PIC: USLME-DIAGNOSTIC 2

USLME Diagnostic Challenge
Test your medical knowledge with our comprehensive USLME Diagnostic Quiz! Designed for healthcare professionals and students, this quiz features a variety of clinical scenarios to enhance your diagnostic skills.
Includes:
- 55 thought-provoking questions
- Detailed case studies
- Immediate feedback on your answers
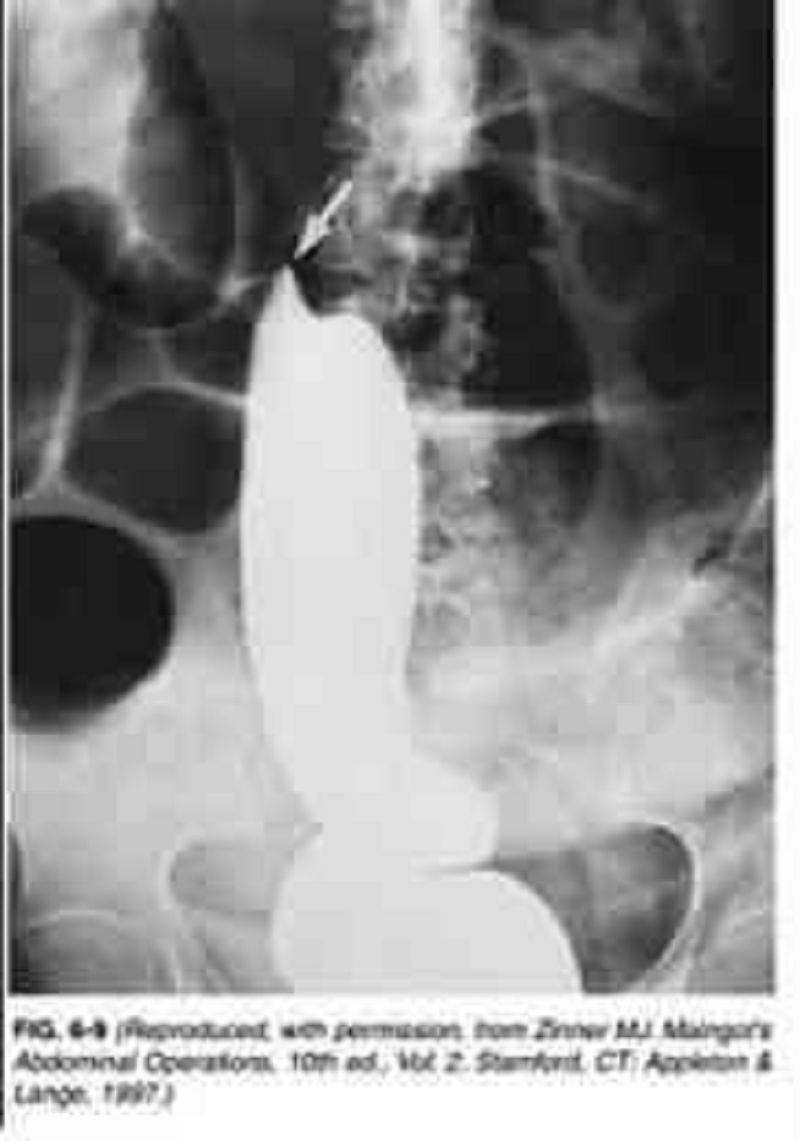
A 75-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department from a nursing home for abdominal pain, distention, and obstipation over the last 2 days. Past history is pertinent for stroke, diabetes, atrial fibrillation, and chronic constipation. Examination reveals a temperature of 98.6°F, pulse rate 90/min and irregularly irregular, and BP 160/90 mmHg. Heart examination reveals irregularly irregular rhythm with no murmurs; lung examination reveals few bibasilar rales; and abdominal examination reveals a distended, tympanic abdomen with mild tenderness and no rebound tenderness. Plain abdominal x-rays reveal dilated loops of bowel, and a barium enema is obtained and shown in Figure 6-9. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Ischemic colitis with stricture
Diverticulitis with obstructio
Cecal volvulus
Sigmoid volvulus
Colon cancer with obstruction
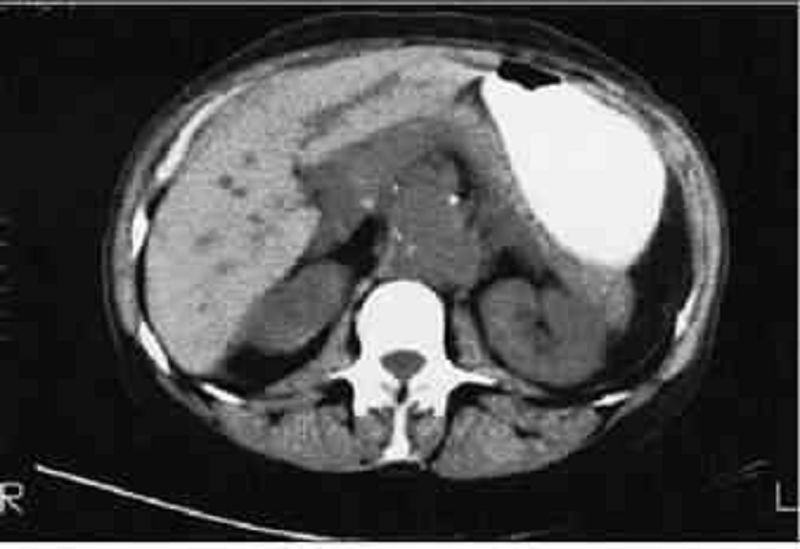
A 76-year-old woman presents with acute onset of persistent back pain and hypotension. A CT scan is obtained (shown below), and the patient is taken emergently to the operating room. Three days after surgery she complains of abdominal pain and bloody mucus per rectum. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Staphylococcal enterocolitis
Diverticulitis
Bleeding arteriovenous (AV) malformation
Ischemia of the left colon
Bleeding colonic carcinoma
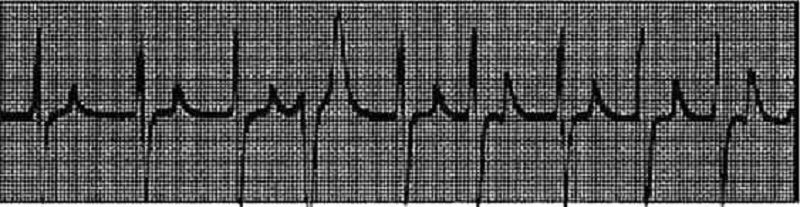
A 78-year-old man with advanced renal disease has the ECG shown in Fig. (lead II). What is the diagnosis?
Hyperkalemia
Hypercalcemia
Hypernatremia
Pericarditis
Ventricular aneurysm
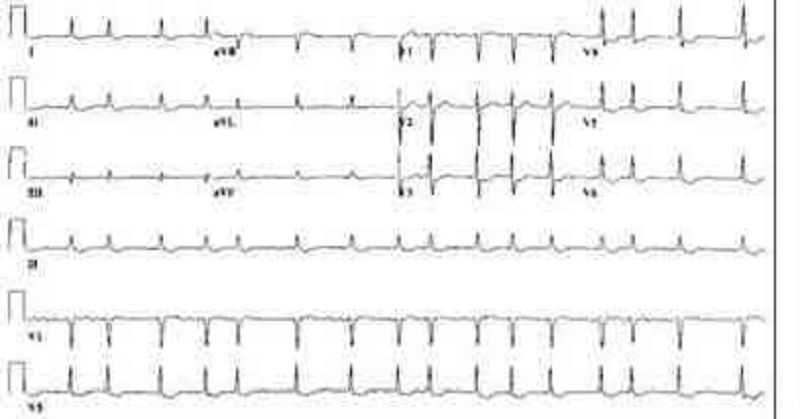
A 78-year-old woman presents to a nursing home physician complaining of palpitations over the past several months. Her episodes are not associated with any chest pain, dizziness, or loss of consciousness. The patient reports that she spent several weeks in the hospital as a child with rheumatic fever. ECG is shown in the image. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Atrial fibrillation
Atrial flutter
Multifocal atrial tachycardia
Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia
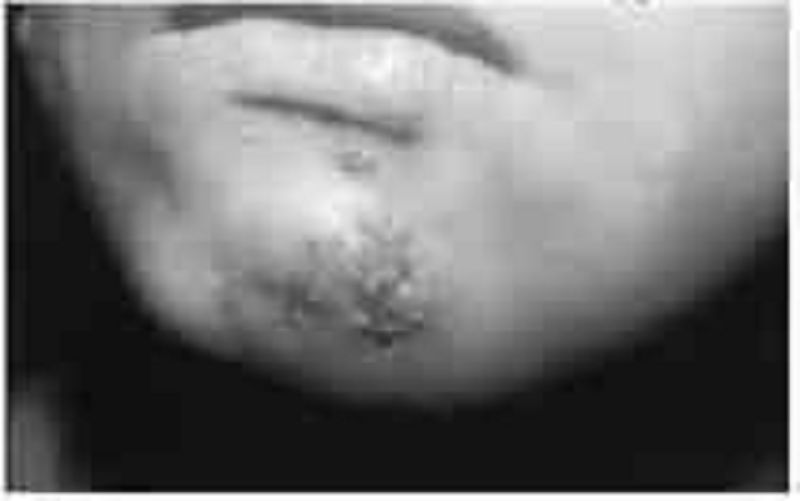
A boy has returned home from visiting his grandmother in a rural area. He spent most of his time swimming, playing in the yard, helping in the gardens, and chasing his Chihuahua; his grandma says “he was generally dirty!” He was noted 2 weeks ago to have “infected mosquito bites” on his neck and chin for which the local doctor had him just scrub with soap; a few remain and are shown in the photograph below. His mother brings him into the office with the complaint of dark urine, swelling around his eyes, and shortness of breath. You also find him to have hypertension and hepatomegaly. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his problem?
IgA nephropathy
Post streptococcal glomerulonephritis
Idiopathic hypercalciuria
Pyelonephritis
Sexually transmitted disease
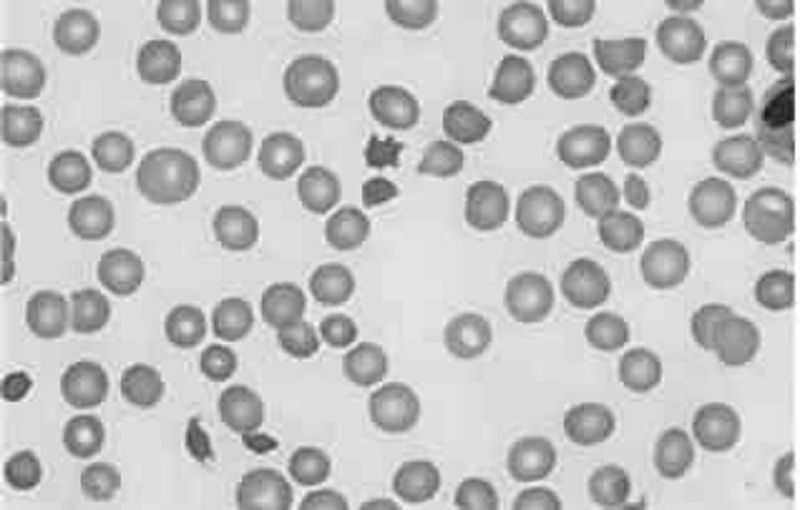
A college sophomore is found by his roommate emergency department. After resuscitation, the man complains of a severe headache and photophobia that is accompanied by dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and neck pain. Physical examination is noteworthy for positive Kernig’s and Brudzinski’s signs as well as petechiae on the trunk and mucocutaneous bleeding. Laboratory studies show: WBC count: 17,000/mm3, Hemoglobin: 11 g/dL, Platelet count: 70,000/mm3, Bleeding time: 10 min, Prothrombin time: 17 sec, Activated partial thromboplastin time: 47 sec, Thrombin time: 18 sec. A peripheral blood smear is shown in the image. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
Factor V Leiden
Immune thrombocytopenic purpura
Protein C deficiency
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
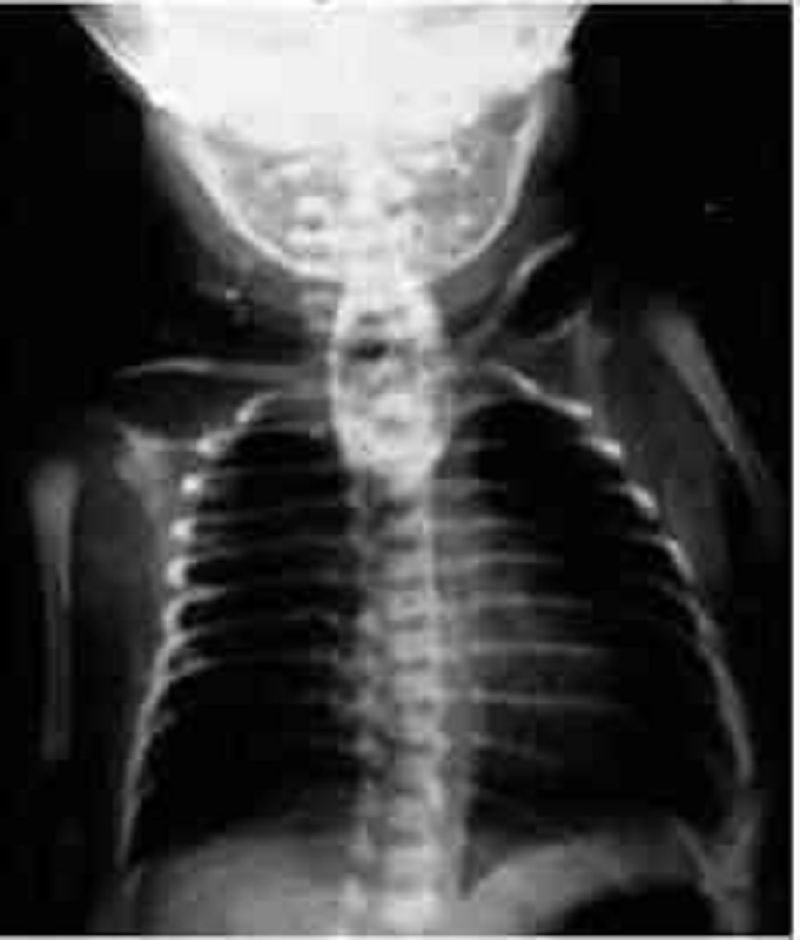
A male infant is delivered at 37 weeks’ gestation via cesarean section for breech presentation. The pregnancy was complicated by polyhydramnios. The 34-year-old mother is rubella immune and has blood type B. She is negative for Rh antibody, Group B streptococci, rapid plasma reagin, hepatitis B surface antigen, gonorrhea, and Chlamydia. At delivery there is no meconium. He has a birth weight of 2.7 kg (6 lb). The baby has a weak cry and is pale and frothing at the nose and mouth. He has nasal flaring and retractions, with a respiratory rate of 56/min. Heart rate is 140/min and he has a regular rhythm and a harsh 2/6 holosystolic murmur that is best heard at the left sternal border. On auscultation he has fine diffuse crackles in his lungs bilaterally. The infant is missing both thumbs and has fusion of the remaining digits of his upper extremities bilaterally. The pediatric resident is able to suction secretions from the patient’s nasopharynx and oropharynx; however, she is unable to pass a nasogastric or orogastric tube more than 10 cm down. X-ray of the chest is shown in the image. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia
Pyloric stenosis
Respiratory distress syndrome
Tracheoesophageal fistula
Transient tachypnea of the new-born
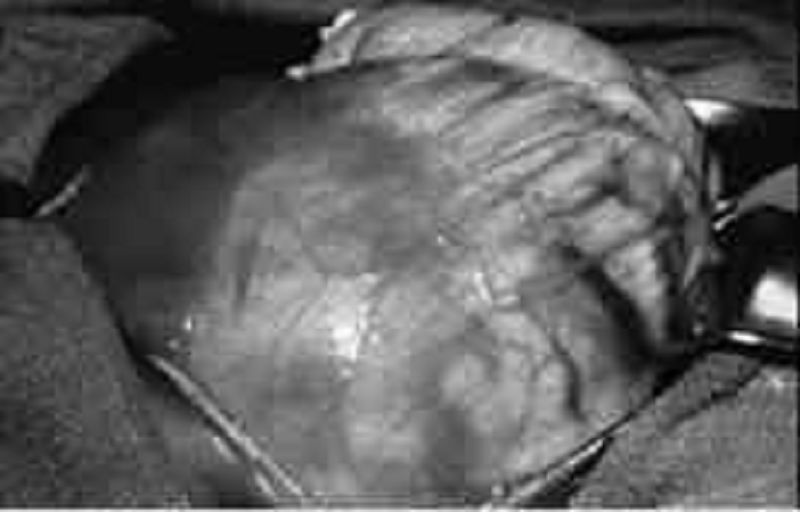
A mother notices an abdominal mass in her 3-year-old son while giving him a bath. There is no history of any symptoms, but the boy’s blood pressure is elevated at 105/85 mm Hg. Metastatic workup is negative and the patient is explored. The mass shown here is found within the left kidney. Genetic testing reveals deletion of 2 genes on chromosome band 11p13. Which of the following anomalies in addition to the identified tumor is associated with these chromosomal deletions?
Cardiac anomalies
Hemihypertrophy
Hypoglycemia
Macroglossia
Aniridia
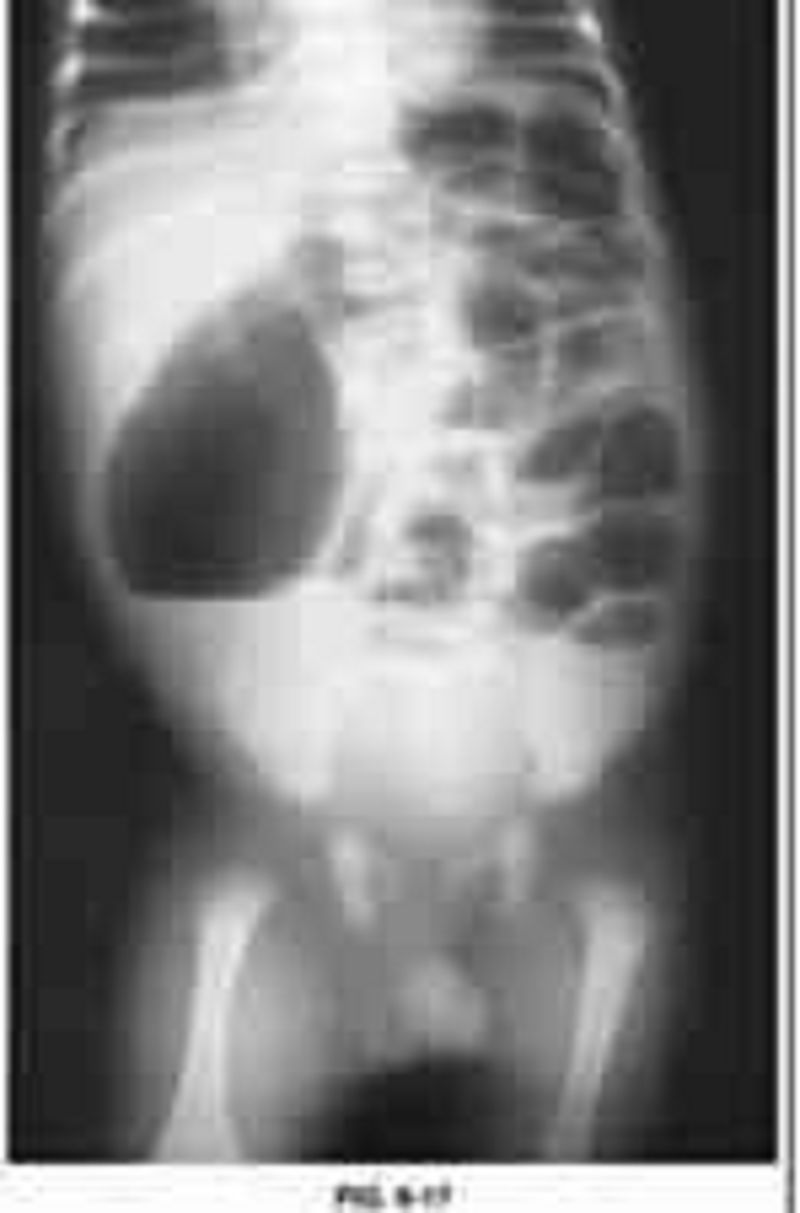
A neonate with bile-stained vomiting, abdominal distention, dilated loops of bowel on plain radiographs, and a small-caliber colon on contrast enema (Figure 6-17). Which one is the most likely diagnosis?
Congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
Annular pancreas
Duodenal atresia
Midgut volvulus
Jejunal atresia
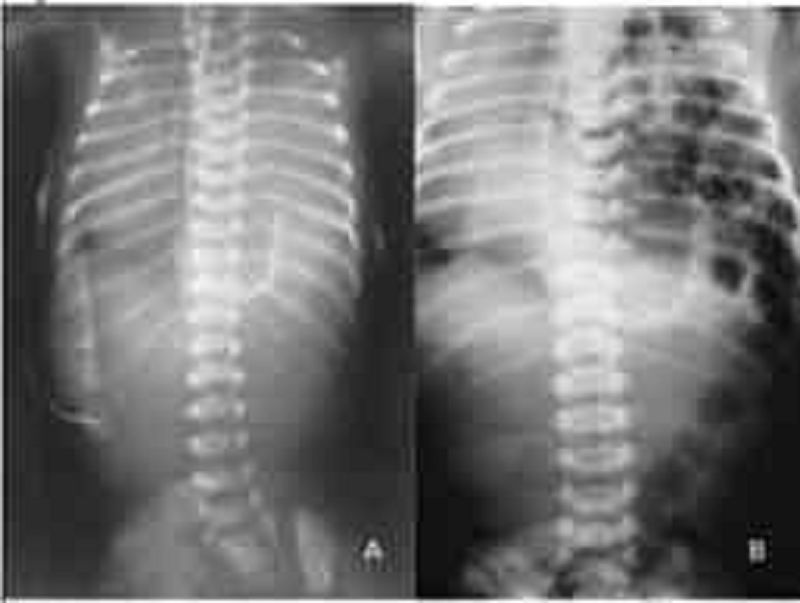
A newborn infant develops respiratory distress immediately after birth. His abdomen is scaphoid. No breath sounds are heard on the left side of his chest, but they are audible on the right. Immediate intubation is successful with little or no improvement in clinical status. Emergency chest x-ray is shown (Image A) along with an x-ray 2 hours later (Image B). Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this infant’s condition?
Pneumonia
Cystic adenomatoid malformation
Diaphragmatic hernia
Choanal atresia
Pneumothorax
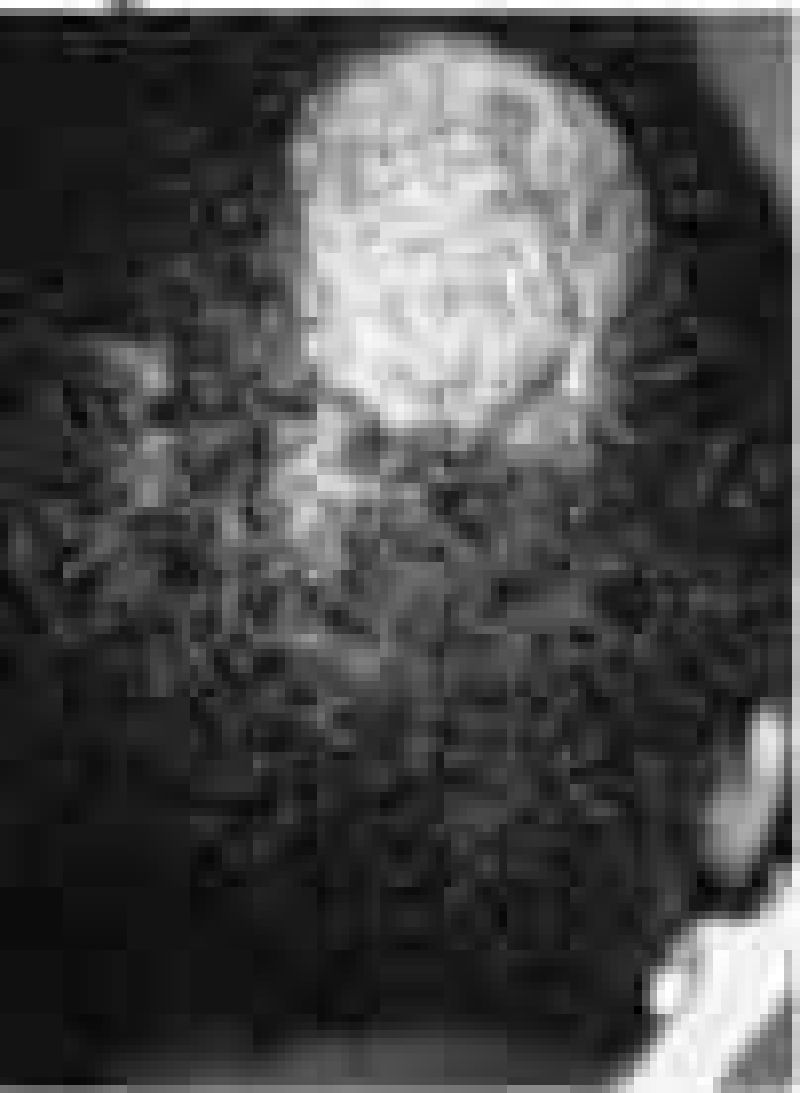
A patient with hair loss is shown below. The lesion does not fluoresce with a Wood lamp and has not responded well to a variety of topical agents. The lesion is boggy, is spreading, and has tiny pinpoint black dots throughout. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Traction alopecia from tight hair braids
Infection with Trichophyton tonsurans
Alopecia areata
Biotinidasedeficiency
Hypothyroidism
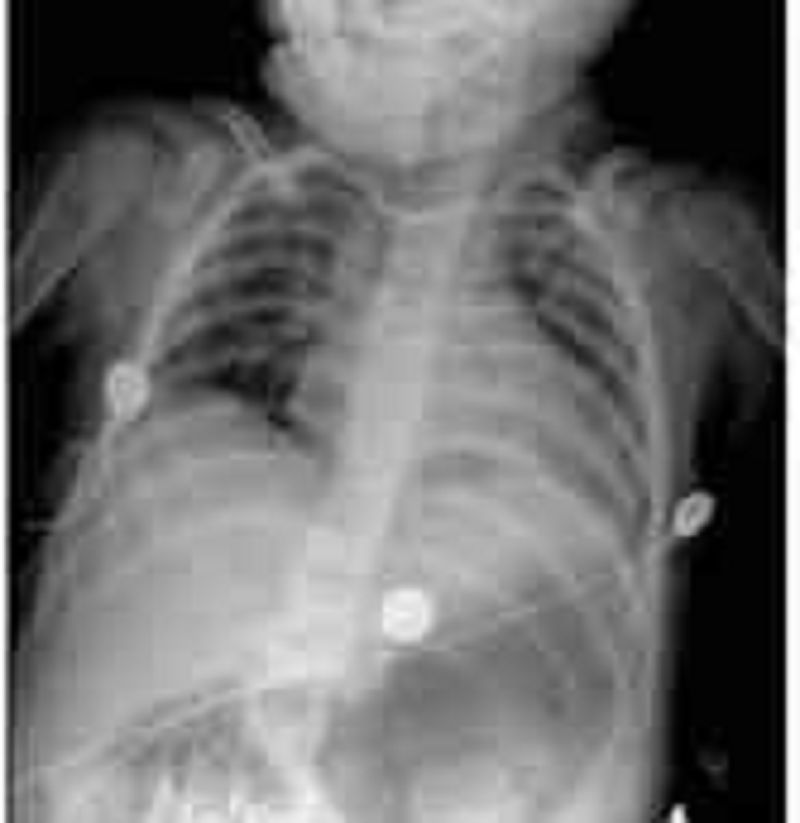
A previously healthy 4-year-old boy is brought to the physician for evaluation of fever and respiratory distress. The patient developed fever three days ago. Since then, he has had increasing fatigue, irritability, and respiratory distress. His temperature is 100 F (38.2C), pulse is 144/min, respiratory rate is 45/min, and blood pressure is 95/60 mm Hg. On examination, the child appears to be in moderate respiratory distress with tachypnea and subcostal retractions. He is tachycardic with an III/IV holosystolic murmur best heard at the cardiac apex. Peripheral pulses are present and capillary refill is three seconds. His liver is palpated three centimeters below the costal margin. A chest radiograph is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
Community-acquired pneumonia
Viral hepatitis
Rheumatic fever
Kawasaki disease
Myocarditis

A previously healthy 4-year-old child pictured below presents to the emergency room (ER) with a 2-day history of a brightly erythematous rash and temperature of 40°C (104°F). The exquisitely tender, generalized rash is worse in the flexural and perioral areas. The child is admitted and over the next day develops crusting and fissuring around the eyes, mouth, and nose. The desquamation of skin shown in the photograph occurs with gentle traction. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Epidermolysis bullosa
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
Erythema multiforme
Drug eruption
Scarlet fever
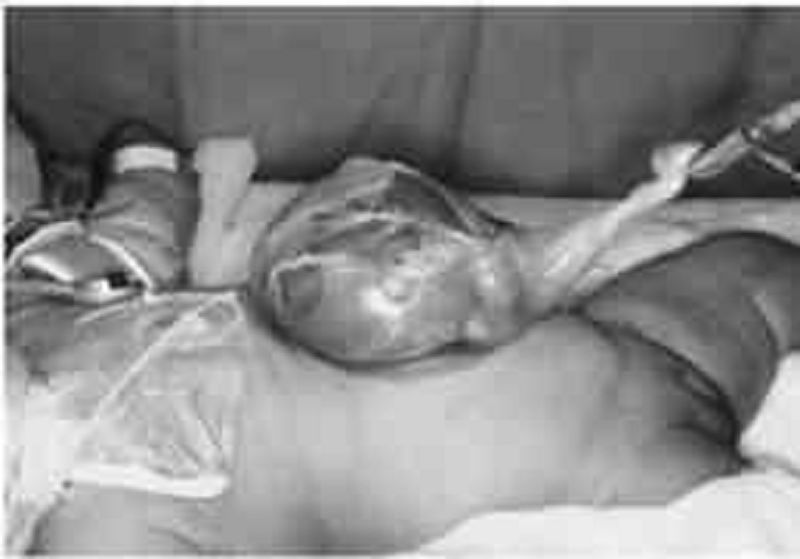
A term infant is born at a small community hospital by caesarean section for failure to progress. The infant is noted to have the following abnormality at birth. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Umbilical hernia
Omphalitis
Omphalocele
Gastroschisis
Traumatic evisceration
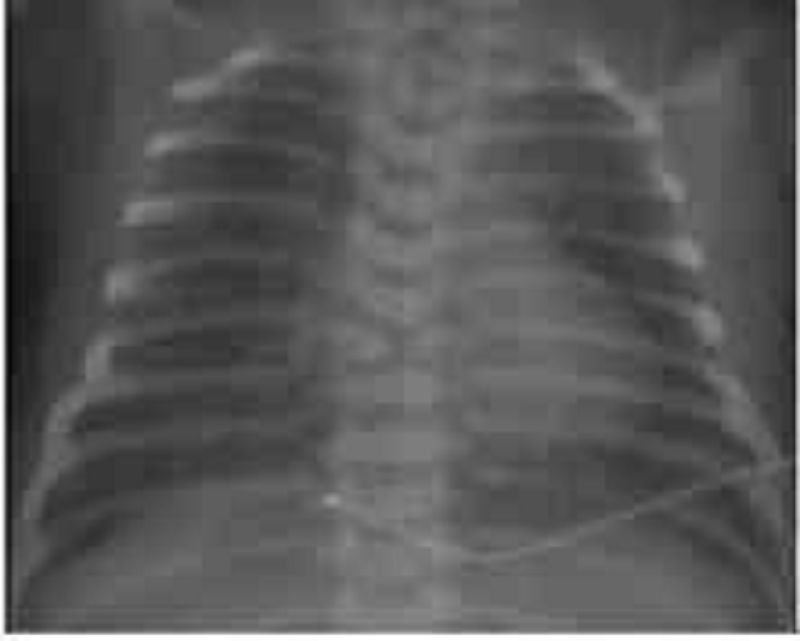
A term, 4200-g (9-lb, 4-oz) female infant is delivered via cesarean section because of cephalopelvic disproportion. The amniotic fluid was clear, and the infant cried almost immediately after birth. Within the first 15 minutes of life, however, the infant’s respiratory rate increased to 80 breaths per minute, and she began to have intermittent grunting respirations. The infant was transferred to the level 2 nursery and was noted to have an oxygen saturation of 94%. The chest radiograph is shown. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Diaphragmatic hernia
Meconium aspiration
Pneumonia
Idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome
Transient tachypnea of the newborn
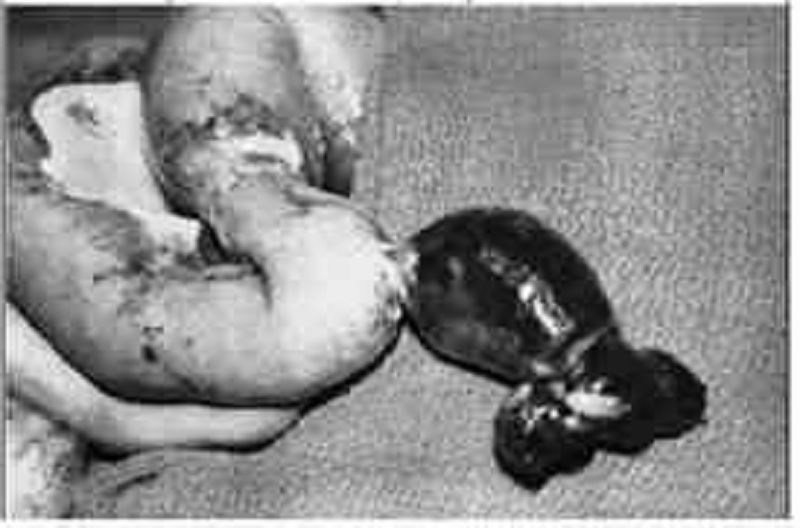
An 18-year-old woman presents with abdominal pain, fever, and leukocytosis. With the presumptive diagnosis of appendicitis, a right lower quadrant (McBurney) incision is made and a lesion 60 cm proximal to the ileocecal valve is identified (see photo). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Intestinal duplication
Mesenteric cyst
Meckel diverticulum
Ileoileal intussusception
�Christmas tree” type of ileal atresia
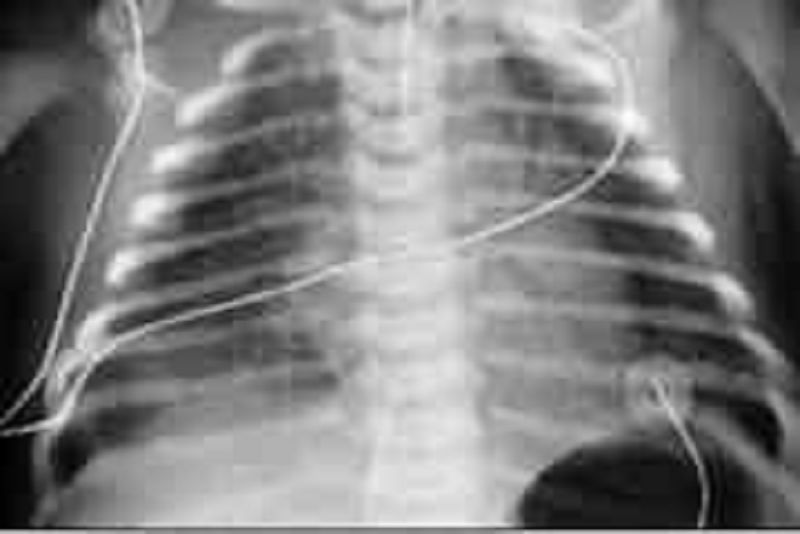
An 8-hour-old infant develops increased respiratory distress, hypothermia, and hypotension. A complete blood count (CBC) demonstrates a white blood cell (WBC) count of 2500/μL with 80% bands. The chest radiograph is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Congenital syphilis
Diaphragmatic hernia
Group B streptococcal pneumonia
Transient tachypnea of the newborn
Chlamydial pneumonia
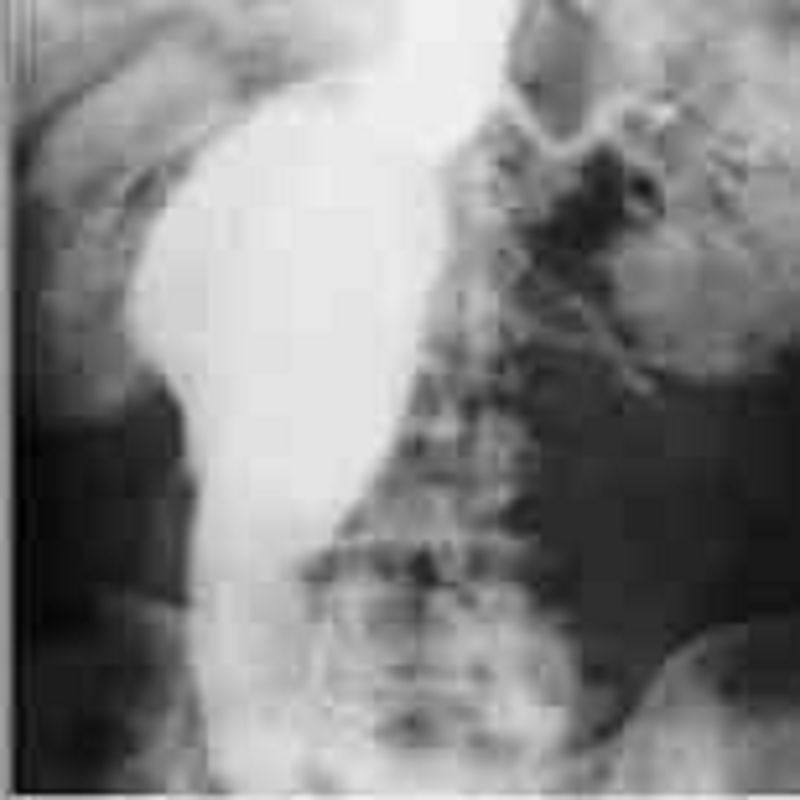
An 80-year-old man is found to have an asymptomatic pulsatile abdominal mass. An arteriogram is obtained (shown below). Which of the following is the most frequent and lethal complication of this condition?
Rupture
Acute thromboembolism
Dissection
High-output congestive heart failure
Myocardial infarction
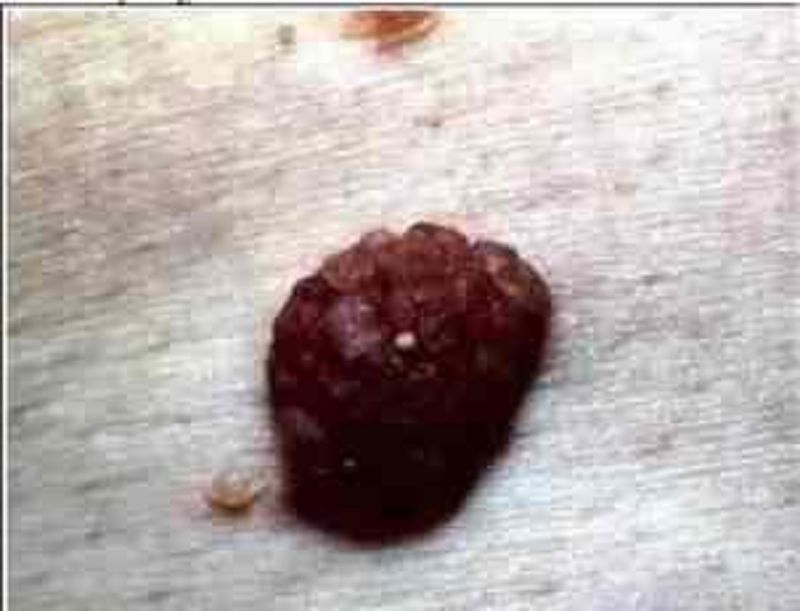
An 80-year-old woman comes to the office and appears very upset. She requests removal of a lesion on her neck because "it is greasy and unsightly." She is tired of people constantly staring at her neck. The lesion has been present "for quite a while," and has been gradually darkening. Aside from occasional itching, there are no other symptoms. A picture of the lesion is shown below. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Basal cell carcinoma
Melanoma
Seborrheic keratosis
Actinic keratosis
Acrochordon
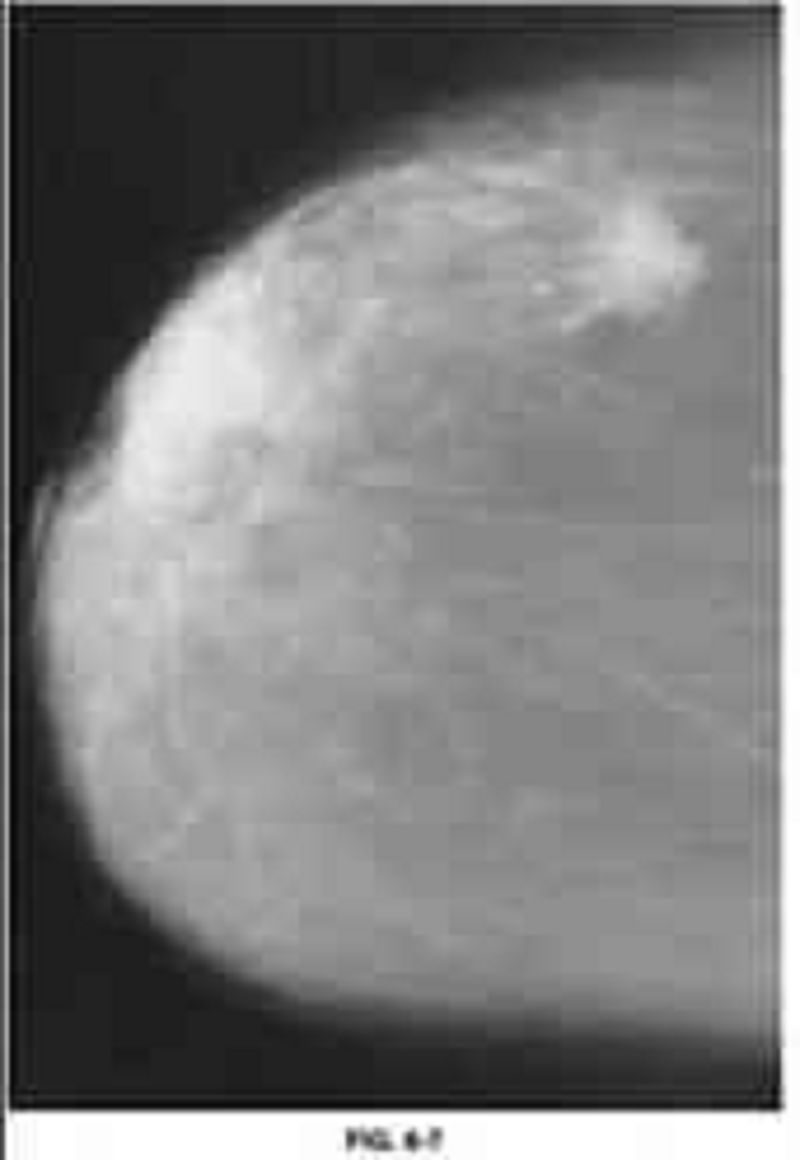
An 83-year-old woman presents to a mammographic facility for a screening mammogram. The technician notices a mass in the lateral right breast. The patient denies any breast pain, nipple discharge, skin changes, or breast trauma. A right breast CC view is shown in Figure 6-7. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Papilloma
Invasive carcinoma
Cystosarcoma phyllodes
DCIS
Fat necrosis
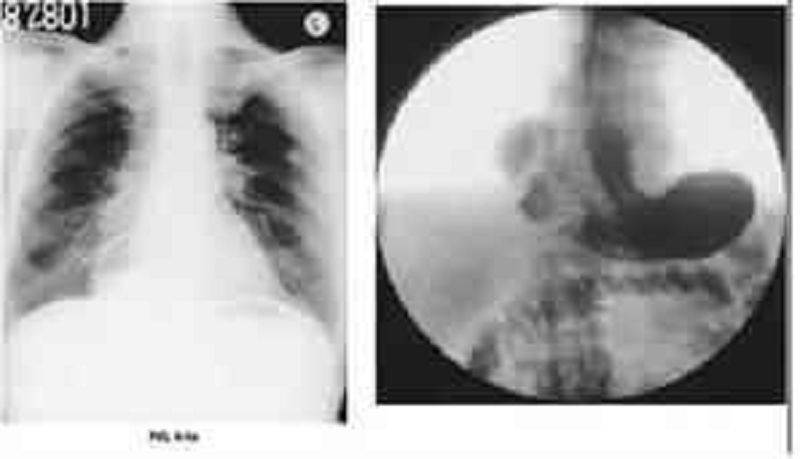
An 85-year-old man presents to the emergency room with an acute onset of midepigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, and hiccups starting 2 days ago. He is unable to keep any food down. Past history is pertinent for a long-standing hiatal hernia, hypertension, and diet-controlled diabetes. Examination reveals vital signs of pulse rate 82/min, BP 100/52 mmHg, respiratory rate 16/min, and temperature 97.2°F. The patient is in no acute distress, but has epigastric tenderness without guarding. Laboratory analysis revealed a hematocrit of 46 and a normal white blood cell (WBC) count. A chest x-ray is shown in Figure 6-5a. A fluoroscopically guided NG tube was placed using contrast, and his stomach was decompressed. After adequate fluid and electrolyte resuscitation, an upper gastrointestinal (UGI) contrast study was obtained and is shown in 6-5b. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Sliding hiatal hernia
Hernia of Bochdalek (posterorlateral congenital diaphragmatic hernia)
Hernia of Morgagni (parasternal congenital diaphragmatic hernia)
paraesophageal hernia
Eventration of the diaphragm (central diaphragm)
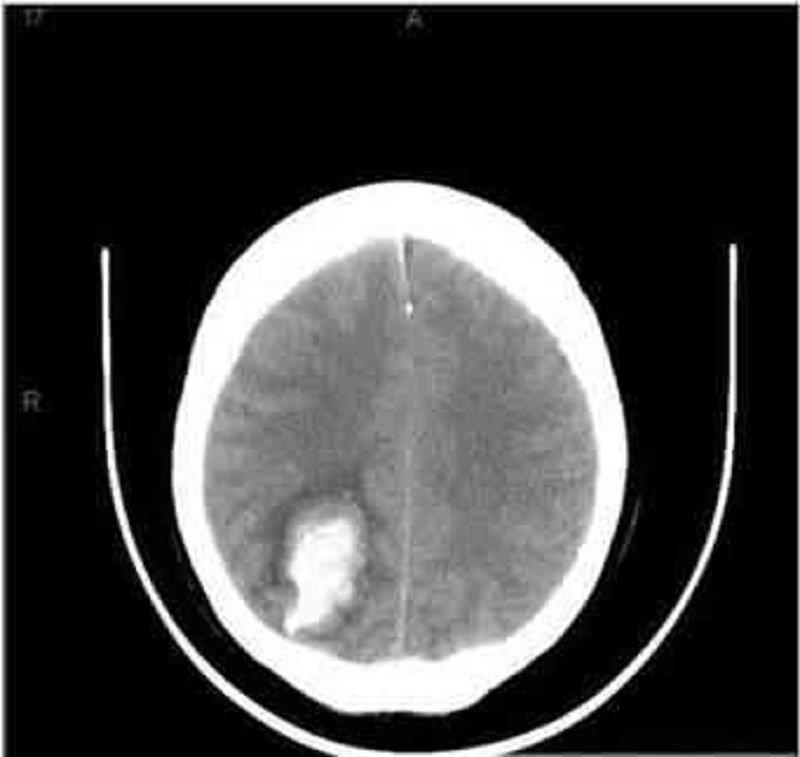
An 86-year -old known hypertensive woman is brought to the emergency department due to weakness of her left side, confusion, drowsiness and slurred speech for the last 2 hours. Her past medical history is significant for an inferior wall myocardial infarction 12 years ago, chronic atrial fibrillation, and severe backache secondary to osteoarthritis. She is currently on aspirin, warfarin, losartan, indomethacin, atenolol, and simvastatin. She doesn't go to anticoagulation clinic regularly. Her blood pressure is 180/110 mm Hg, temperature is 38°C (100°F), respirations are 16/min, and pulse is 70/min, irregularly irregular. The pertinent physical findings are: carotid bruit on both sides, 2/5-muscle strength in the left arm and leg, and slurred speech. Her deep tendon reflexes are exaggerated on the left side, and the Babinski sign is positive. EKG reveals atrial fibrillation. Her CT scan (performed in the ED) is shown below. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Cerebral haemorrhage
Cerebellar hemorrhage
Cerebral infarction
Lacunar infarction
Subarachnoid haemorrhage
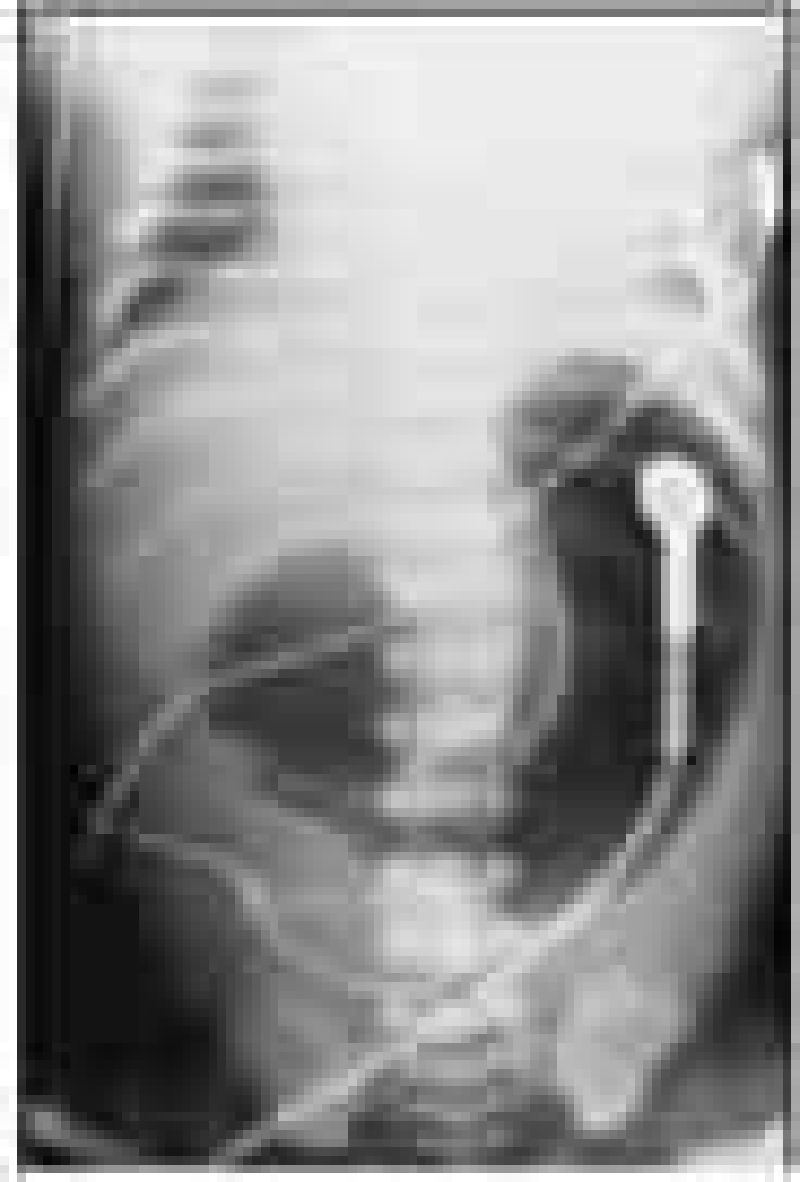
At the time of delivery, a woman is noted to have a large volume of amniotic fluid. At 6 hours of age, her baby begins regurgitating small amounts of mucus and bile-stained fluid. Physical examination of the infant is normal, and an abdominal x-ray is obtained (see below). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis of this infant’s disorder?
Gastric duplication
Pyloric stenosis
Esophageal atresi
Duodenal atresia
Midgut volvulus
Auscultation of the heart of a 17-year-old boy reveals an increased intensity of the pulmonary component of the second heart sound. He complains of dyspnea on exertion but no other cardiac or pulmonary symptoms. Which of the following explanations is the most likely cause of his dyspnea?
Pulmonary stenosis
Aortic stenosis
MI
Pulmonary hypertension
Systemic hypertension

For the past year, a 12-year-old boy has had recurrent episodes of swelling of his hands and feet, which has been getting worse recently. These episodes occur following exercise and emotional stress, last for 2 to 3 days, and resolve spontaneously. The last episode was accompanied by abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea. The results of routine laboratory workup are normal. An older sister and a maternal uncle have had similar episodes, but they were not given a diagnosis. He presents today with another episode as shown in the photographs on the next page. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Focal glomerulosclerosis
Congenital nephrotic syndrome
Hereditary angioedema
Henoch-Schönlein purpura
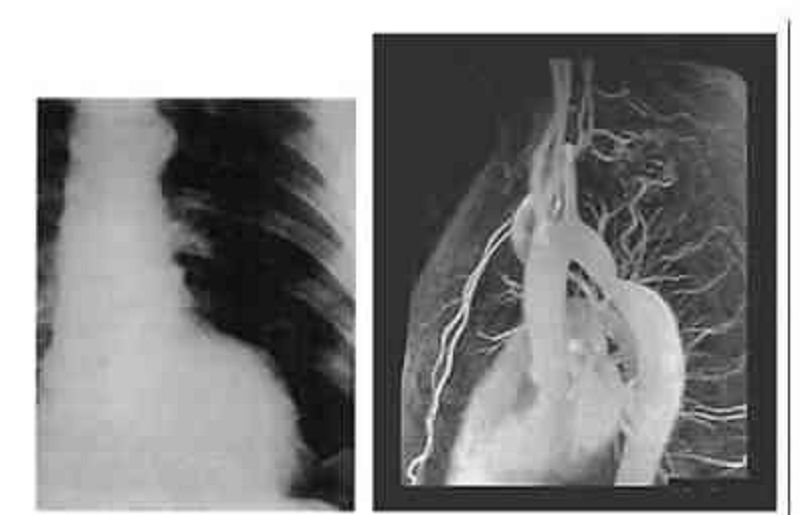
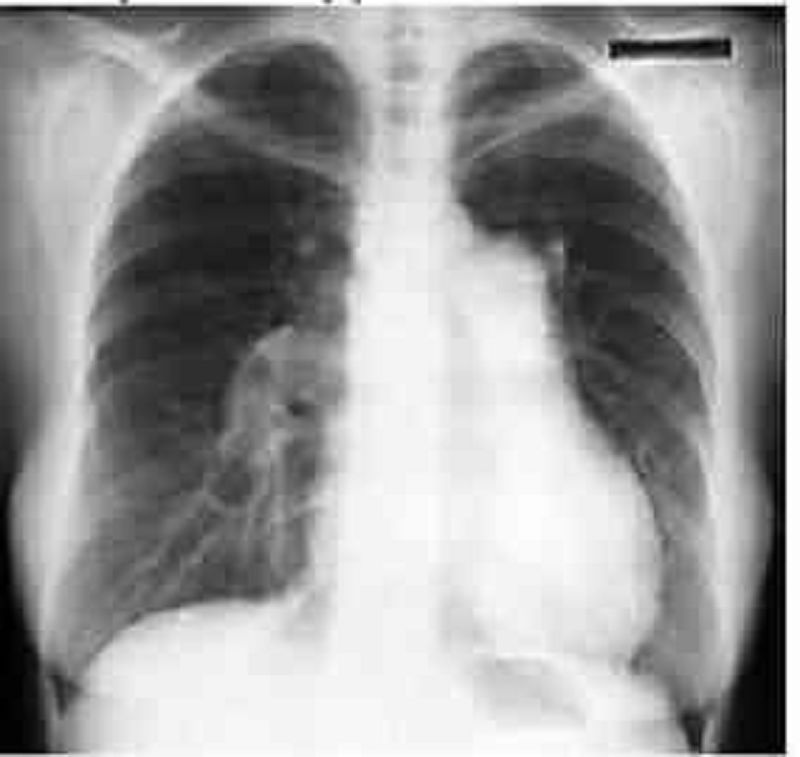
Image below is an x-ray of an asymptomatic 64-year-old male executive coming in for his regular annual medical checkup. He had an anterior Q wave MI 4 years ago. What is your diagnosis?
Calcific pericarditis
Left ventricular aneurysm
Hydatid cyst
Pleuropericarditis
Normal
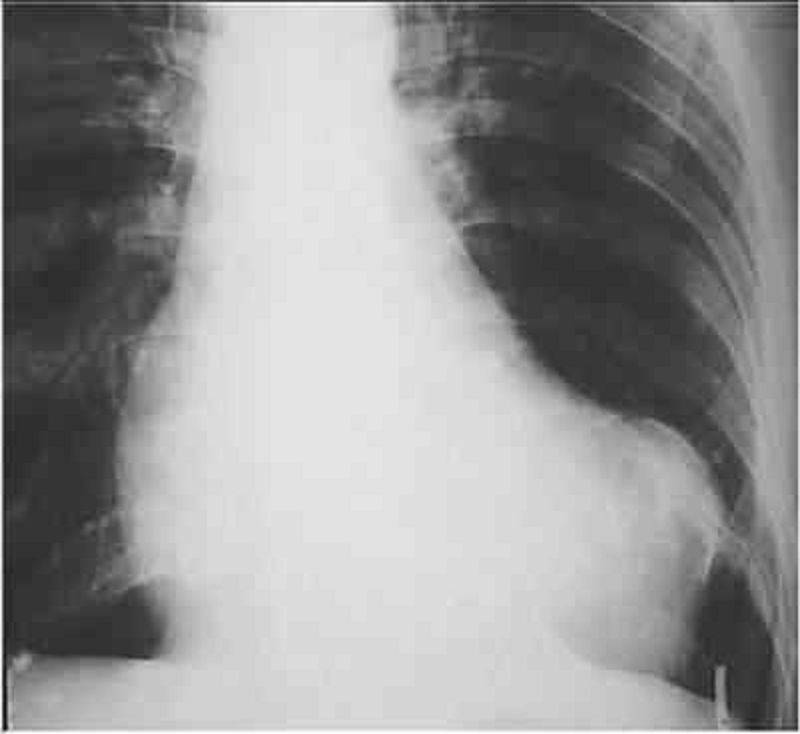
Image below is the x-ray and MR of an 8-year-old boy who had easy fatigability and a soft, continuous murmur in the upper back. ECG revealed minimal LVH. What is your diagnosis?
Aortic stenosis
Patent ductus arteriosus
Coarctation of the aorta
Pulmonary valvular stenosis
Peripheral pulmonary stenosis
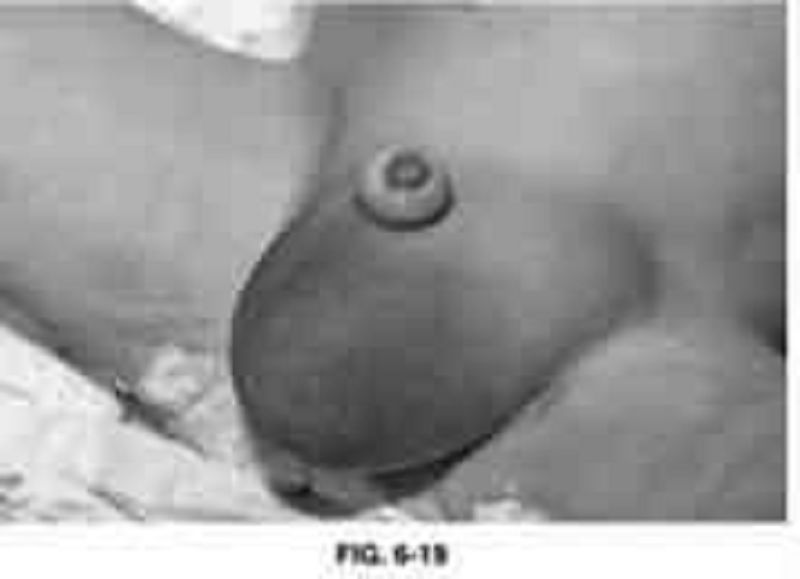
In a 6-month-old previously healthy male infant, an abnormality is revealed during a routine diaper change, as illustrated in Figure 6-19. The parents have noted this finding on and off on several occasions over the last month. On each occasion, the child has been feeding well, and is content and playful. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Noncommunicating hydrocele
Inguinal adenitis
Reducible inguinal hernia
Incarcerated inguinal hernia
Undescended testes
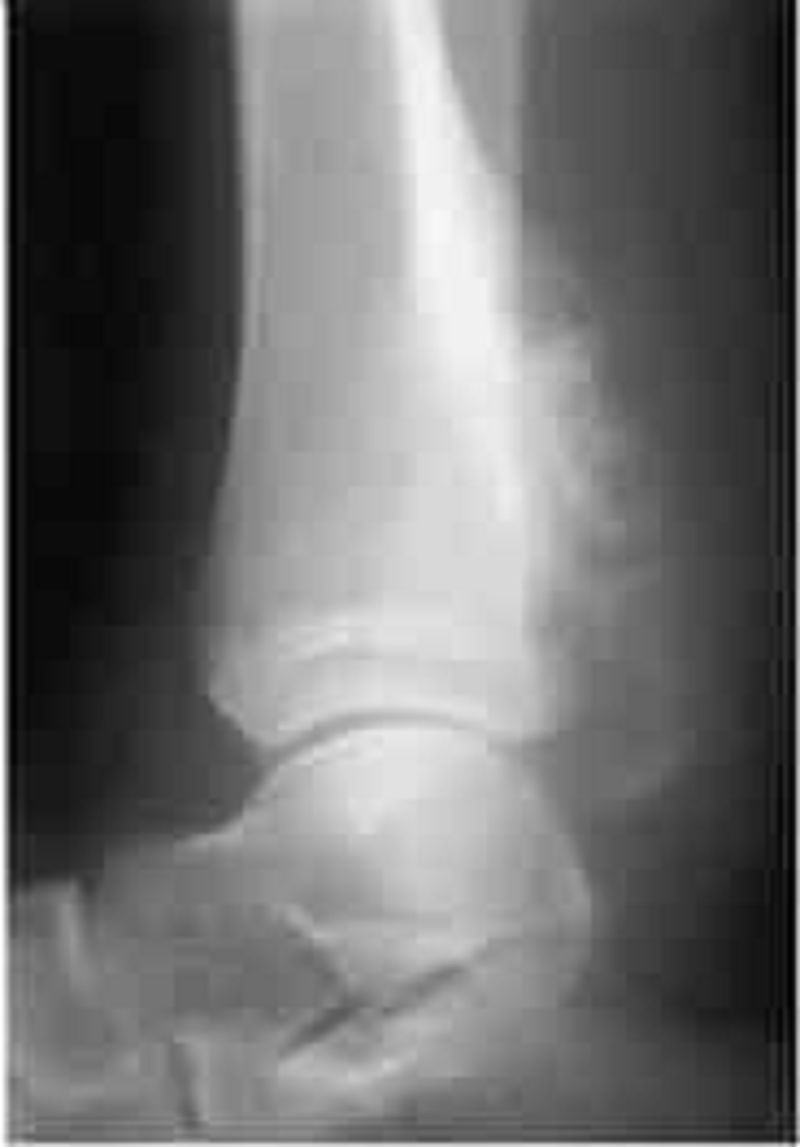
Over the previous 2 to 3 weeks, a very active 13-year-old white boy is noted by his family to have developed deep pains in his leg that awaken him from sleep. The family brings him to your office with a complaint of a swelling over his distal leg, which he attributes to his being kicked while playing soccer about 1 week ago. He has had no fever, headaches, weakness, bruising, or other symptoms. A radiograph of the leg is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for his pain?
Growingpains
Leukemia
Osteomyelitis
Bone fracture
Osteosarcoma
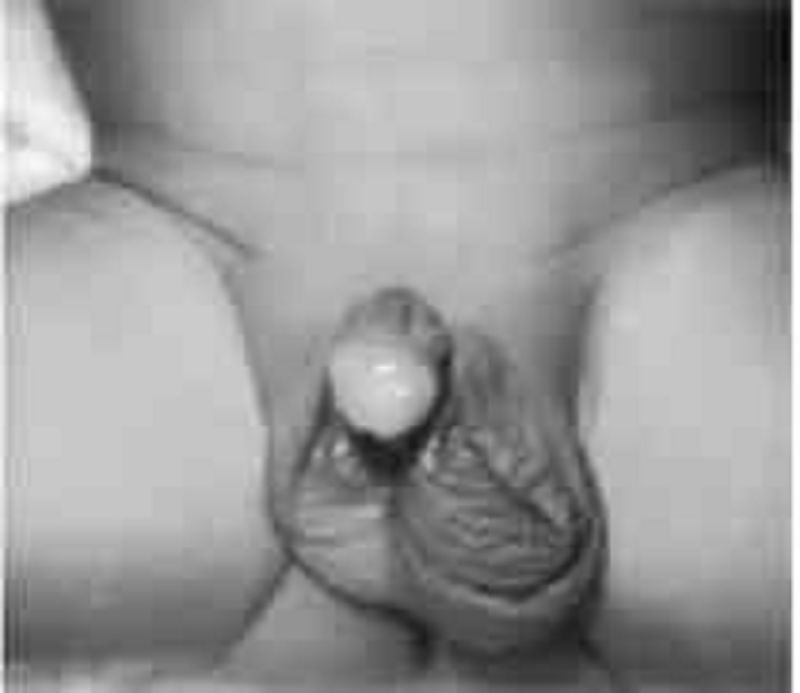
The 1-year-old boy in the photograph below, who recently had a circumcision, requires an additional operation on his genitalia that will probably eliminate his risk of which of the following?
Testicular malignancy
Decreased sperm count
Torsion of testes
Urinary tract infection
Epididymitis
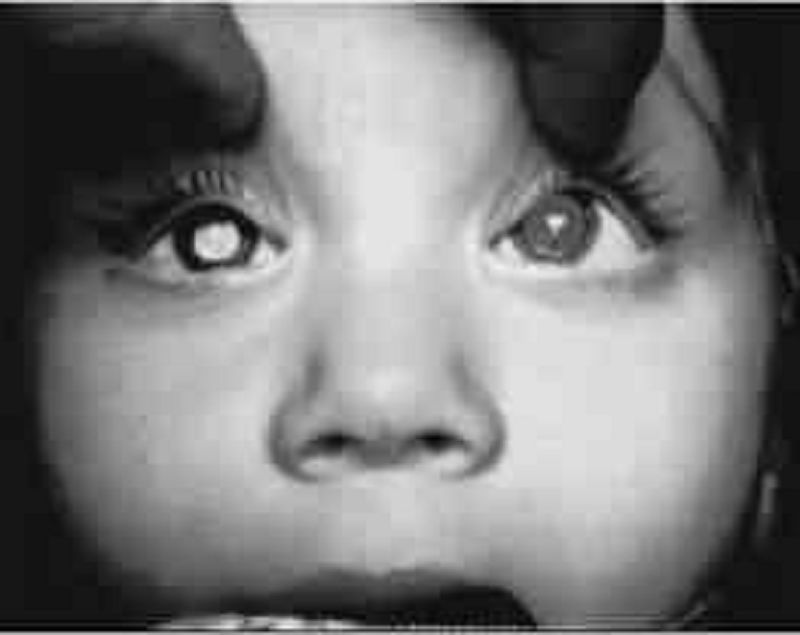

The 16-month-old male infant pictured below was recently brought from a developing country to the United States. The family history reveals that his father had an eye and a leg removed. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Coloboma of the choroid
Retinaldetachment
Nematode endophthalmitis
Retinoblastoma
Persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous
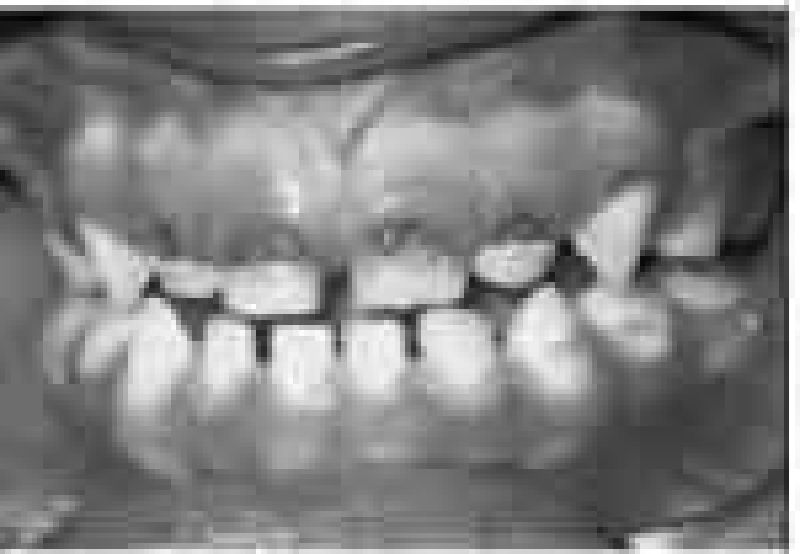
The 4-year-old child pictured below is noted to have the tooth decay as shown. This characteristic pattern of tooth decay is caused by which of the following?
Excessive use of fluoride
Tetracycline
Use of bottled water that lacks fluoride
Prolonged use of a baby bottle
Consumption of too much candy
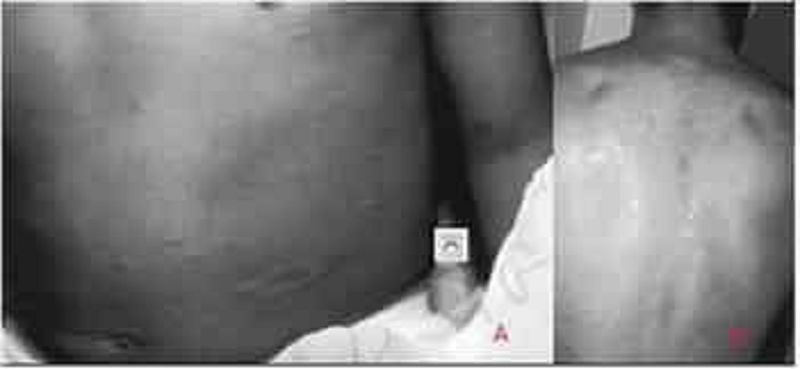
The adolescent shown presents with a 14-day history of multiple oval lesions over her back. The rash began with a single lesion over the lower abdomen (Image A); the other lesions developed over the next days (image B). These lesions are slightly pruritic. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Contact dermatitis
Pityriasis rosea
Seborrheic dermatitis
Lichen planus
Psoriasis
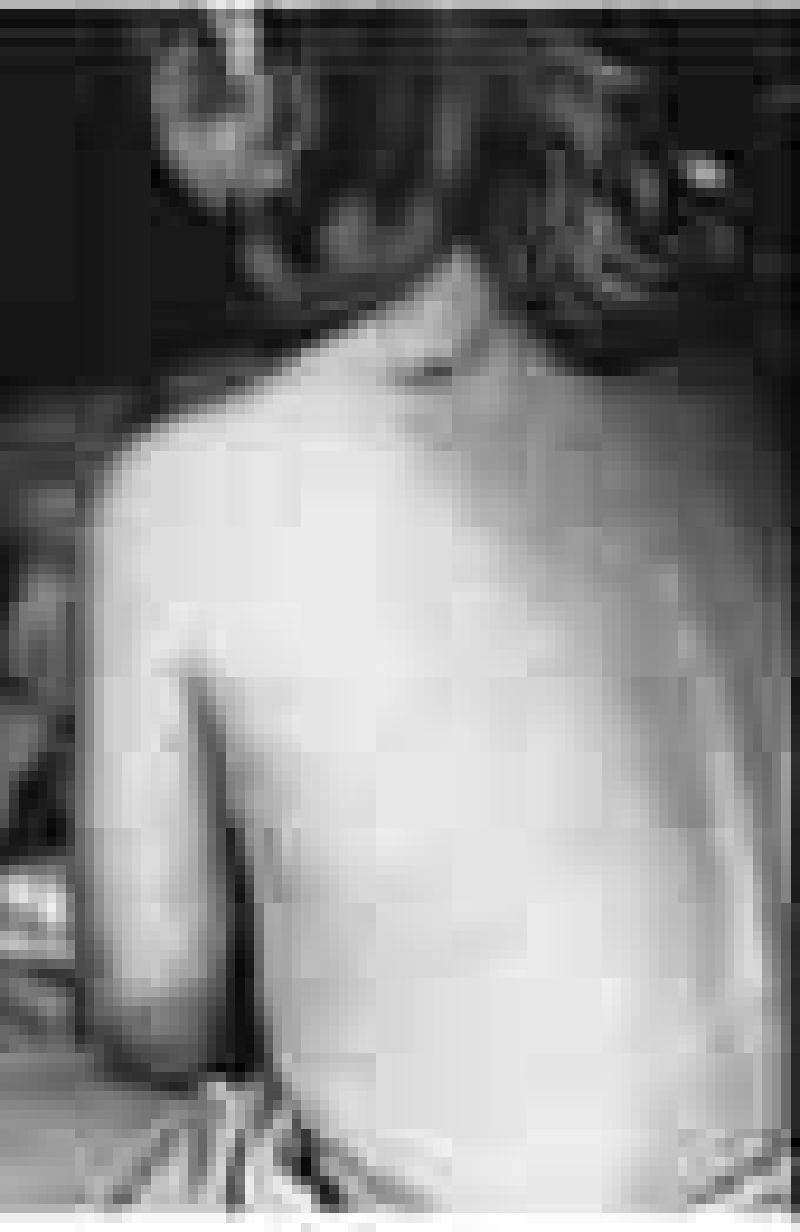
The child shown below presents with a 3-day history of malaise, fever to 41.1C (106F), cough, coryza, and conjunctivitis. He then develops the erythematous, maculopapular rash pictured. He is noted to have white pinpoint lesions on a bright red buccal mucosa in the area opposite his lower molars. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Parvovirus
Rubella
Herpes
Rubeola
Varicella
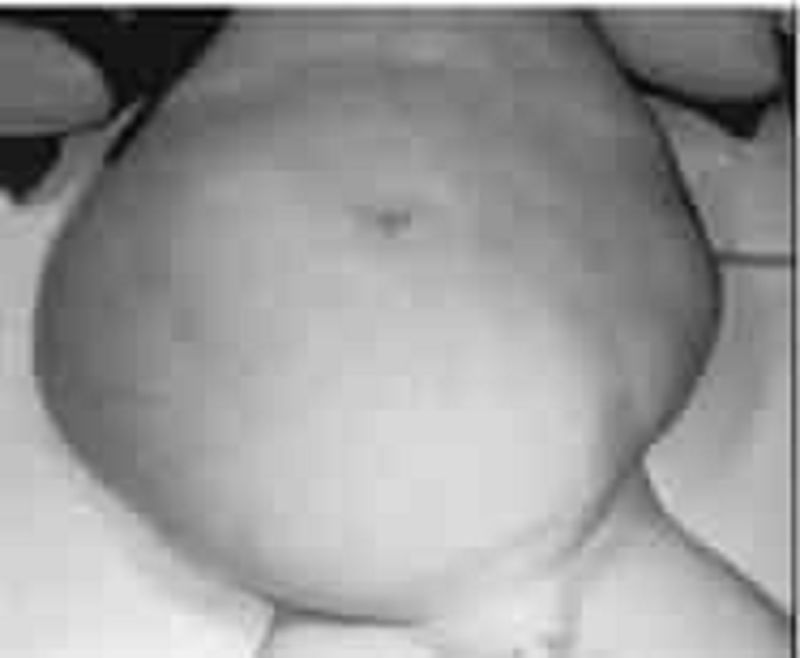
The delivery of a newborn boy is remarkable for oligohydramnios. The infant (pictured) is also noted to have undescended testes and clubfeet, and to be in respiratory distress. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis to explain these findings?
Surfactant deficiency
Turner syndrome
Prune belly syndrome
Hermaphroditism
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
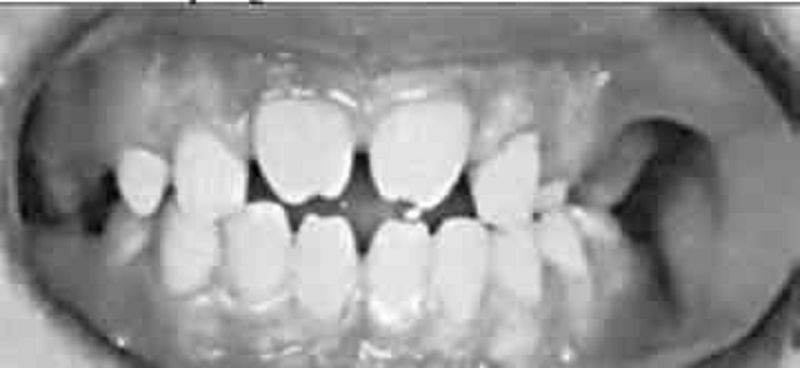
The dental condition illustrated in Fig is usually associated with a congenital infectious disease. The teeth are characterized by centrally notched, widely spaced, peg-shaped upper central incisors and molars that have poorly developed cusps. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Congenital rubella
Congenital syphilis
Congenital toxoplasmosis
Congenital HIV
Congenital measles
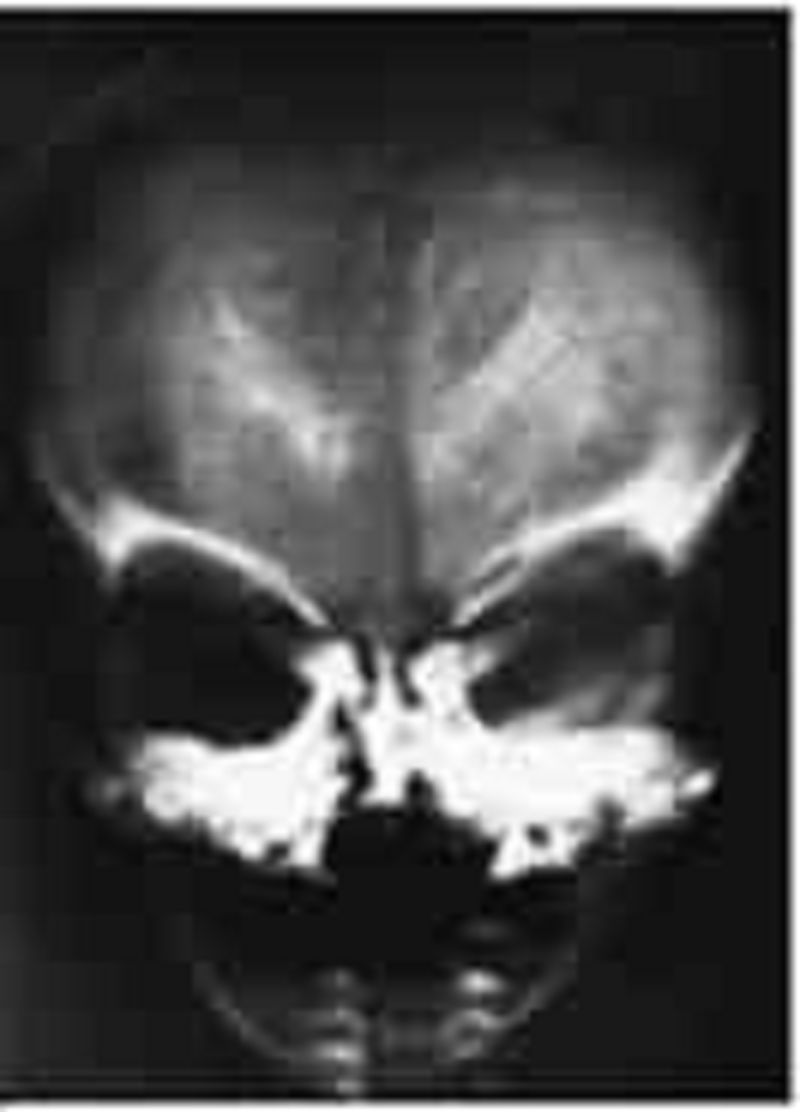
The developmentally delayed 6-month-old child in the picture below had intrauterine growth retardation (including microcephaly), hepatosplenomegaly, prolonged neonatal jaundice, and purpura at birth. The calcific densities in the skull x-ray shown are likely the result of which of the following?
Congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection
Congenital toxoplasmosis infection
Congenital syphilis infection
Tuberculous meningitis
Craniopharyngioma
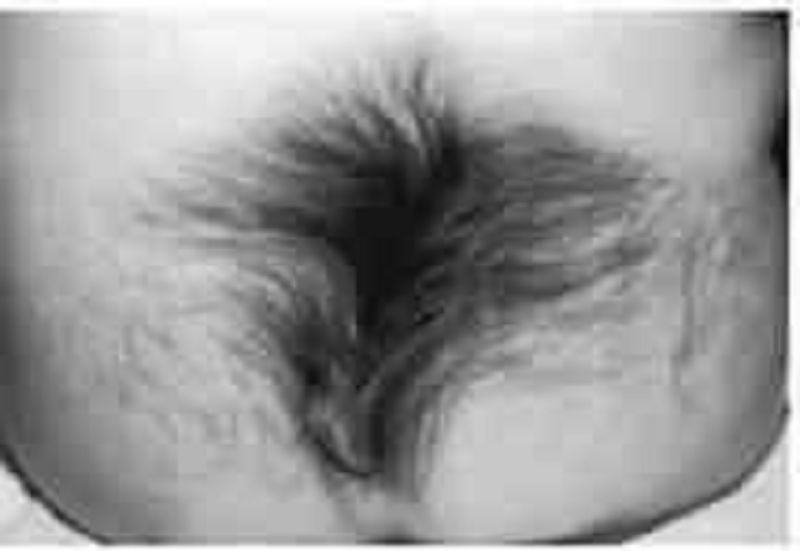
The examination of a child’s back is shown below. Evaluation with ultrasound of this lesion may demonstrate which of the following?
Epsteinpearl
Mongolian spot
Cephalohematoma
Omphalocele
Occult spina bifida
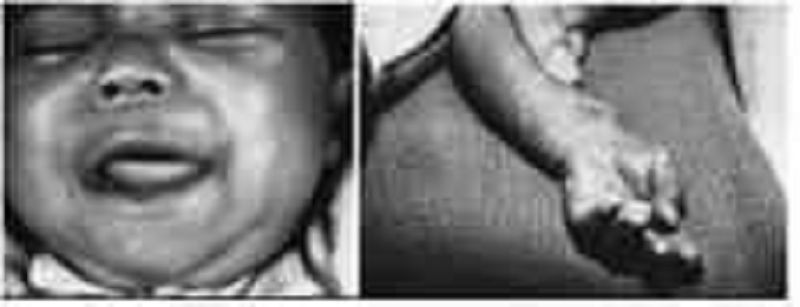
The infant in the following picture presents with hepatosplenomegaly, anemia, persistent rhinitis, and a maculopapular rash. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis for this child?
Toxoplasmosis
Glycogen storage disease
Congenital hypothyroidism
Congenital syphilis
Cytomegalovirus disease
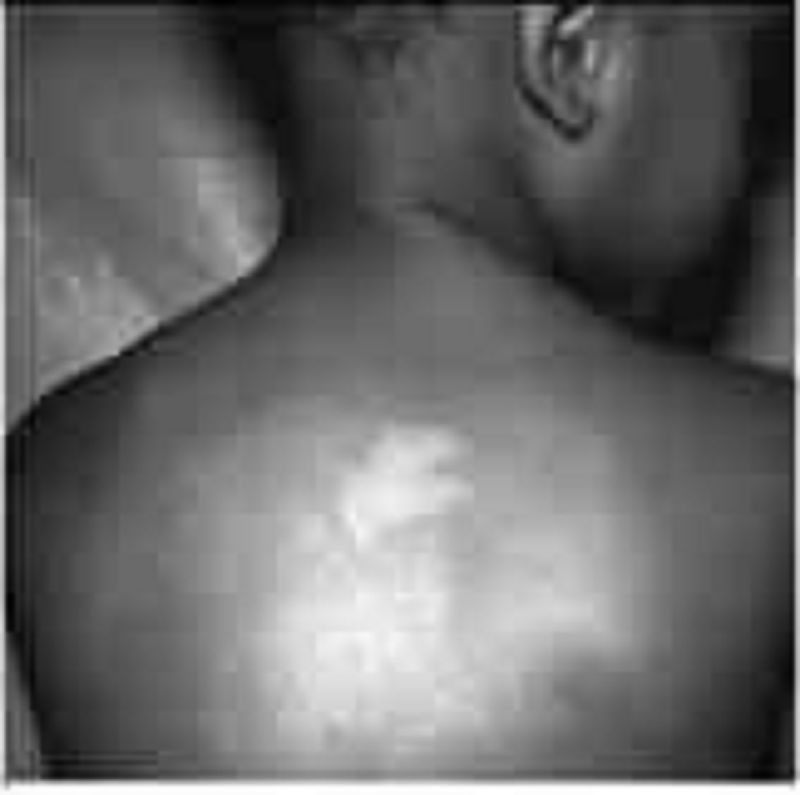
The infant pictured below develops infantile spasms. Which of the following disorders is most likely to be affecting this infant?
Neurofibromatosis
Tuberous sclerosis
Incontinentia pigmenti
Pityriasis rosea
Psoriasis
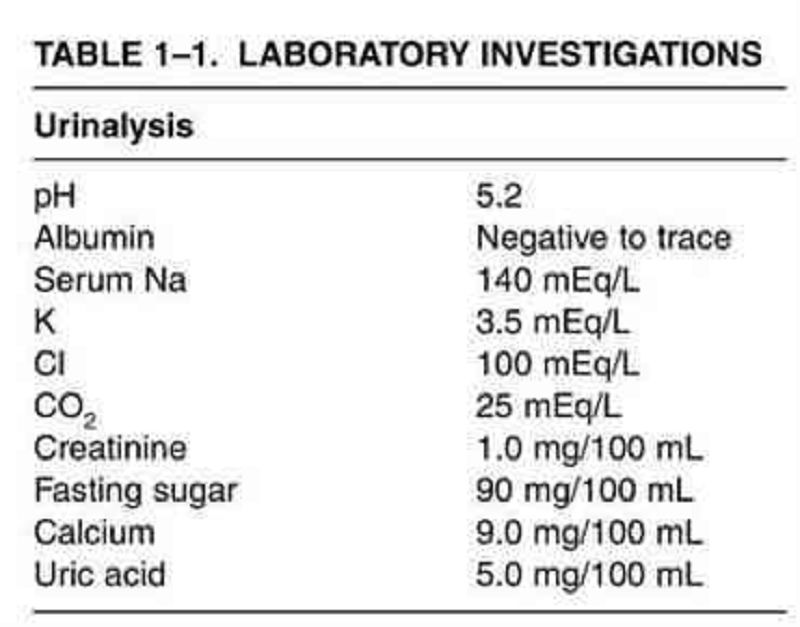
The laboratory results shown in Table 1–1 are obtained from the investigation of a 37-year-old African-American woman who has a blood pressure at rest of 140/100 mmHg. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Cushing’s syndrome
Primary aldosteronism
Essential hypertension
Pyelonephritis
Bilateral renal artery stenosis
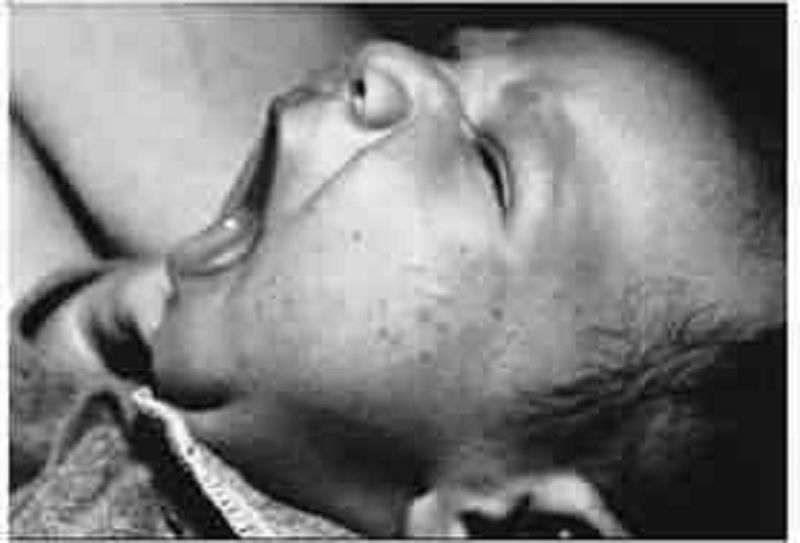
The mother of a 3-day-old infant brings her child to your office for an early follow-up visit. The mom notes that the child has been eating well, has had no temperature instability, and stools and urinates well. She notes that over the previous 3 days the child has had a progressive rash on the face as pictured here. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Herpes
Neonatal acne
Milia
Seborrheic dermatitis
Eczema
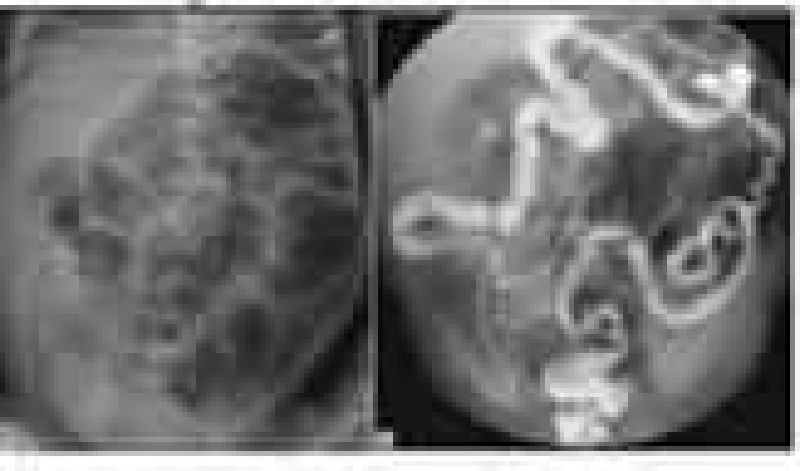
The newborn nursery calls to notify you that a 1-day-old baby boy has developed abdominal distension and bilious emesis. Prenatal history was significant for areas of echogenic bowel seen on ultrasound. You order an abdominal radiograph; based on the results you order a contrast enema. Both are shown here. This infant is most likely to have which of the following?
Duodenal atresia
Cystic fibrosis
Gastroenteritis
Malrotation with volvulus
Hirschsprung disease
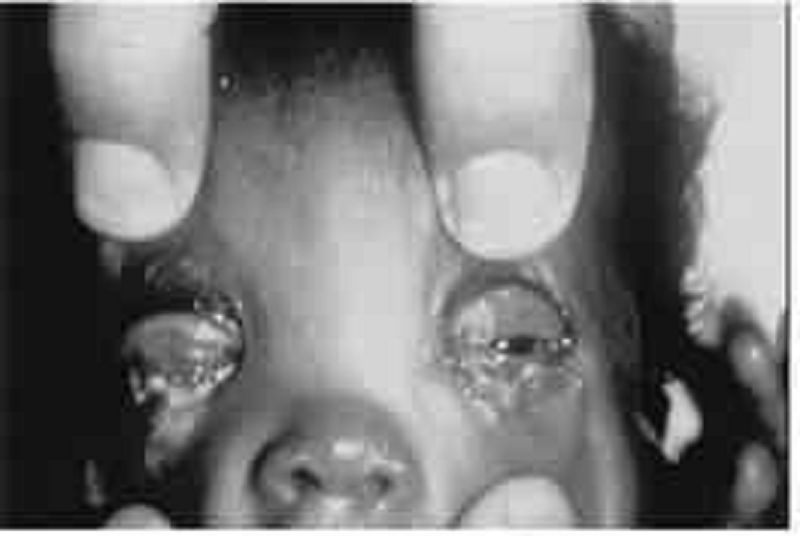
The newborn pictured below was born at home and has puffy, tense eye- lids; red conjunctivae; a copious amount of purulent ocular discharge; and chemosis 2 days after birth. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Dacryocystitis
Chemical conjunctivitis
Pneumococcal ophthalmia
Gonococcal ophthalmia
Chlamydial conjunctivitis
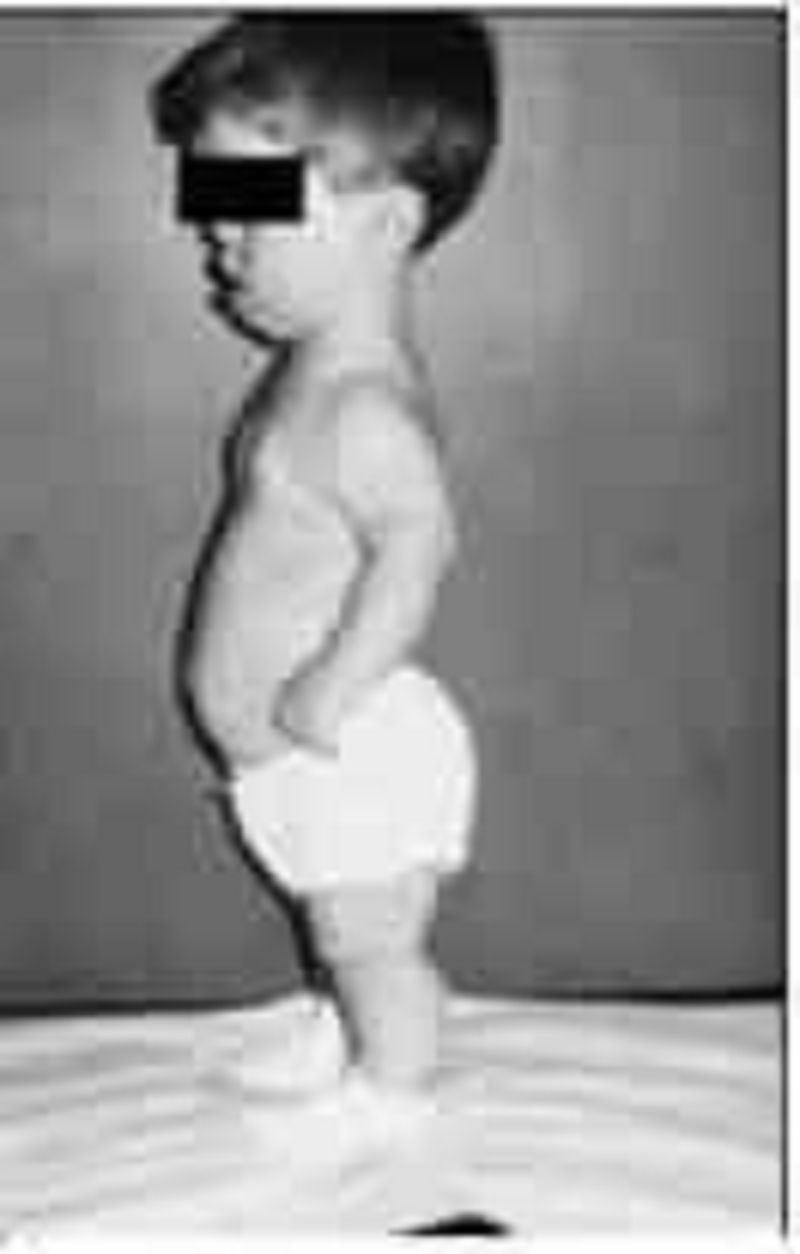
The parents of the child pictured below bring him to the office for evaluation of short stature. At 5 years of age, he is the shortest child in his kindergarten class. His development is normal, and he is reading on a first grade level. Both parents are of normal height, and this child resembles no one in the family. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Achondrogenesis
Achondroplasia
Metatropic dysplasia
Thanatophoric dwarfism
Chondroectodermal dysplasia
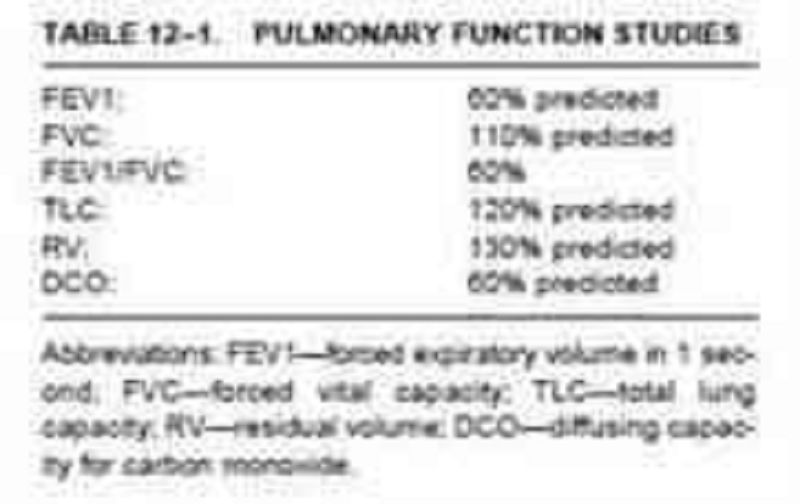
The pulmonary fun
Emphysema
Lobar pneumonia
Chronic bronchitis
Acute bronchitis
CHF
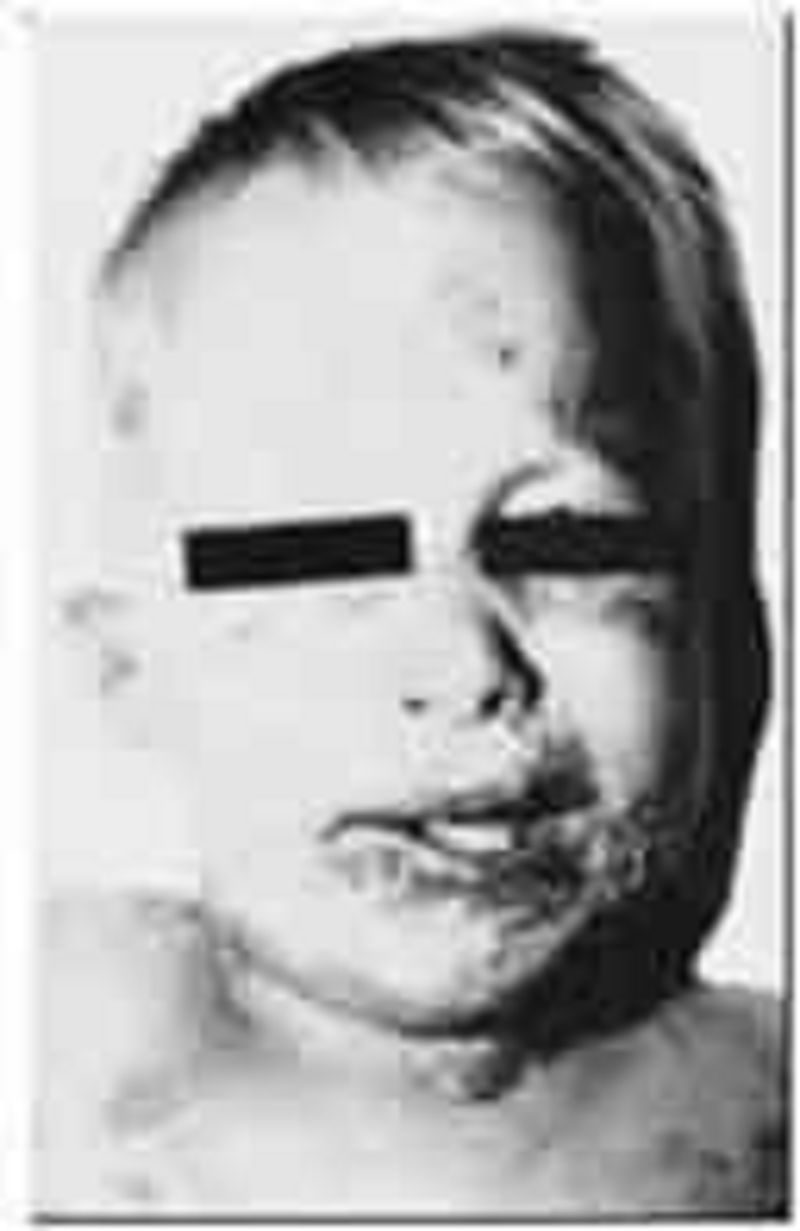
The rash and mucous membrane lesions shown in the photograph below develop in an infant 5 days into the course of an upper respiratory infection with otitis media; the child is being treated with amoxicillin. The child’s condition is likely which of the following?
Urticaria
Rubeola
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Kawasaki diseas
Scarlet fever
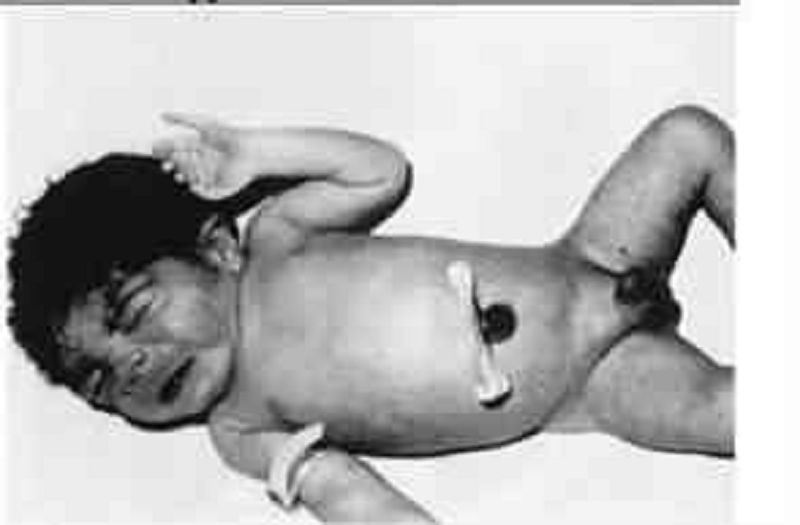
The term infant pictured below weighs 2200 g (4 lb, 14 oz). He is found to have a ventricular septal defect on cardiac evaluation. This infant appears to have features consistent with which of the following?
Perinatal phenytoin exposure
Trisomy 21
Alport syndrome
Fetal alcohol syndrome
Infant of diabetic mother
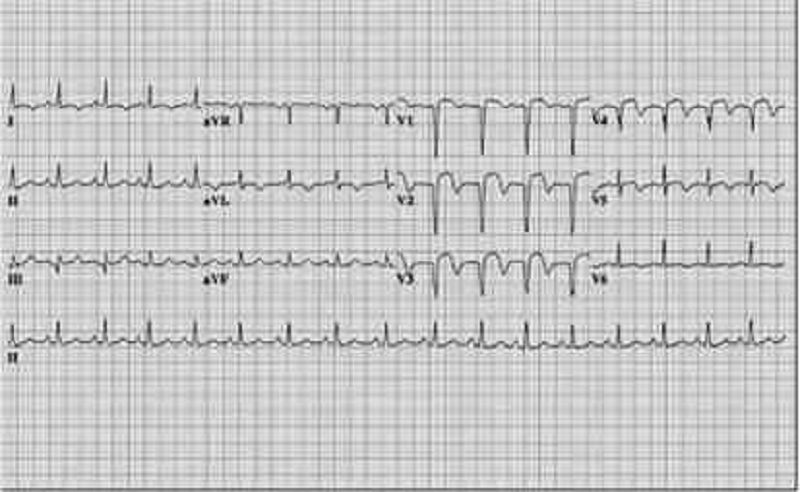
Three months after an anterior MI, a 73-year-old man has a follow-up ECG. He is clinically feeling well with no further angina symptoms. His ECG shows Q waves in the anterior leads with persistant ST-segment elevation. The current ECG is most compatible with which of the following diagnosis?
Ventricular aneurysm
Hibernating myocardium
Acute infarction
Silent infarction
Early repolarization
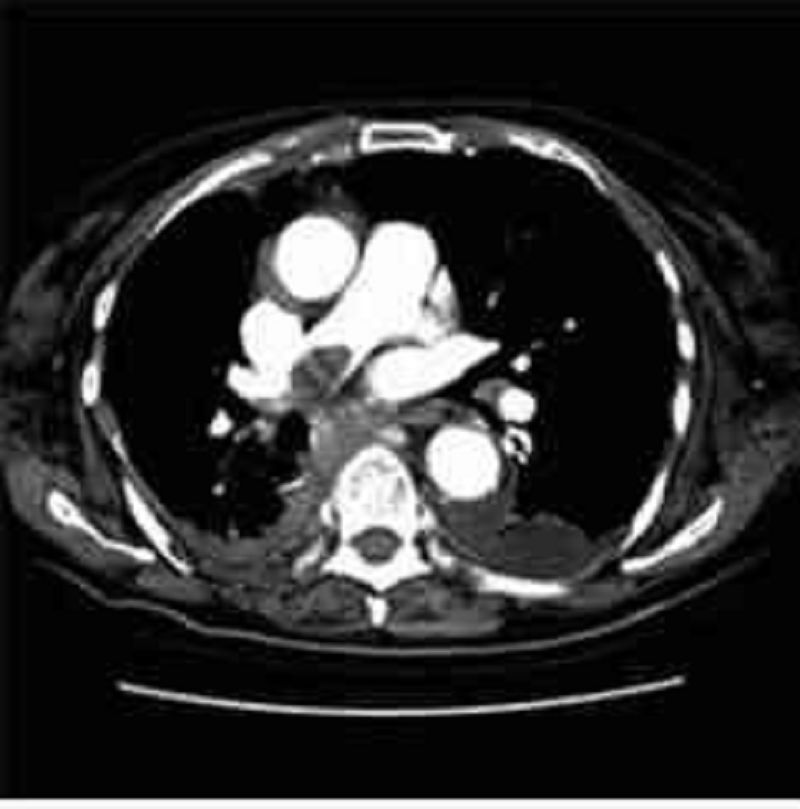
Two and a half weeks after coronary artery bypass grafting, a 63-year-old man returns to the emergency department acutely short of breath. The patient states that he began having chest pain and shortness of breath approximately 1 hour earlier. He has a history of hypertension, diabetes, and two myocardial infarctions. On examination he is hypoxic with an oxygen saturation of 86% on room air. Other vital signs and results of a physical examination are normal. ECG shows no interval change from his most recent ECG. CT of the chest is shown in the image. What is the most likely etiology of this patient’s shortness of breath?
Aortic dissection
Exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Myocardial infarction
Pleural effusion
Pulmonary embolus
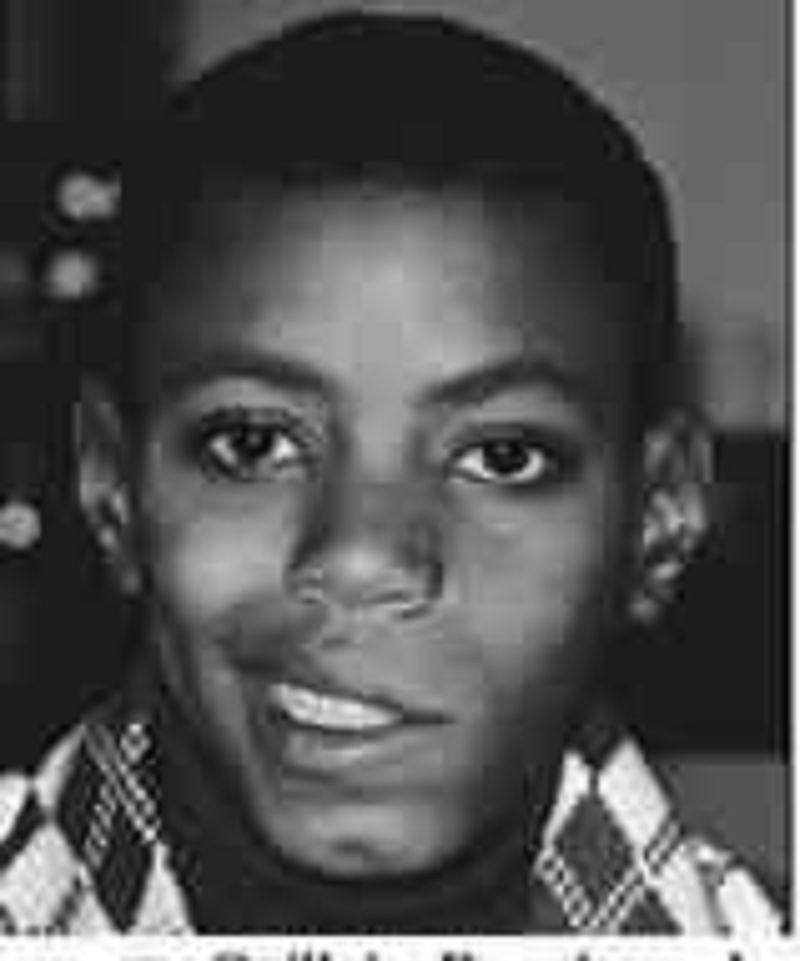

Two weeks after a viral syndrome, a 9-year-old boy presents to your clinic with a complaint of several days of weakness of his mouth. In addition to the drooping of the left side of his mouth, you note that he is unable to completely shut his left eye. His smile is asymmetric, but his examination is otherwise normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Guillain-Barré syndrome
Botulism
Cerebral vascular accident
Brainstem tumor
Bell palsy
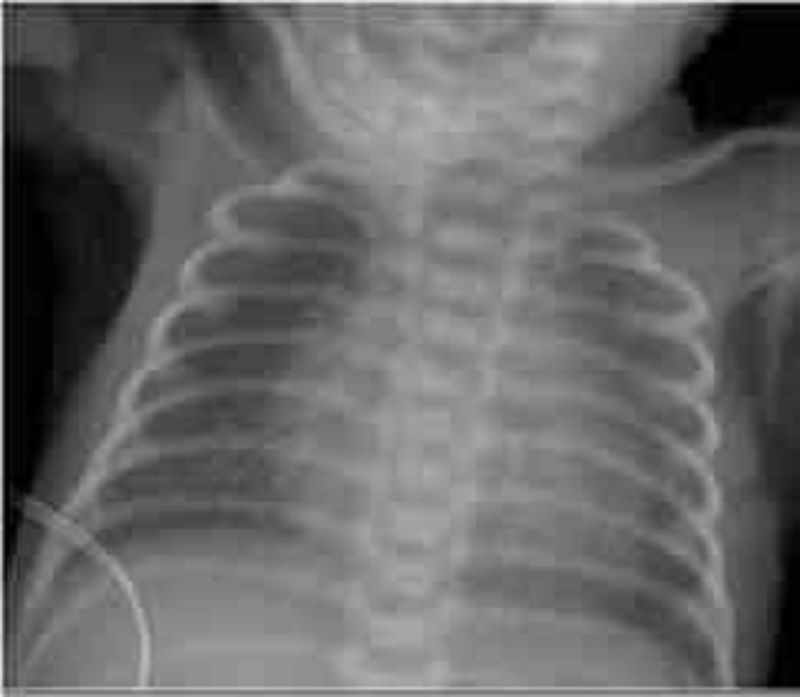
You are called to the delivery room to evaluate an infant born at 28-weeks gestational age. The infant is tachypneic and cyanotic. Examination reveals intercostal and subcostal retractions along with nasal flaring. Lungs have coarse breath sounds bilaterally. After initial resuscitation, the patient is given respiratory support with continuous positive airway pressure and admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit. The patient's respiratory status continues to worsen over the next 24 hours. A chest radiograph from the patient is shown below. In addition to prematurity, which of the following is a risk factor for the development of this disease?
Prolonged rupture of membranes
Intrauterine growth restriction
Maternal diabetes
Maternal hypertension
Antenatal corticosteroids
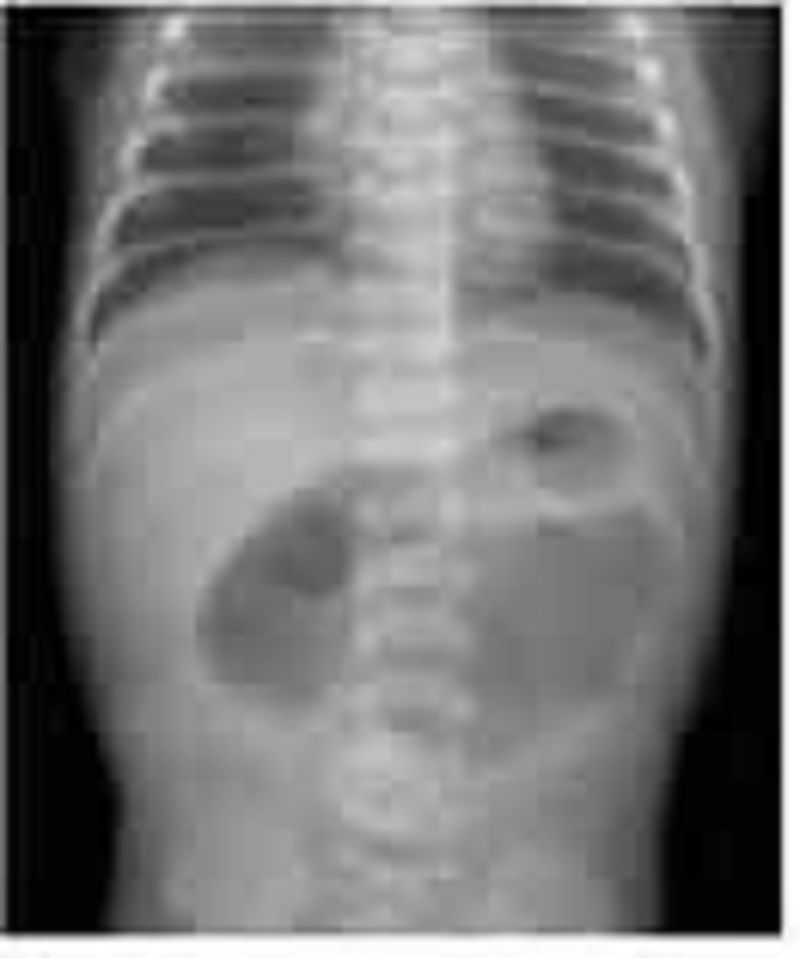
You are called to the newborn nursery to evaluate a term infant with bilious emesis. Although the mother had poor prenatal care, she had a normal vaginal delivery with no complications. The infant began having bilious vomiting several hours after birth. The infant has urinated, but has not had a bowel movement. Vital signs are temperature 36.9 0C (98.4 0F), pulse 150/min, and respiratory rate 40/min. On examination, the abdomen is distended and there are decreased bowel sounds. The remainder of the physical examination is unremarkable. An abdominal radiograph is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Pyloric stenosis
Intestinal atresia
Hirschsprung disease
Necrotizing enterocolitis
Gastroesophageal reflux
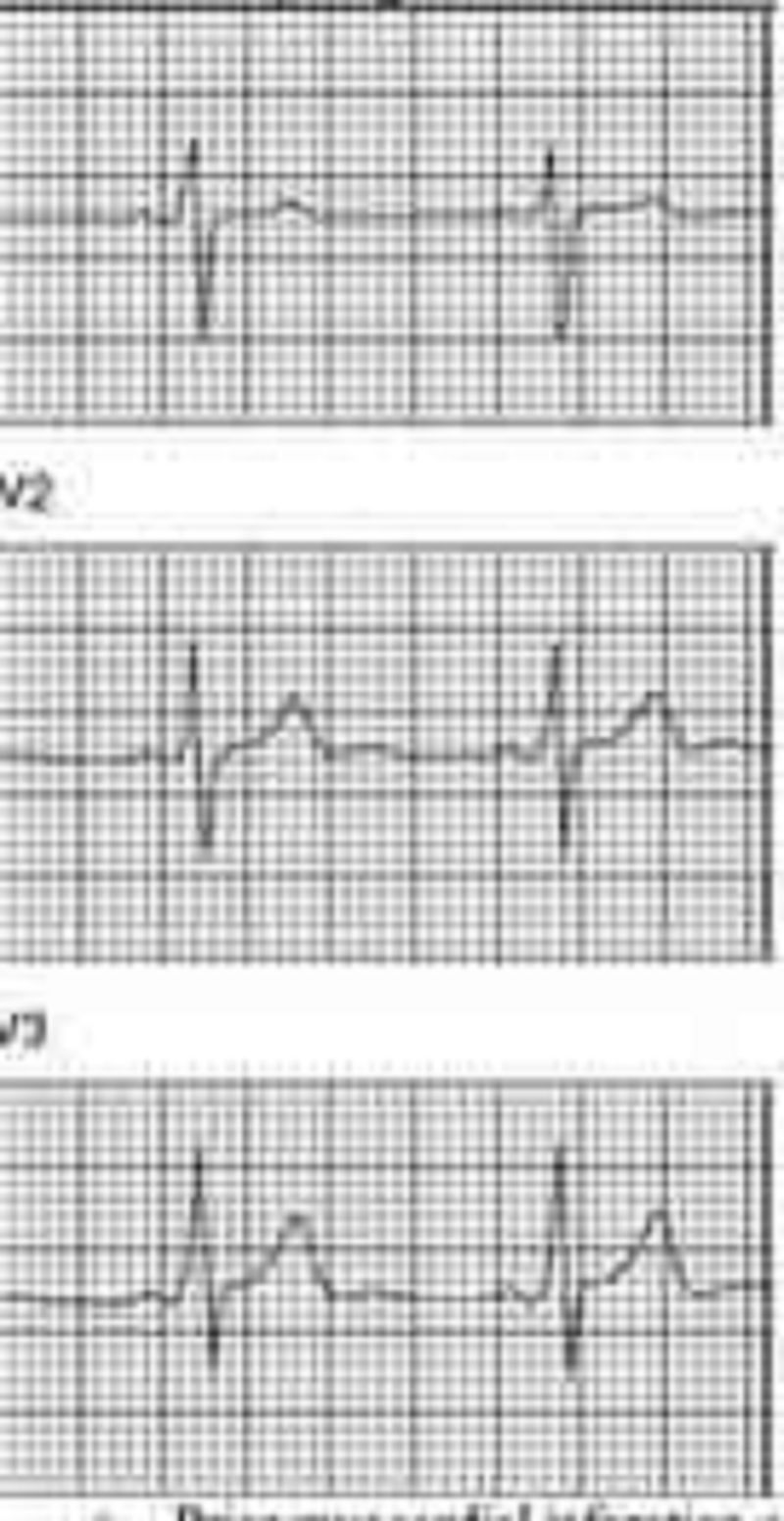
You are performing medical screening of new military recruits when an 18-year-old male reports several episodes of palpitation and syncope over the past several years. Physical examination is unremarkable. An ECG is obtained with excerpts shown below. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Prior myocardial infarction secondary to coronary artery disease
Congenital prolonged QT syndrome
Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM)
Preexcitation syndrome (Wolff-Parkinson-White)
Rheumatic mitral stenosis
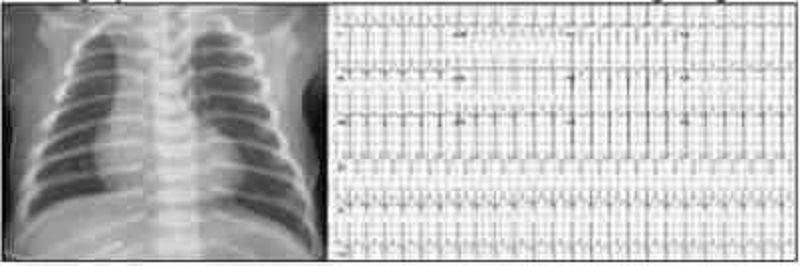
You are seeing a 2-year-old boy for the first time. His father denies any past medical or surgical history, but does note that the child’s day care recently sent a note home asking about several episodes, usually after the child does not get what he wants, when he “breathes funny” and sits in a corner with his knees under his chin for a few minutes. The day-care staffers think this “self-imposed time-out” is a good thing, but they worry about the breathing. One teacher even though he once looked blue, but decided that it was probably because of the finger paints he had been using. On examination, you identify a right ventricular impulse, a systolic thrill along the left sternal border, and a harsh systolic murmur (loudest at the left sternal border but radiating through the lung fields). His chest radio- graph and ECG are shown. Which of the following congenital cardiac lesions would you expect to find in this child?
Patent ductus arteriosus
Right ventricular outflow obstruction
Atrial septal defect (ASD)
Transposition of the great vessels with a patent foramen ovale
Hypoplastic left heart
{"name":"PIC: USLME-DIAGNOSTIC 2", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your medical knowledge with our comprehensive USLME Diagnostic Quiz! Designed for healthcare professionals and students, this quiz features a variety of clinical scenarios to enhance your diagnostic skills.Includes: 55 thought-provoking questionsDetailed case studiesImmediate feedback on your answers","img":"https:/images/course6.png"}
More Quizzes
Part 41 (75QCM)
75380
Part 4O
65320
Written Test No.3
1580
Greek Theater
10516
Forearm, Hand & Wrist Anatomy - Carpal Bones
201019431
Social Styles Test - Find Your Type with Free
201017141
Finnish Language for Beginners - Free Online
201016439
What Podcast Should I Listen To? Free to Find Out
201017460
Financial Accounting Online - Notes, Discounts & Bad Debt
201017079
Which Assassin Are You? Free Personality
201018449
Pharynx Anatomy - Name the Parts (Free)
201016494
Real Housewives of Beverly Hills Trivia - Free
201021780