Cell Labeling Quiz: Name the Parts of a Cell
Quick, self-graded label the cell quiz. Instant feedback.
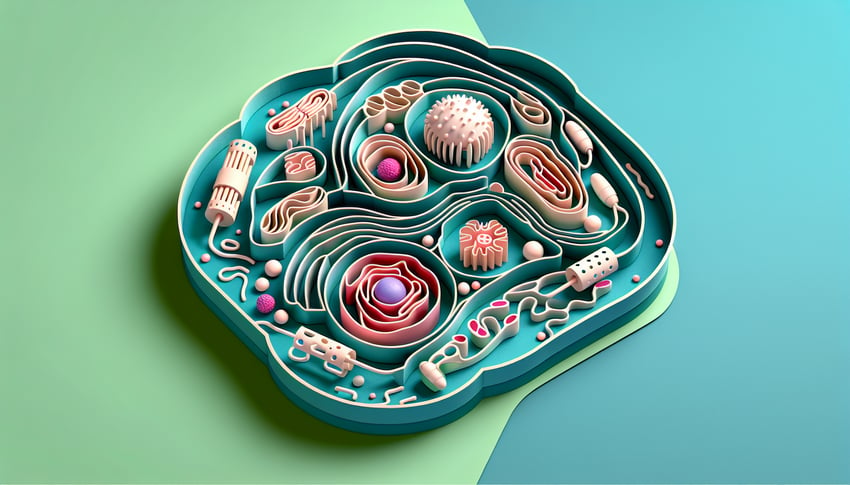
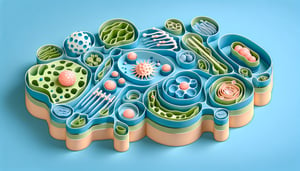
This cell labeling quiz helps you identify and name the main cell parts, building speed and accuracy as you go. Practice with clear diagrams and get instant feedback on organelles from nucleus to mitochondria. When you're done, try a plant cell labeling quiz, explore an animal cell structure quiz , or review functions in our organelle function quiz.
Study Outcomes
- Identify Key Cell Organelles -
Recognize and accurately label major cell structures such as the nucleus, mitochondria, cell membrane, and cytoplasm on a diagram.
- Describe Organelle Functions -
Explain the primary functions of each labeled part, linking structure to its role in cellular processes.
- Differentiate Cell Types -
Distinguish between various cell types and their structural differences when presented with different diagrams.
- Analyze Cellular Organization -
Examine how organelles interact within the cell and infer how their arrangement supports overall cell function.
- Apply Labeling Techniques -
Utilize best practices for diagram labeling to ensure clarity and accuracy in identifying cell parts.
- Assess Your Knowledge -
Use quiz feedback to gauge your understanding of cell structures and pinpoint areas for further study.
Cheat Sheet
- Cell Theory Foundations -
The three pillars - cells as the basic unit of life, all living organisms composed of cells, and cells arising from preexisting cells - form the core of any cell labeling quiz. Remember "All Cells Come Pre-Packaged" to recall the tenets quickly (University of California, Berkeley). This principle underpins the structure of cell quiz and guides identification of every part.
- Plasma Membrane and Transport -
The fluid mosaic model describes the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that regulate entry and exit of molecules (Alberts et al., Molecular Biology of the Cell). Consider the mnemonic "PICK" for Passive, Ion channel, Carrier, Kinase to remember transport types. Mastering this is key for cell and structure quiz questions to ask about cells' selective permeability.
- Nucleus: Command Center -
The nucleus houses DNA and is surrounded by a selectively permeable double membrane with nuclear pores for mRNA export, highlighting its role in genetic control (NIH Genetics Home Reference). Associate "Nuclear Envelope = Double Deck" to recall its dual lipid layers. Labeling this correctly boosts your parts of the cell quiz score.
- Energy Organelles: Mitochondria & Chloroplasts -
Mitochondria convert glucose to ATP via oxidative phosphorylation, while chloroplasts perform photosynthesis using the Calvin cycle in plant cells (Cambridge University Press). Use "CHOMP" - Chloroplasts House Oxygen Making Photosynthesis - to remember their function. These are often high-value items on a cell labeling quiz.
- Cytoskeleton Networks -
Microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules provide shape, support, and intracellular transport, with motor proteins like kinesin and dynein "walking" along microtubules (National Institutes of Health). Recall "A MID Map" - Actin, Intermediate, Dynein/Microtubules - to keep the types straight. Understanding this helps you tackle advanced cell labeling and structure of cell quiz challenges.