIAL CONTEST
251221
(NEW)part8(2000-2039).......(1785-2039)7brettpit
108540
Chapter 47
20100
Lab cycle 2 - 2022
392071
MCQs for Family Master
5221