PMS Final Practice Quiz

PMS Final Practice Quiz
Prepare yourself for success with the PMS Final Practice Quiz! This comprehensive quiz is designed to help students and professionals alike solidify their understanding of critical concepts in neuroscience, anatomy, and genetics. With a variety of question formats, the quiz will challenge your knowledge and boost your retention.
Key features include:
- Multiple-choice questions
- Covers essential topics
- Score tracking for progress assessment
Which of the following arteries in the neck DOES NOT supply the brain?
Left internal carotid
Vertebral arteries
Left external carotid
Right internal carotid
What type of pain is caused by changes in CNS secondary to peripheral nerve damage?
Visceral pain
Neuropathic pain
Thalamic pain
Central pain
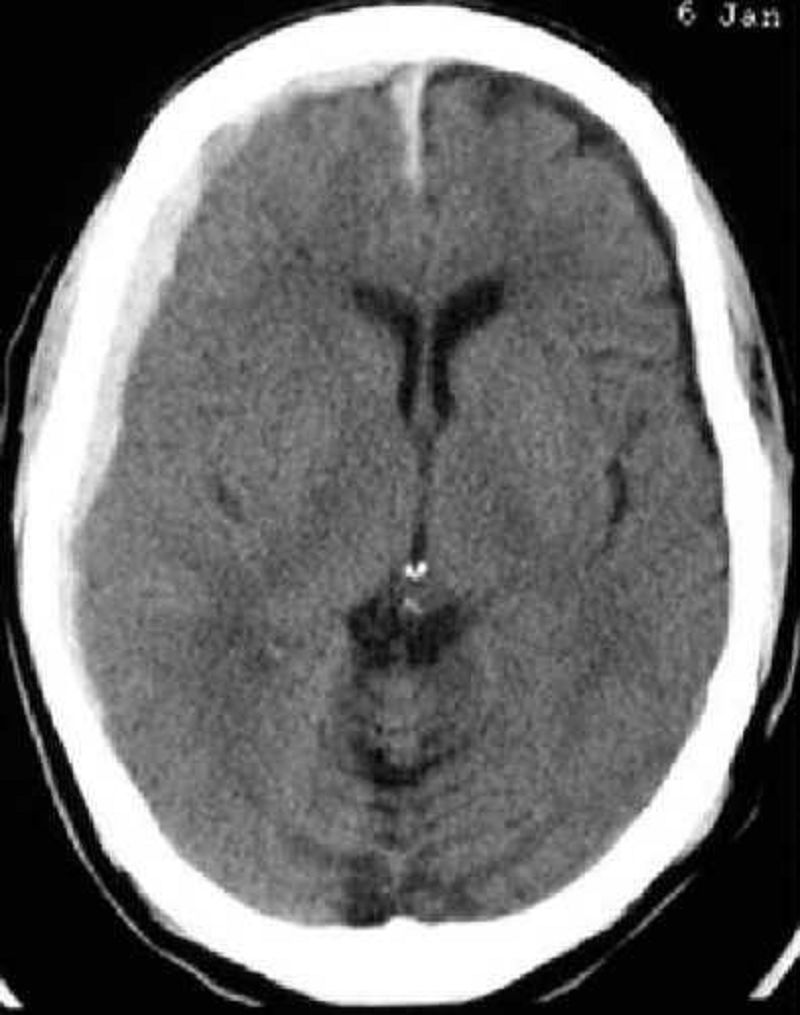
On your EM rotation, your preceptor pulls up the above scan and asks you to read it. What does this image show?
Normal head CT
Acute epidural hemorrhage
ICH
Acute subdural hemorrhage
Which of the following is NOT caused by excessive trinucleotide repeats?
Fragile X Syndrome
Friedrich's ataxia
Mytotonic dystrophy
Cystic Fibrosis
What kind of stroke is known as a pure motor stroke?
Internal capsule stroke
Pons stroke
Cerebellar stroke
MCA stroke
T/F: point mutations are a result of an error in DNA transcription
True
False
Which part of the brain needs more oxygen?
White matter
Grey matter
They both require the same amount of O2
A 65 y/o patient with a history of uncontrolled HTN comes in to the ED complaining of a terrible HA that started suddenly after she hit her head on the corner of a cabinet in her kitchen. She admits to feeling nauseous and having some visual disturbances. What is her most likely diagnosis?
ICH
SAH
TIA
Bells Palsy
What is an inversion?
During crossing over in meiosis, a portion of a chromosome fails to properly locate and gets excised
Additional copy of a segment is incorporated into the chromosome
A section of the chromosome is excised and inserted upside down
Relocation of a segment between non-homologous chromosomes
All of the following are findings you could see on a non-contrast CT of the head of a person with focal neurologic deficit EXCEPT:
Mass effect
Ischemia
Blood within subarachnoid space in cisterns and fissures
Hydrocephalus
Which of the following is an example of an infectious neuropathy?
SLE
Guillain-Barre
Hepatitis B
Rheumatoid arthritis
T/F: ICH occurs in up to 30% of Caucasian patients and up to 10-15% of African Americans and Asians.
True
False
_____ are only visible during cell division
Histones
Chromosomes
Nucleosomes
RNA
Which of the following modalities is thought to be shared with pain?
Pressure
Vibration
Temperature
None of the above
Regarding the previous question, choose the correct pairs.
Sharp cutting shares a pathway with hot temperature
Sharp cutting shares a pathway with cold temperature
Deep aching shares a pathway with hot temperature
Dull burning shares a pathway with cold temperature.
T/F: Autosomal Aneuploidy can occur at any of the autosomes, but most do not survive to birth.
True
False
MCA supplies all of the following areas EXCEPT:
Deep portions of the internal capsule and basal ganglia
Cortical motor area
Lateral aspect of the frontal, temporal and parietal lobes
Visual association area
T/F: Nociceptors cannot be sensitized by prolonged stimulation.
True
False
T/F: CO2 is a vasodilator
True
False
All of the following are X-linked recessive genetic conditions EXCEPT:
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
Red-green color blindness
Marfan Syndrome
What does the Hunt and Hess scale assess?
Universal scoring system used to measure how severe of a CVA a person is having
How quickly the patient will need an MRI after original non-contrast head CT was performed
Predicts ICH/SAH mortality outcome
Predicts when you will need to intubate a person presenting with a CVA
T/F: The PCA provides blood to the Midbrain, basal ganglia and thalamus.
True
False
Which of the following is due to a nondisjunction event in meiosis I OR II?
Turner syndrome
Down syndrome
Klinefelter syndrome
Edward syndrome
The anterior brain is supplied by the:
A. R ICA
B. Vertebral arteries
C. L ICA
D. Both a and c
Which of the following Karyotypes describes Turner Syndrome?
45, X
47, XXY
47, XY, +21
48, XXXY
Which of the following could present with homonymous hemianopsia with macular sparing in someone with a CVA?
ACA
MCA
PCA
None of the above
Which of the following is NOT an example of allodynia?
Sunburned skin
Peripheral neuropathy
Radiculopahy
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)
A 16 year old male patient is brought to your ED on a stretcher after being the driver involved in an MVC just prior to arrival. Your patient has a neck brace on and is in and out of consciousness. On PE, you notice clear fluid from bilateral nares, (+) right sided hemotympanum, and (+) Battle’s sign on the right side. Upon noticing these findings, what is at the top of your differential?
Concussion
Brain Contusion
Basilar skull fracture
Vertebral fracture
T/F: Cystic Fibrosis affects all organs.
True
False
Which intracranial aneurysm is more than 25mm in size and is common in the basilar system or terminal internal carotids?
Fusiform aneurysm
Traumatic dissecting aneurysm
Berry aneurysm
Saccular aneurysm
The components contributing to cerebral oxygenation are all of the following EXCEPT:
Cerebral blood flow (CBF)
Cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP)
Cerebral blood volume (CBV)
Cerebral pressure volume (CPV)
Which of the following is an autonomic reaction to somatic pain?
Vocalization
Flexion reflex
Piloerection
Postural adjustment
A 40 y/o male fell down the steps two weeks ago while carrying beach chairs down from the attic in preparation for their vacation to the OBX, which they recently returned from a few days ago. At the time of the injury, patient hit the right side of his head, but had no LOC and reports just a small scalp laceration, which has since healed. Since the injury the patient complains of a progressively worsening, constant headache and progressively worsening fatigue. His wife noticed he was acting confused this morning, prompting today’s visit. You order a non-contrast head CT which shows a crescent shaped hypodense area to the right side of the head with mass effect and brain parenchyma compression. What does your patient have?
Concussion
Subacute subdural hematoma
Chronic epidural hematoma
Chronic subdural hematoma
Hemorrhagic CVA
Which of the following is NOT true about Gaucher’s disease?
It is the most common lysosomal storage disease
It is caused by an autosomal recessive mutation on Chromosome 2
Causes organ dysfunction in the spleen, kidney, liver, bone marrow and brain
It is caused by a defect in the glucocerebrosidase enzyme that breaks down glucosylceramide
T/F: Progesterone only OCPs are recommended in female patients with migraines.
True
False
Which pain fiber is responsible for initial sensation of pain and has a fast conduction?
C fibers
Delta fibers
A Gamma fibers
A Delta fibers
The ACA supplies all of the following EXCEPT:
Basal ganglia
Corpus callosum
Broca's area
Medial aspect of the frontal lobe
{"name":"PMS Final Practice Quiz", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Prepare yourself for success with the PMS Final Practice Quiz! This comprehensive quiz is designed to help students and professionals alike solidify their understanding of critical concepts in neuroscience, anatomy, and genetics. With a variety of question formats, the quiz will challenge your knowledge and boost your retention.Key features include:Multiple-choice questionsCovers essential topicsScore tracking for progress assessment","img":"https:/images/course2.png"}
More Quizzes
Week 5 Neuro Review
10513
Neuro
603051
Science thingy
1368
Tools u Adobe Photoshop CS6
840
Free 7th Grade Science Review
201021893
Free Trig Identities
201027833
Free MMPI-2 Online Test - Uncover Your Personality Today
201030742
Ultimate Sanity Test Online: Discover Your Sanity Level!
201029363
Test Your Knowledge: National Ice Cream Sandwich Day
201038903
Platform 93/4 Trivia: Only True Wizards Can Ace It
201036549
Test Your Kirin Japan Unicorn Knowledge - Free Trivia
201028727
Test Your Princess Diaries Trivia: Meg Cabot Book
201032704