How the Papilla Supplies Nourishment to the Hair Bulb: Quiz
Quick, free hair bulb nourishment quiz. Instant results and brief explanations.
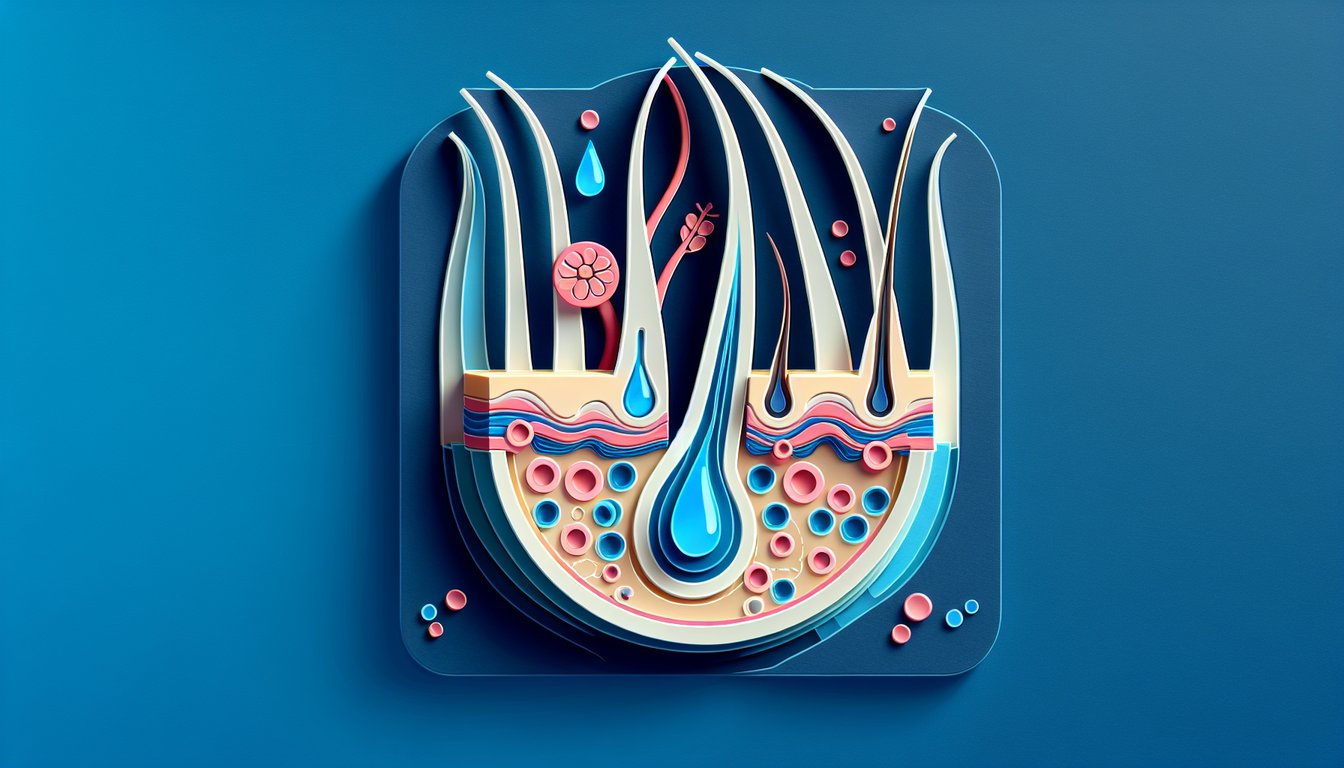

This quiz helps you check how the papilla supplies nourishment to the hair bulb and the role of capillaries and matrix cells in growth. Get instant results, short explanations, and tips to study faster. Keep learning with our dermal papilla quiz, a hair anatomy quiz, and a hair and scalp properties quiz.
Study Outcomes
- Identify Nourishing Hair Structures -
Pinpoint which hair structure supplies nourishment to the hair bulb by examining key follicle components revealed in the quiz.
- Explain Hair Bulb Nutrition -
Articulate how nutrient exchange at the dermal papilla supports hair bulb nutrition and influences healthy hair growth.
- Analyze Scalp Anatomy Quiz Findings -
Interpret scalp anatomy quiz results to map out each layer's role in delivering nutrients to the hair follicle.
- Apply Trichology Quiz Insights -
Utilize knowledge gained from the trichology quiz to inform effective hair care strategies and treatments.
- Evaluate Hair Structure Quiz Performance -
Assess your understanding of hair structure quiz concepts to identify strengths and areas for further study in trichology.
Cheat Sheet
- Dermal Papilla: The Primary Nourisher -
Often asked in a trichology quiz, the dermal papilla is the hair structure that supplies nourishment to the hair bulb via an extensive capillary network. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, its blood vessels deliver oxygen and nutrients directly to germinal matrix cells. Remember the mnemonic "DP = Direct Provider" to ace any hair structure quiz question!
- Capillary Network & Microcirculation -
The scalp's dense capillary bed around the follicle underpins hair bulb nutrition by regulating blood flow - Poiseuille's law (Q ∝ r❴) highlights how small vessel diameter changes hugely impact nutrient delivery. University research shows that enhanced microcirculation techniques can boost hair growth phases. Visualize 'r to the fourth power' to recall how crucial vascular health is for which hair structure supplies nourishment to the hair bulb.
- Germinal Matrix Cell Proliferation -
The germinal matrix inside the bulb relies on dermal papilla nutrients to fuel rapid cell division, producing the hair shaft and inner root sheath (International Journal of Trichology). A solid grasp of this link is key for the scalp anatomy quiz, as these cells define hair growth rates. Think "Matrix = Make More" when reviewing hair bulb nutrition concepts.
- Sebaceous Glands vs. Vascular Supply -
While sebaceous glands secrete sebum for scalp lubrication, they don't feed the hair bulb - this common trichology quiz pitfall highlights the difference between nourishment and protection. Official sources like the Journal of Dermatological Science clarify that sebum maintains the hair shaft, whereas the dermal papilla's capillaries handle true hair bulb nutrition. Use the phrase "sebum for sheen, papilla for protein" to lock in this distinction.
- External Factors Affecting Hair Nutrition -
Hormonal shifts, nutrient deficiencies, and certain medications can alter scalp blood flow and impede the structure that supplies nourishment to the hair bulb (National Institutes of Health studies). Regularly testing yourself with a hair structure quiz ensures you stay sharp on how lifestyle impacts hair bulb nutrition and overall scalp anatomy. A quick self-quiz - "Which factor slows Q in Poiseuille's law?" - boosts retention and confidence.